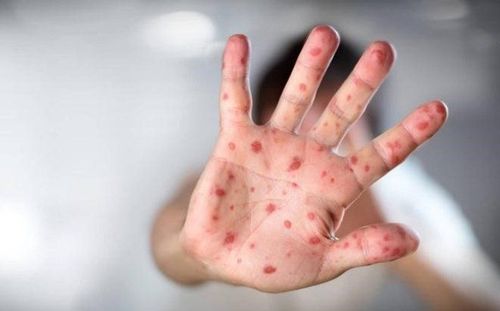
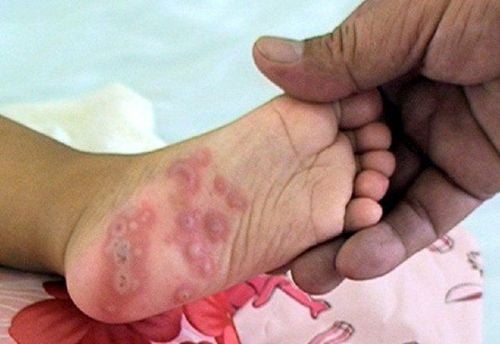
This is an automatically translated article.
Hand, foot and mouth disease in children appears in many parts of the world, mainly caused by Enterovirus 71 in Southeast Asian countries. In Vietnam, hand, foot and mouth disease in children is scattered all year round in most localities, the number of cases is concentrated from March to May and from September to December. The disease is common in children under 10 years old. more than under 5 years old, concentrated in under 3 years old, peaking at 1-2 years old. Some of the following specimens will be used to diagnose hand, foot and mouth disease.
1. Sources of hand, foot and mouth disease transmission in children
The source of the virus is sick and healthy people carrying the virus. The virus exists in secretions from the nose, pharynx, throat, saliva, secretions from skin blisters, burns or feces of an infected person.
Hand, foot and mouth disease in children is transmitted by faeces, mouth and direct contact, but mainly by contact with secretions from the nose, pharynx, throat, saliva, fluid from blisters on the skin or contact contact with the patient's excreta on personal items, toys, furniture, floors. Especially when children are suffering from respiratory diseases, sneezing, coughing, and talking will help the virus spread directly to other children.
However, not all children infected with the virus will show signs of illness, hand, foot and mouth disease in children is common in children under the age of 15, especially children under 5 years of age have a higher incidence.
2. Stages of hand, foot and mouth disease in children
Incubation period: lasts from 3 to 7 days Transmission period: Hand, foot and mouth disease spreads rapidly from a few days before the patient's onset of illness until the mouth sores and blisters disappear, usually most contagious during the first week of illness. The virus enters the body through the mucosa of the mouth or intestines and then multiplies, then enters the blood, from there to sensitive organs such as skin, mucous membranes, brain, meninges, heart muscle... these agencies. In some cases, the development of respiratory and circulatory failure is due to a combination of inflammatory and neurologic responses rather than to direct viral attack.
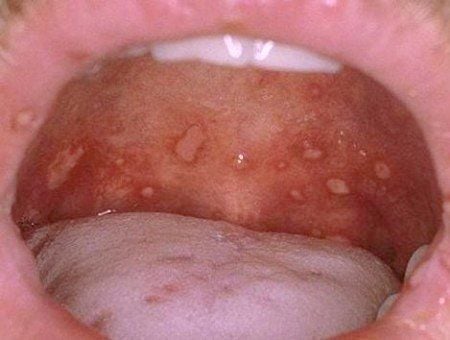
Thời kỳ lây truyền bệnh nhân xuất hiện các vét loét miệng
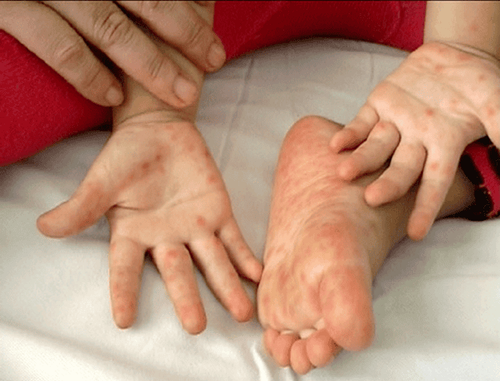
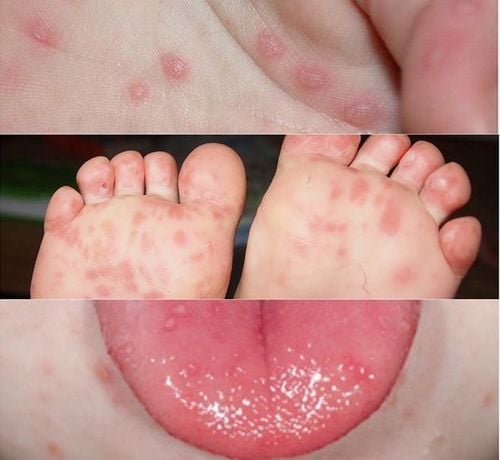
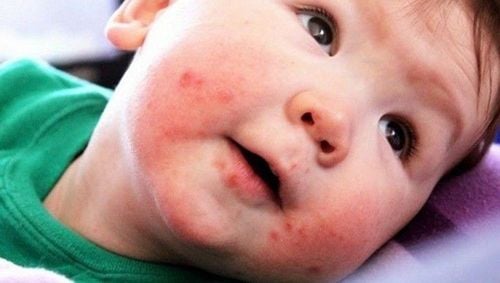
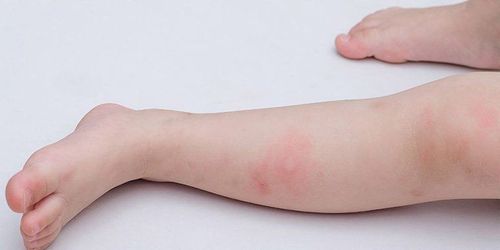
3. Symptoms of hand, foot and mouth disease in children
Place of rash: palms, soles, elbows, knees, buttocks, abdomen, mouth Rash shape: red, vesicles, lumpy, erythematous, gray, oval, when healed without scarring . Sensation: no pain, no itching.
4. Specimens used in hand, foot and mouth diagnosis
Types of specimens used to test for hand, foot and mouth disease in children include:
Stools, throat swabs, fluid from blisters, fluid from blisters on the skin, cerebrospinal fluid, blood, and a serological reaction to determine the effectiveness of the test. specific antibody price.
5. Methods of testing for hand, foot and mouth disease in children
Virus isolation method: culture the patient's specimen into monkey kidney cells or human embryonic cells., the virus will destroy cells; RT-PCR test helps detect the RNA code of the virus; Serological tests help identify specific antibodies by neutralization reaction, immunofluorescence reaction. In which, the diagnosis is confirmed when the culture test is positive for virus isolation or PCR from one of the following specimens: skin blister fluid, throat swab, stool, blood, and cerebrospinal fluid.
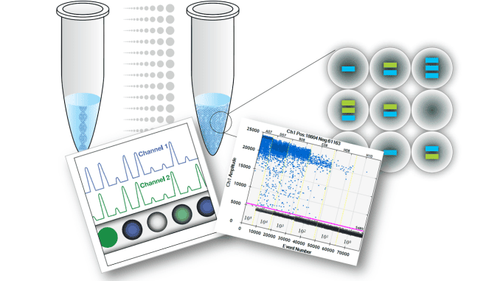
Kỹ thuật xét nghiệm RT- PCR được sử dụng trong xét nghiệm bệnh tay chân miệng
6. Grading of hand, foot and mouth disease in children, when to be hospitalized?
Grade 1: only mouth ulcers and/or skin lesions Grade 2: muscle tremors, restlessness, confusion, changes in cerebrospinal fluid (> 5 cells/mm3) Grade 3: weakness, paralysis, paralysis Cranial nerve, convulsions, coma (glasgow score < 10) Grade 4: respiratory failure, pulmonary edema, hypertension, cardiovascular collapse. Parents need to quickly take the child to the hospital for treatment when there are signs:
Grade 1: the child has one of the following symptoms: high fever > 39 degrees Celsius, fever for more than 3 days, vomiting a lot, somnolence, leukorrhea Blood platelets > 17,000. The child has signs of grades 2 – 4.
7. How to prevent hand, foot and mouth disease in children effectively
Currently, there is no specific treatment for hand, foot and mouth disease as well as a preventive vaccine, so it is very important to adhere to hand, foot and mouth prevention measures. Some methods to prevent hand, foot and mouth are as follows:
Personal hygiene, wash hands with soap (especially after changing clothes, diapers, after contact with feces, urine, saliva). Wash toys, utensils, floors. Isolate sick children in the first week. Do not share cups or personal items with sick people. Do not send the patient to school or daycare until the symptoms are gone. Ask your doctor about when to send your child back to school.
Although hand, foot and mouth does not pose much danger, it is contagious and causes pain and discomfort to children. Therefore, when there are signs of suspecting that a child has an illness, parents should soon take their child to a medical center for examination and treatment. Especially during the epidemic season, to avoid overcrowding and overcrowding at the hospital, making the baby tired or cross-infecting some other diseases, parents should also choose reputable and specialized medical facilities. Karma.
Vinmec International General Hospital is the address for receiving and examining respiratory diseases that infants and young children are susceptible to: viral fever, bacterial fever, respiratory infection, pneumonia In children, hand, foot and mouth....With modern equipment, sterile space, minimizing the impact as well as the risk of disease spread. Along with that is the dedication from the doctors with professional experience with pediatric patients, making the examination no longer a concern of the parents.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.