This is an automatically translated article.
The article was consulted with Dr. Le Ngoc May - Internal Oncologist - Cancer Center - Radiation Therapy - Vinmec Times City International Hospital.Scalp and neck cancer is one of the skin cancers. Scalp and neck cancers include melanoma and squamous cell cancer. Currently, there are many methods of treating this disease with high results, both in terms of aesthetic and functional results.
1. Signs of Scalp and Neck Cancer
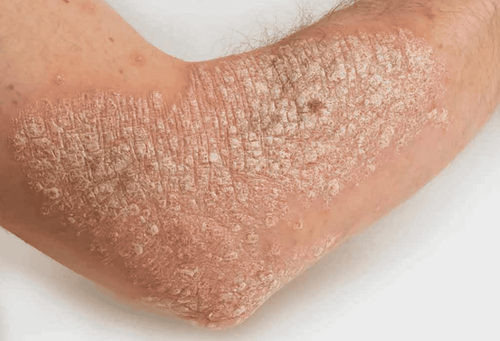
Scalp or neck cancers often show signs of abnormal growths on the skin. This growth can be on the face or neck the appearance of a wart, an ulcer, a mole, a rough, scaly area, or a bump on the skin. The above symptoms may or may not bleed or may be painful. If you have a pre-existing mole, if there is any change in its characteristics such as raised skin contour, irregular shape, change in color, increase in size, itching, or bleeding, it can be a warning sign of malignancy. Sometimes the first sign of melanoma or squamous cell cancer is enlarged lymph nodes in the neck.2. Causes of Scalp and Neck Cancer
Scalp or neck cancer occurs when the DNA of skin cells is mutated. Mutations cause cells to grow out of control and form a mass of cancer cells.Cells involved in skin cancer: Skin cancer starts in the top layer of the skin, which is the epidermis. The epidermis is a thin layer that protects the underlying skin cells, and this layer is constantly shedding. The epidermis contains three main types of cells: The squamous cell layer is located just below the outer surface of the skin and acts as an inner lining of the skin. Basal cells are the layer that produces new skin cells. The location of this cell is below the squamous cells. Melanocytes are responsible for producing melanin, which is the pigment that gives skin color. This cell is located in the lower part of the epidermis. Melanocytes produce more melanin when you're out in the sun to help protect the deeper layers of the skin. Where the cancer begins is a factor in determining the type of cancer and its treatment
Ultraviolet rays and other potential causes: The majority of DNA damage in skin cells is caused by radiation of ultraviolet (UV) rays present in sunlight and in light used in tanning beds. Other factors that can contribute to the risk of scalp or neck cancer include exposure to toxic substances or having a disease that weakens the immune system.

3. Risk factors
Factors that can increase the risk of scalp and neck cancer include:Fair skin: Anyone, regardless of skin color, can get skin cancer. However, people with less melanin (white skin) have less protection than people with darker skin from the harmful effects of UV radiation. So, people with blonde or red hair, light-colored eyes and prone to freckles or sunburn are more likely to get skin cancer than people with darker skin. History of sunburn: Having one or more sunburns as a child or teen increases your risk of developing skin cancer as an adult. Even sunburn in adulthood is a risk factor. Excessive sun exposure: Anyone who spends significant time in the sun can develop skin cancer, especially if the skin is not protected by sunscreen or clothing. Sunbathing, which includes exposure to lamps and tanning beds, also puts you at risk. When the skin is tanned, it is the skin's damage response to too much UV radiation. People living in warm, sunny climates are exposed to more sunlight than people living in cold climates. Living in an elevated area close to sunlight also exposes you to more radiation. Moles: People with multiple moles or abnormal moles called dysplastic nevi have an increased risk of skin cancer. These abnormal moles that look irregular and are usually larger than normal moles are more likely to become cancerous. Family history of skin cancer: If one of your parents or siblings has had skin cancer, you may be at increased risk. History of skin cancer: If you have had skin cancer once and have been cured, there is a chance that it will come back. Weakened immune system: People with weakened immune systems are at increased risk of skin cancer, including people with HIV/AIDS and people taking immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant. Exposure to radiation therapy: People who receive radiation therapy for skin conditions such as eczema and acne may have an increased risk of skin cancer, especially basal cell carcinoma. Exposure to certain substances, such as arsenic, can increase the risk of skin cancer.
4. Diagnosis of Scalp and Neck Cancer
Diagnosis is made by clinical examination and biopsy. Basal cell and squamous cell cancers are staged according to their size and extent of growth. Basal cell cancers rarely metastasize to the lymph nodes, but they can grow quite large and invade surrounding structures. Squamous cell cancer has many lymph nodes in the neck and parotid glands and can spread along nerves.To stage, scalp or neck cancer is not based on size but on how deep it invades skin layers. Therefore, superficial biopsies will not provide accurate information to guide treatment. Scalp or neck cancer is difficult to predict and can spread to distant organs. Malignant tumors often require a sentinel node biopsy, a technique performed by a head and neck surgeon, to determine if cancer has spread to the lymph nodes. lymphatic or not.

5. Head and neck skin cancer treatment
Early-stage basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell cancer can be removed with Mohs surgery. The technique is to remove each layer and be examined with a microscope until the entire cancer tissue is removed. This allows maximum protection of the healing tissue and ensures the highest level of treatment results. Tumors that involve nerves, lymph nodes, or are large are not suitable for Mohs surgery and require a combination of different treatments such as surgery and radiation or chemotherapy.Limit your exposure to the sun's ultraviolet rays, especially between 10am and 4pm, when the sun's rays are strongest is your dermatologist's advice. Wear a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher (both lips and ears) when outdoors while wearing a hat, sunglasses, and sun-protective clothing. If you notice changes in your skin like new growths, the appearance of a mole, or a sore that won't heal, see your doctor right away.
Early diagnosis for timely treatment helps increase the recovery ability for skin cancer patients. A skin biopsy is one of the methods used to diagnose skin cancer. At Vinmec International General Hospital, the skin biopsy technique is currently being applied in a sterile environment. The doctor performing the procedure is experienced and highly qualified, professional medical examination and treatment services.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: Hopkinsmedicine.org, Mayoclinic. org