This is an automatically translated article.
Hand, foot and mouth disease is a common disease in many Asian countries, including our country. Therefore, who and what age are most susceptible to hand, foot and mouth disease, as well as how to prevent the disease, is a matter of great interest to many people.1. Overview of hand, foot and mouth disease
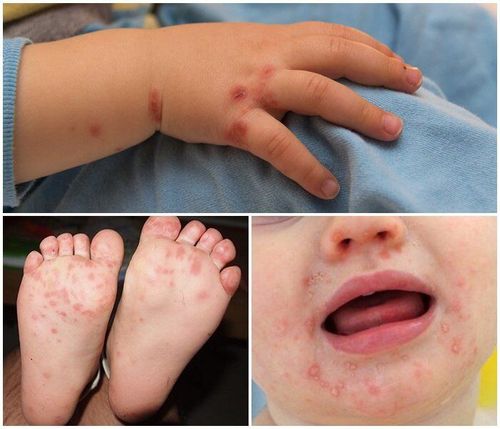
Hand, foot and mouth disease is an acute infectious disease caused by viruses belonging to the Enterovirus group. The route of transmission of the disease is from person to person, through direct contact with the patient, or indirectly with utensils and objects contaminated with the virus present in the nasopharyngeal secretions as well as the blisters of the infected person. Typical symptoms of people with hand, foot and mouth disease are:
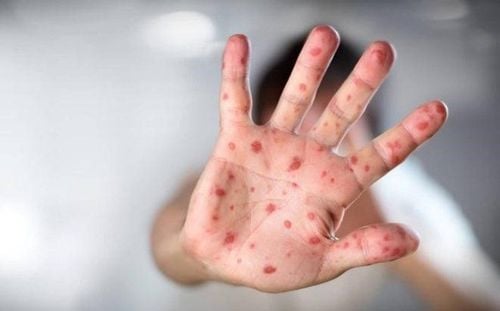
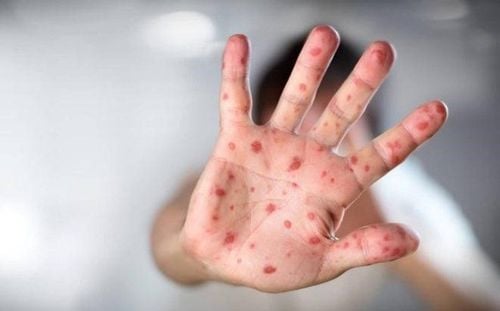
Fever accompanied by sore throat; The appearance of sores on the mouth, gums (gums) and tongue; There are blisters on palms, feet, knees and buttocks. Currently, the World Health Organization (WHO) has reported that hand-foot-and-mouth disease is common in many Asian countries, and an outbreak occurs in many different regions of the globe a few years later. Over the past ten years, the Western Pacific region has reported outbreaks of hand, foot and mouth disease. In addition, Asian countries that have recorded a rapid increase in hand, foot and mouth disease cases recently include: China, Hong Kong, Taiwan, South Korea, Malaysia, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam. Male.
Đại dịch tay chân miệng đã quay trở lại
2. The causative agent of hand, foot and mouth disease
The causative agents of hand, foot and mouth disease are viruses of the Enterovirus group, including many different types such as:
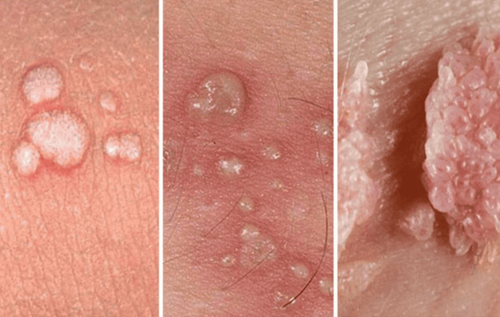
Poliovirus; Coxsackievirus; Echovirus; And other Enteroviruses. In general, hand, foot and mouth disease, which is mainly caused by the Coxsackievirus A16 virus, usually has few complications and goes away on its own. However, hand, foot and mouth disease can also originate from Enterovirus group viruses, including Enterovirus 71 (EV71), which comes with many dangerous and sometimes life-threatening sequelae.
Virus EV71 là tác nhân gây ra bệnh tay chân miệng
3. Subjects prone to hand foot and mouth disease
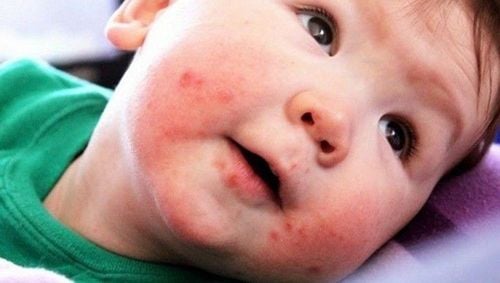
3.1. Children's hand, foot and mouth disease Children are more susceptible to viral infections and hand, foot and mouth disease than adults. The reason is because children have relatively weak resistance and immunity, so they are easily attacked by viruses. Hand, foot and mouth disease occurs most commonly in children under 10 years old, especially those younger than 5 years old. The younger the child, the more severe the symptoms of the disease, but not all children who have been infected with the virus have symptoms of hand, foot and mouth disease.
It should be noted that the human body will not be completely immune to HFMD, this means that a person is likely to contract hand, foot and mouth disease many times in a lifetime. Explaining this problem, doctors believe that hand, foot and mouth disease is caused by many different viral agents, while each disease the body only produces antibodies to a certain virus. Therefore, even if the patient has been infected before, the patient is still at risk of getting hand, foot and mouth disease again if attacked by another virus of the Enterovirus group.
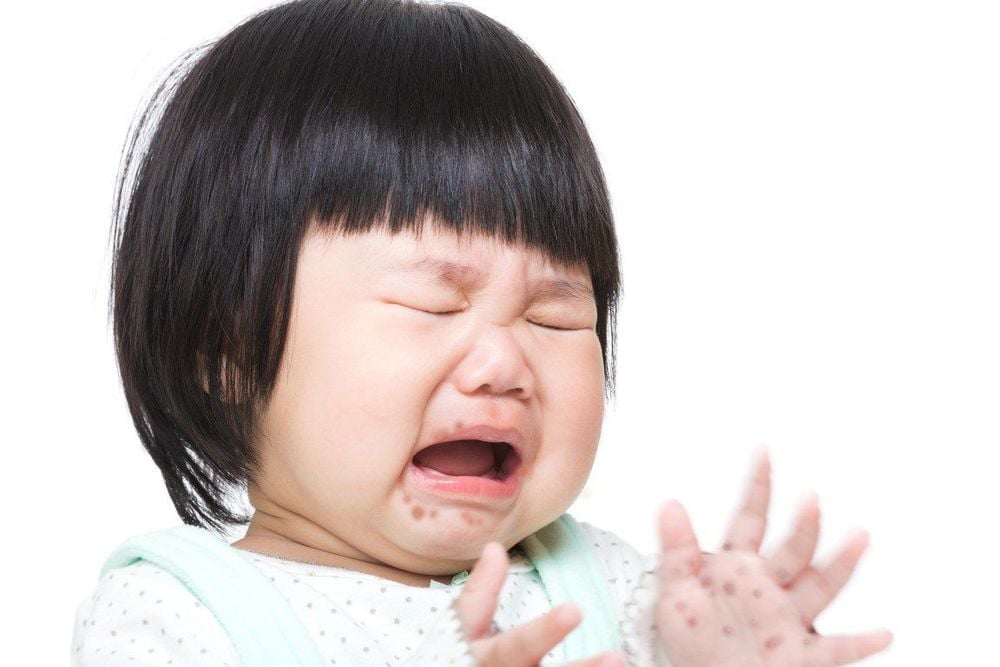

Trẻ em là đối tượng dễ mắc tay chân miệng nhất
3.2. Hand, foot and mouth disease in adults Besides children, all other people, whether or not they have ever had the disease, are at risk of infection if they come into direct contact with the virus or indirectly through the tools that the patient touches. before. Although HFMD cases in adults are not uncommon, most adolescents and adults are already immune so they won't show many signs of HFMD.
More specifically, pregnant women are at risk of infecting and transmitting the virus to the fetus right before labor or during delivery. Therefore, it is necessary to pay attention to prevent disease by not going to crowded places when there is an epidemic or having close contact with infected children.
4. How to prevent hand, foot and mouth disease
So far there is no specific medicine to treat hand, foot and mouth disease, so the patient is only asked to drink lots of water and take more medicine to control symptoms, help reduce fever and relieve pain caused by ulcers. If the patient develops more serious symptoms, prompt medical intervention as well as regular hygiene measures should be applied to reduce the risk of infection.
With the goal of positive prevention and minimizing the health effects of hand, foot and mouth disease in children and young children, the Department of Preventive Medicine - under the Ministry of Health especially recommends that parents and relatives take the initiative Take some preventive measures as follows:
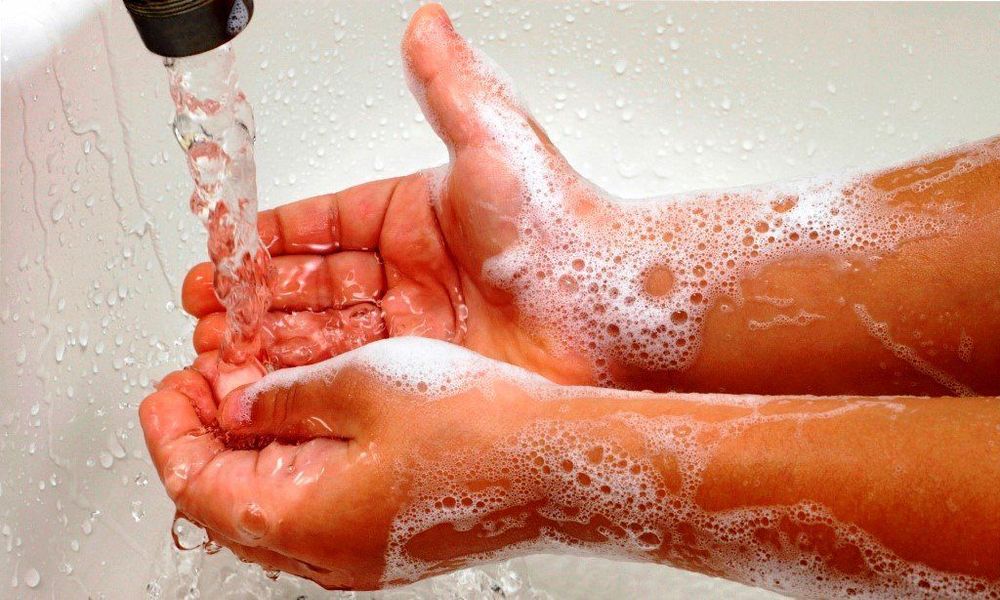

Rửa tay bằng xà phòng diệt khuẩn nhằm phòng ngừa bệnh tay chân miệng
4.1. Wash hands with antibacterial soap Both adults and children should wash their hands often, several times a day with soap under running water, especially when:
Before preparing food; Before eating or feeding the child; Before holding the baby; After going to the toilet; After returning home from going out; After changing diapers and cleaning the baby. 4.2. Eating and drinking hygiene Ensure the diet is full of nutrients; Eat ripe, drink ripe; Wash or soak eating utensils with boiling water before use; Use clean water in daily activities; Do not give food to children; Do not let children eat, suck and suck on toys; Do not allow children to share personal items that have not been disinfected, such as handkerchiefs, cups, bowls, plates, spoons and toys...

Tuyệt đối không cho trẻ ngậm đồ chơi tránh lây nhiễm bệnh tay chân miệng
4.3. Cleaning the living environment Families, kindergartens, and home care facilities need to pay attention to regularly use soap or detergents to clean surfaces and daily contact objects such as:
Toys of children; Learning tools; Door handles, stair handrails; Table/chair, floor; Toilet. In addition, it is necessary to clean up, collect feces and dispose of children's waste in a hygienic place.
Because children under 6 years of age are susceptible to HFMD, parents and teachers must actively monitor their children's health to promptly detect hand, foot and mouth disease. em. Children with symptoms of illness should not go to class, limit contact and play with other children. People with hand, foot and mouth disease must be taken immediately to medical facilities for early treatment, as well as organized isolation for at least 10 days to prevent spread.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.