This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Master, Doctor Nguyen Nhu Thu Truc - Obstetrician and Gynecologist - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.
Screening for birth defects before birth is the conduct of certain tests to provide information to parents about whether the fetus has a genetic disorder that leads to any birth defects.
1. What is a genetic disorder?
Genetic disorders occur when there is a change in a person's genes or chromosomes. An aneuploidy is an extra or missing chromosome. Triploid is when there is an extra chromosome, and haploid is when one is missing. Genetic disorders occur when there is a change in a gene called a mutation.
Genetic disorders include many different diseases and birth defects, such as sickle cell disease, cystic fibrosis, Tay - Sachs disease,... In most cases, both parents have to If the mutated gene is passed on to the offspring, the affected offspring will be affected.
2. What are the main types of prenatal genetic disorder testing?
Usually prenatal genetic disorder tests fall into two main categories:
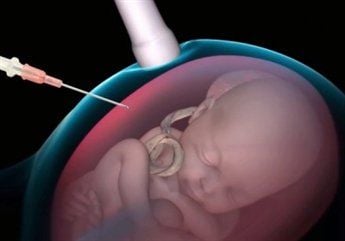
Prenatal screening tests: the results of these tests indicate the possibility of a fetus having an aneuploidy or some other disorder. Prenatal diagnostic tests: these tests can confirm whether the fetus really has a genetic disorder. Samples are cells taken from an amniocentesis or chorionic villus biopsy. Both of these tests apply to all pregnant women.
3. What are the types of prenatal genetic screening tests?
Prenatal genetic screening tests indicate the chance of a fetus having certain genetic disorders, including carrier screening tests and prenatal genetic screening tests:Human screening tests carrying disease genes: conducted for parents (or intending parents), by taking blood or tissue samples (inside the cheeks) for testing. The results of the test will show if the person doing the test carries the disease gene associated with certain genetic disorders. This test can be done before or during pregnancy. Prenatal genetic screening test: the pregnant woman's blood will be tested, and the pregnant woman will have an ultrasound to screen for genetic disorders of the fetus such as aneuploidies, neural tube defects (brain, spinal cord). life), and some birth defects of the abdomen, heart, and maxillofacial. Specific prenatal genetic screening tests include: first trimester screening, second trimester screening, first and second trimester combined screening, and acellular DNA testing . 3.1. What is first trimester screening? First trimester screening is performed between the 10th and 13th weeks of pregnancy. Early screening will detect up to 95% of pregnancies with Down syndrome and 97 percent of trisomy 18/13 cases.
Fetal malformation test in the first trimester is a combination of fetal ultrasound and Double test (taking maternal blood).
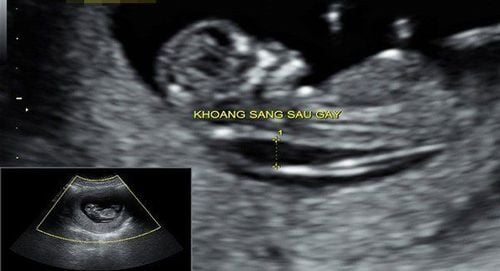
Ultrasound, specifically nuchal translucency ultrasound, will measure the thickness of the space at the nape of the fetus. If the measured value is abnormal, it means the fetus is at higher risk of having Down syndrome or another genetic disorder. It has also been linked to other birth defects such as the heart, abdominal wall, and bones. Double test is done by taking a sample of the mother's blood to evaluate the levels of freeBeta hCG and PAPP-A. This test detects about 95% of pregnancies with Down syndrome. This test is indicated in all pregnant women in the first trimester, especially those with a family history of birth defects, women over 35 years old, pregnant women with diabetes or HIV infection. virus during pregnancy. In addition, the Double test combined with nuchal translucency has the ability to assess the risk of trisomy 18 and 13 syndrome. Down syndrome and trisomy 18 and 13 are abnormal sets of chromosomes in cells. This is one of the genetic diseases that can be screened as early as the 9th week of pregnancy. With the outstanding advantage of being non-invasive, completely harmless to the fetus and can be performed as early as the 8th week, NIPT is recommended to be indicated for high-risk subjects and performed regularly. at Vinmec. Trisomy 21 (Trisomy 21): also known as Down syndrome due to an extra chromosome 21. This syndrome can cause mental and physical retardation in children along with some heart defects. Trisomy 18 (Trisomy 18): also known as Edward's syndrome due to an extra chromosome 18. Pregnant women with this syndrome often have early miscarriages, and are born with severe structural defects. Trisomy 13 (Trisomy 13): also known as Patau syndrome due to an extra chromosome 13. Babies with this defect often do not have a long life or are born with many defects in the body. 3.2. What is the second trimester screening? Second trimester screening includes the following tests:
Triple test: also known as the triple test done between 15 and 22 weeks of pregnancy, it is a screening test uses maternal blood to find out the risk of certain birth disorders, to screen for Down syndrome, trisomy 18 and 13, and neural tube defects. The three substances used in this test are AFP, hCG and Estriol. AFP (alpha-fetoprotein) is a protein produced by both the yolk sac and the fetal liver. AFP is present in the amniotic fluid and crosses the placenta into the mother's blood. Increased AFP levels suggest that the fetus is at risk for neural tube defects such as spina bifida, anencephaly.
Decreased AFP levels if combined with decreased hCG and estriol, the fetus has an increased risk of Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome or other chromosomal abnormalities. In addition, abnormal AFP can also signal a number of malformations such as neural tube defects, fetal abdominal wall defects, cleft lip and palate, maternal malignancy or acute hepatitis ...
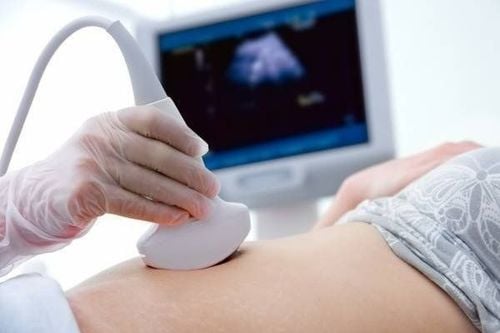
4d ultrasound: performed between the 18th and 20th weeks of pregnancy, to detect most birth defects in the brain and spinal cord, maxillofacial, abdomen, heart and extremities. 3.3 What is the NIPT (non-invasive prenatal screening) test? During pregnancy, from the 5th to 6th week of the fetus, a large amount of fetal DNA is released and moves freely in the mother's blood. Based on this feature, through maternal peripheral blood collection, scientists separate these free DNA and conduct genetic analysis to assess fetal risk with the aim of limiting invasive tests. harm to mother and baby (amniocentesis, chorionic villus sampling).
The NIPT test is most appropriate for women who are at high risk of carrying a fetus with a chromosomal disorder. The NIPT test is limited to women carrying multiples.
NIPT test allows to screen the risk of diseases such as: Trisomy 21,18,13, sex chromosome abnormalities (Turner syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome) and some microdeletion syndromes.
NIPT test can be performed from the 10th to the 22nd week of pregnancy.
The NIPT non-invasive prenatal screening technique at Vinmec is considered the "key" to decode fetal malformations, bringing significant improvement in prenatal screening results. Analytical results will be available in about 1-2 weeks and will be evaluated by genetic pathologists at the Institute of Stem Cell and Gene Technology. Customers will be consulted specifically about possible risks, especially for false positive / negative cases to have appropriate intervention direction.
4. What do the results of the prenatal screening test mean?
The results of a blood test that screen for a genetic disorder expressed in terms of the degree of risk that the genetic disorder may occur:
A positive result means that the fetus is at a higher risk of developing the genetic disorder Compared with the population average, the fetus is not necessarily sick. A negative result means that the fetus has a lower risk of developing a genetic disorder than the population average, but it does not mean that the fetus does not have the disease. Amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling are definitive, and are good screening tests for birth defects in all pregnant women. Experts will advise and carefully explain the meaning of the test results as well as what to do next.
5. How accurate is prenatal genetic disorder screening?
With any test there is a certain rate of false negatives and false positives.
False negative: the result is negative, but in fact has the disease False positive: the result is positive, but in fact there is no disease The specialist will advise on the rate of false negatives and false positives for each test.
6. What should be noted before prenatal genetic screening test?
The information that results from prenatal genetic screening and birth defects screening can help with pregnancy. Even a positive screening result only means that the fetus is at higher risk for Down syndrome or other disorders. For definitive results, amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling should be performed. Knowing in advance of genetic disorders and birth defects of the fetus can help parents better understand their child's disease as well as make necessary preparations in the future, or in some bad situations, parents may decide to terminate the pregnancy after careful consultation from a specialist.
>> See also: Birth defects from statistics to causes – Article written by Doctor Do Phuoc Huy, Vinmec High Technology Center
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Article referenced source: acog.org