This is an automatically translated article.
Article by Dr. Le Thi Huong - General practitioner - Department of Examination - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital
Early health checks can help prevent diseases like cancer, diabetes and osteoporosis in the first place, when diseases can be accessed earlier. Screening tests can detect the disease even before you have symptoms. The screening tests a woman needs depends on her age, family history, personal health history, and other risk factors.
1. Breast Cancer Screening Test
The earlier you detect breast cancer, the better the chance of a cure. Small breast cancers are less likely to spread to the lymph nodes and vital organs such as the lungs and brain. If you're in your 20s or 30s, a breast exam should be done as part of your routine checkup every 1-3 years. You may need more frequent screening if you have any additional risk factors.
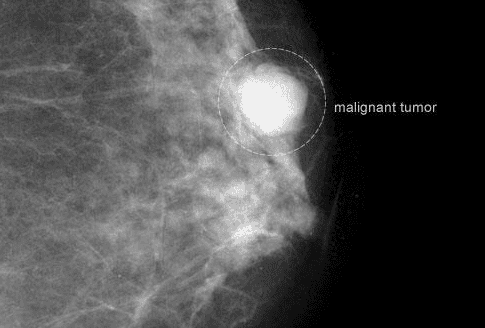
A mammogram is a low-dose X-ray that can often find a tumor before you feel it, although a normal result does not completely rule out cancer. Some experts recommend that once you're in your 40s, you should have a mammogram every year. Then between the ages of 50 and 70, you can take a 2-3 year break. Of course, your doctor may recommend more frequent checkups if you're at higher risk for the disease.
2. Cervical Cancer Screening
Cervical cancer is easy to prevent. The cervix is a narrow passageway between the uterus (where babies develop) and the vagina (birth canal). Your doctor may use a Pap smear and/or HPV test to screen you. Cervical cytology tests find abnormal cells on the cervix, which can be removed before they turn cancerous. The main cause of cervical cancer is the human papillomavirus (HPV), a sexually transmitted disease (STD).
2.1. Cervical cancer screening
During a Pap smear, your doctor will take some cells from your cervix and send them to a lab for analysis. Your doctor will talk to you about whether you need a Pap test alone or in combination with an HPV test and about how often you need to be screened. If you're sexually active and at risk, you'll need a vaginal test for chlamydia and gonorrhea every year.
2.2. Cervical cancer vaccine
The HPV vaccine can protect women under age 26 from some strains of HPV. However, the vaccine does not protect against all cancer-causing strains of HPV, and not all cervical cancers start with HPV. Therefore, regular cervical cancer screening is still very important.
3. Osteoporosis and Fracture
Osteoporosis is a condition in which a person's bones are weak and break easily. After menopause, women begin to lose more bone, but men also develop osteoporosis. The first symptom is usually pain from a sudden fall, bump, or twist. In Americans age 50 and older, the disease contributes to about half of all breaks in women and a quarter in men. Fortunately, you can prevent and treat osteoporosis.
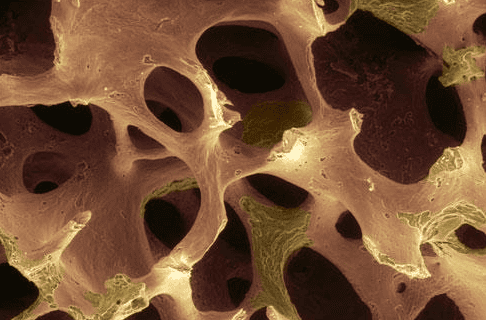
A special type of X-ray called dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) can measure bone density and find osteoporosis before fractures. It can also help predict future fracture risk. This test is recommended for all women 65 years of age and older. If you have risk factors for osteoporosis, you may need to start earlier.
4. Skin cancer
There are several types of skin cancer and early treatment can work for all of them. The most dangerous are melanoma, which affects the cells that give a person's skin color. Sometimes people have a genetic risk for this type of cancer, which can be increased with overexposure to the sun. Basal cell and squamous cell are common non-melanoma skin cancers.
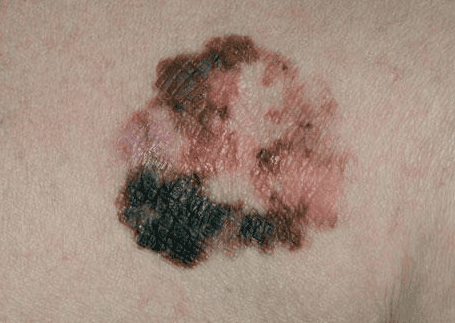
Notice any changes in your skin, including moles and freckles. Notice the changes in their shape, color and size. Some experts recommend that you also have your skin checked by a dermatologist or other medical professional during a routine physical exam.
5. Check for high blood pressure
As you age, your risk of high blood pressure increases, especially if you are overweight or have certain bad health habits. High blood pressure can cause life-threatening heart attacks or strokes without any warning. So, checking in with your doctor to get it under control can save your life. Lowering blood pressure can also prevent long-term dangers like heart disease and kidney failure.
Blood pressure measurement results include two numbers. The first (systolic) is the pressure of the blood when the heart beats. The second (diastolic) is the pressure between beats. Normal adult blood pressure is less than 120/80mmHg. High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is 140/90mmHg or higher. Your doctor will help you with how often to check your levels.
6. Check cholesterol level
High cholesterol can cause plaque to clog your arteries Plaque can build up for years without symptoms, eventually causing a heart attack or stroke. High blood pressure, diabetes, and smoking can also cause plaque to build up. It's a condition known as hardening of the arteries or atherosclerosis. Lifestyle changes and medication can reduce your risk.
To check your cholesterol, you may need to fast for 9 to 12 hours before the test. You will then have blood tests to measure your total cholesterol, LDL "bad" cholesterol, HDL "good" cholesterol, and triglycerides (blood fats). Your doctor will talk to you about when to start and how often to check your levels.
7. Type 2 diabetes
One-third of Americans with diabetes don't know they have it. Diabetes can cause heart or kidney disease, stroke, blindness from damage to the blood vessels of the retina, and other serious problems. You can control your diabetes with diet, exercise, weight loss, and medication, especially when you find it early (pre-diabetes). Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of the disease. Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and young adults.
You may need to fast for 8 hours or longer before having a blood test for diabetes. A blood glucose level of 100-125mg/dl may indicate prediabetes; 126 mg/dl or higher could be diabetes. Other tests include an A1C test and a sugar tolerance test that provide additional diagnostic information. Your doctor will talk to you about when to start and how often to check your levels. Talk to your doctor about getting tested if you have a higher risk, such as a family history of diabetes.
8. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
HIV is the virus that causes AIDS. It is spread through the transmission of blood or bodily fluids with an infected person, such as through unprotected sex or dirty needles. Pregnant women with HIV can pass the infection on to their babies. There is currently no cure or vaccine, but early treatment with anti-HIV drugs can help the immune system fight off the virus.
HIV can be asymptomatic for many years. The only way to know if you have the virus is to have a blood test. An ELISA or EIA test looks for antibodies to HIV. If you get a positive result, you'll need a second test to confirm the result. All sexually active people should get tested. It is recommended that clinicians screen for HIV infection in adolescents and adults aged 15 to 65 years. Adolescents and older adults at increased risk should also be screened.

Most newly infected people test positive about two months after being exposed to the virus. But in rare cases, it can take up to 6 months for HIV antibodies to develop. Use condoms during sex to avoid contracting or transmitting HIV or other sexually transmitted diseases. If you have HIV and are pregnant, talk to your doctor to reduce the risk to your unborn baby.
9. Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal cancer is the second most common cause of cancer death after lung cancer. Most colon cancers arise from polyps (abnormal masses) that grow on the inner lining of the large intestine. The polyps may or may not be cancerous. If it does, the cancer can spread to other parts of the body. Removing polyps early, before they become cancerous, can be completely prevented.
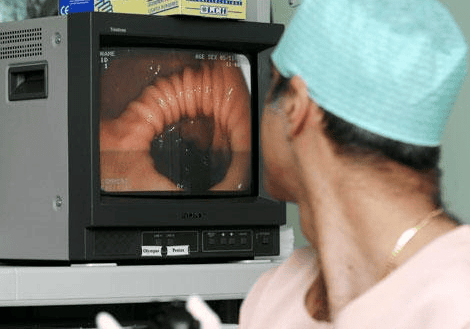
Colonoscopy is a common screening test for colorectal cancer. While you are lightly sedated, your doctor will thread a small flexible tube with a camera attached to your colon. If a tumor is found, it can usually be removed immediately. Another type of test is a flexible sigmoidoscopy, which looks into the lower part of the colon. If you're at average risk, screening usually begins at age 50. Your doctor can also screen you with a home stool test.
10. Glaucoma
Glaucoma occurs when pressure builds up inside your eye. If left untreated, it can damage the optic nerve and cause blindness. Usually, it doesn't cause symptoms until your vision has been damaged.
How often you should get your eyes checked depends on your age and risk factors. They included African-American or Hispanic, over 60 years of age, eye injury, steroid use, and a family history of glaucoma. Talk to your doctor about how often and when to start screening for glaucoma.
You should talk to your doctor about screening tests. Some tests, such as a Pap test or a breast exam, should be a regular part of all women's health care. Other tests may be needed based on your risk factors. Proper screening doesn't always prevent the disease, but it can often catch it early enough to give you the best chance of overcoming it.
Cancer inherently does not spare anyone, it is estimated that every year in the world there is a very large proportion of people dying from cancer. In fact, if the cancer can be detected at an early stage, the prognosis for treatment is very high, even if it is completely cured and not recurred. Therefore, cancer screening is essential, especially for high-risk patients.

Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has been implementing cancer screening packages, including the General (intensive) Cancer Early Detection Package - Female. At Vinmec, there are full modern diagnostic facilities such as: PET/CT, SPECT/CT, MRI..., blood marrow test, histopathology, immunohistochemistry test, gene test, lab test molecular biology, as well as a full range of targeted drugs, the most advanced immunotherapy drugs in cancer treatment. Multimodal cancer treatment from surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, targeted therapy, immunotherapy in cancer treatment, new treatments such as autoimmunotherapy body, heat therapy...
After having an accurate diagnosis of the disease and stage, the patient will be consulted to choose the most appropriate and effective treatment methods. The treatment process is always closely coordinated with many specialties: Diagnostic Imaging, Biochemistry, Immunology, Cardiology, Stem Cell and Gene Technology; Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Department of Endocrinology, Department of Rehabilitation, Department of Psychology, Department of Nutrition... to bring the highest efficiency and comfort to the patient. After undergoing the treatment phase, the patient will also be monitored and re-examined to determine whether the cancer treatment is effective or not.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.