This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Master, Doctor Ngo Thi Oanh - Pediatrician - Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital.Hypoglycemia in children is when a child's blood sugar (glucose) is too low. Glucose is the main source of nutrients for the brain and body. The normal blood sugar level in children is about 70 to 140 mg/dL. Hypoglycemia is a common clinical problem in neonates, less commonly in infants and toddlers, and rare in older children.
1. Causes of hypoglycemia in children
Hypoglycemia in children can be a medical condition or it can be a complication of diabetes or another disorder. Usually occurs when too much insulin is taken, also known as insulin shock or insulin reaction.Causes of hypoglycemia in children can include:
Taking too much insulin or hypoglycemic drugs Using the wrong type of insulin Incorrect blood glucose results Skipping a meal A meal delayed Eating no enough food for insulin intake Exercise more than usual Diarrhea or vomiting Trauma, illness, infection, or emotional stress Other health problems, such as Celiac disease or adrenal problems Use of sulfonylurea diabetes medications Congenital problems with the way the body metabolizes glucose and starch Rare genetic disorder
2. What are the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia in children?
The signs and symptoms that occur can vary from child to child, including:Tremors Dizziness Dizziness Sweating Hunger Headaches Irritability Pale skin Sudden mood or behavior changes, such as crying reasons or tantrums Clums or jerky movements Difficulty paying attention Confusion Tingling sensation around mouth Convulsions Nightmares and confusion upon waking Signs of low blood sugar in children can be like other health conditions. Children should be taken to a hospital or other health care facility for a definitive examination and diagnosis.

Các dấu hiệu của hạ đường huyết ở trẻ em có thể giống như các tình trạng sức khỏe khác
3. How is hypoglycemia in children diagnosed?
The doctor will ask about your child's symptoms and medical history. In addition, there may be questions about family health history.Your child may have a blood test to check blood sugar. When children with diabetes have symptoms of hypoglycemia, the most common cause is insulin shock.
For children with symptoms of hypoglycemia without diabetes, the doctor may order:
Measure blood sugar and different hormones when the child has symptoms Monitor to see if symptoms does it get better when the child eats food or sugar Have tests to measure insulin action
4. How is hypoglycemia in children treated?
Treatment for hypoglycemia in children will depend on the child's symptoms, age, and general health. Also, it depends on the severity of the condition.For children with diabetes, the goal of treatment is to maintain safe blood sugar levels. This is done by:
Checking blood sugar regularly Help your child learn to recognize the symptoms Treat the condition quickly To treat low blood sugar quickly in children, it is recommended that the child eat or drink something something sugary like:
Cakes Sweets Do not use starchy, protein-rich foods like milk or nuts. They can increase insulin's response to dietary starches causing hypoglycemia.
Blood glucose levels should be checked every 15 to 20 minutes until they are above 100 mg/dL. If hypoglycemia is severe, your child may need an injection of glucagon.
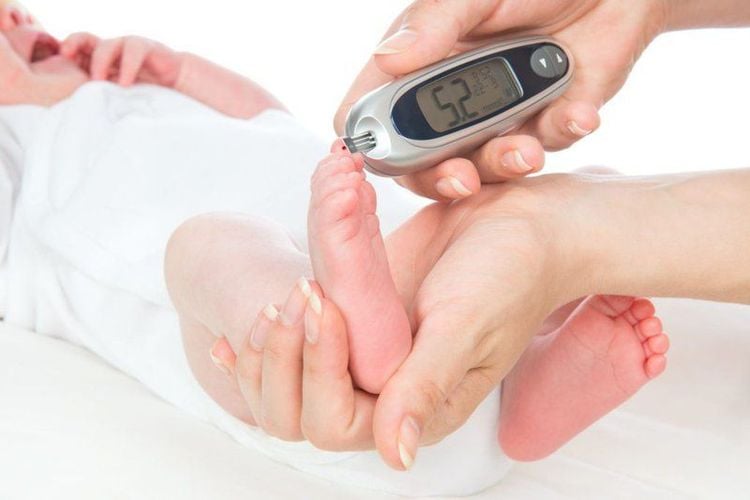
Cần kiểm tra đường huyết thường xuyên ở trẻ em
5. Possible complications and measures to prevent hypoglycemia in children
5.1. Complications
A baby's brain needs glucose in the blood to function. Insufficient glucose can impair the brain's ability to function. Severe or prolonged hypoglycemia can cause seizures and serious brain injury in a child.5.2. Preventative method
Not all episodes of hypoglycemia are preventable. Most children with type 1 diabetes will develop hypoglycemia. The chance of severe hypoglycemia decreases as the child gets older. But we can help children prevent severe episodes of hypoglycemia by:Checking your child's blood sugar often, including at night Checking to make sure blood glucose test strips are not outdated and matched with a blood glucose meter Recognize symptoms Treat medical conditions quickly Other ways to reduce or prevent hypoglycemia include making sure your child:
Take medication at the right time Eat the right amount of food Don't skip meals Check blood sugar before exercise Eat a healthy snack if needed. The snack should include complex carbohydrates and some fat, if possible. To actively control hypoglycemia in children, you should have regular health checkups on schedule. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has general health checkup packages suitable for each age, gender and individual needs of customers with a reasonable price policy, including:
Health checkup package general Standard 2020 VIP general health check-up package 2020 General health check-up package Special 2020 Patient's examination results will be returned to your home. After receiving the results of the general health examination, if you detect diseases that require intensive examination and treatment, you can use services from other specialties at the Hospital with quality treatment and services. outstanding customer service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: stanfordchildrens.org