This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Phan Ngoc Toan - Emergency Medicine Doctor - Emergency Department - Vinmec Danang International Hospital.Emergency situations are situations in which the patient's life is in danger and basic life functions are not guaranteed. Placing the patient in a safe position is one of the most important steps in determining the effectiveness of first aid.
1. What is the safe position in emergency?
Emergency situations that are dangerous to human life such as injury, traffic accident, drowning, electric shock can happen at any time and in any situation in life. At that time, it is important to do basic first aid to protect the life of the victim at the scene, while waiting for the professional rescue team to arrive.First aid is a sequence of actions that must be taken quickly, including freeing the casualty from the danger zone, resuscitating respiratory arrest if present, stopping bleeding, and placing the patient in an upright position. safe position. These actions, if done well, will limit the dangers affecting the patient, prevent a worse progression, maintain the patient's life and determine the effectiveness of the treatment later.
A safe position in an emergency is a position that ensures the airway circulation, an essential organ that determines the survival of the victim. The choice of a safe position depends on the characteristics and circumstances of each different hazardous situation. For a comatose victim, a safe side position is recommended so that the tongue does not fall backward causing obstruction of the pharynx and narrowing of the upper airway.
The safe side-lying position is also applied when the victim vomits a lot, to avoid aspiration of vomit into the airways, causing respiratory failure. However, trauma victims suspected of having cervical spine injury should be fixed with a straight cervical spine so as not to injure the cervical spinal cord, the patient should not be tilted if the operator is alone or has no experience. first aid test. When performing basic cardiopulmonary resuscitation, the patient should be placed in the supine position to facilitate the implementation and monitoring of the patient's pulse, blood pressure and consciousness.
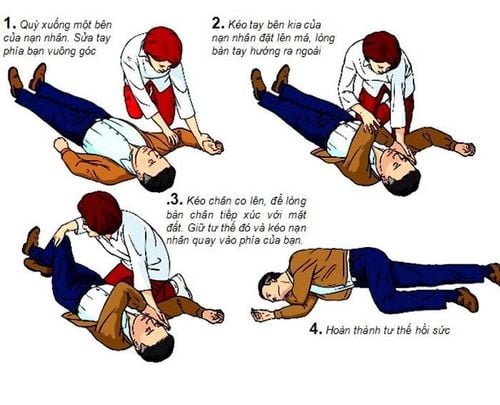
Tư thế nằm nghiêng an toàn được khuyến cáo để lưỡi không bị tụt về phía sau
2. Safe side lying position in emergency
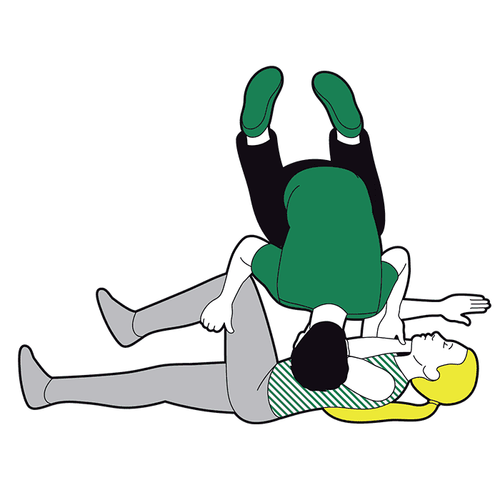
The safe side lying position is the position recommended by most emergency care associations in most cases. In this position, the patient should be placed so that:Tilt the patient completely to one side. The head is close to the ground so that the neck is higher than the mouth. The arms are extended straight, perpendicular to the body or the upper arm is flexed. gently grasp the lower arm that is straightening the lower leg straight with the body, the upper leg slightly bent and crossed over the other leg If having difficulty, the first aider can use objects available at the scene to set up on both sides of the patient to fix the posture, it is best to use a pillow or soft cloth to avoid causing other unnecessary injuries. The safe side-lying position is considered appropriate for most emergency situations, with the exception of cases where cervical spine injury is suspected. The safe side-lying position offers many benefits such as:
Creates ventilation for the upper airway, preventing the tongue from falling backwards. Bring sputum and foreign objects out, creating more favorable conditions for cleaning the mouth and throat. Avoid choking vomit back into the respiratory tract, causing respiratory failure. Steps to follow are as shown below:
Step 1:
If you find a person unconscious, perform initial assessment if possible (shake, pinch, listen for breathing, watch for chest movement) move, take pulse). Quickly call for help from surroundings or the emergency system, turn on speakerphone and follow professional instructions If victim is unconscious but breathing on their own, place them in a safe position on their side
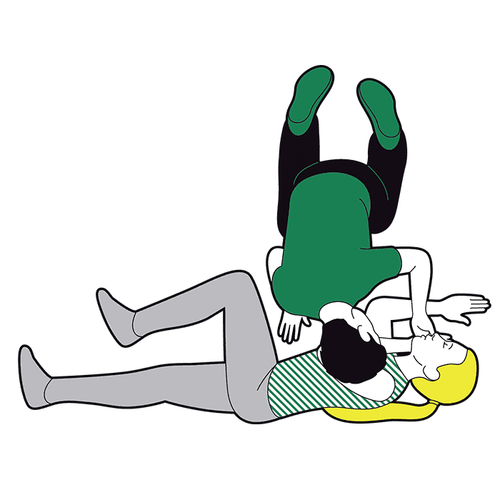
Kneel beside the casualty, straighten the victim's legs If they are wearing glasses, or have any obstructions in their pockets, remove them. Don't check their bags for small items that won't get in the way.
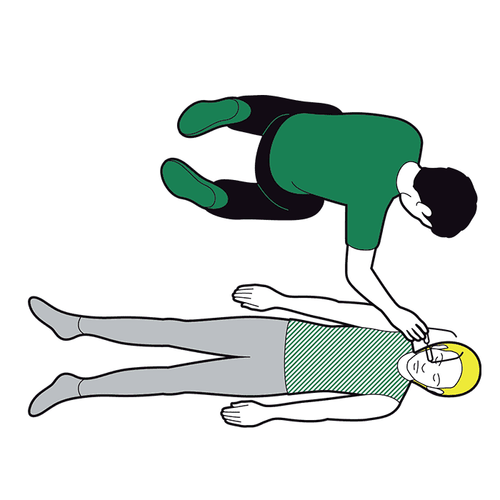
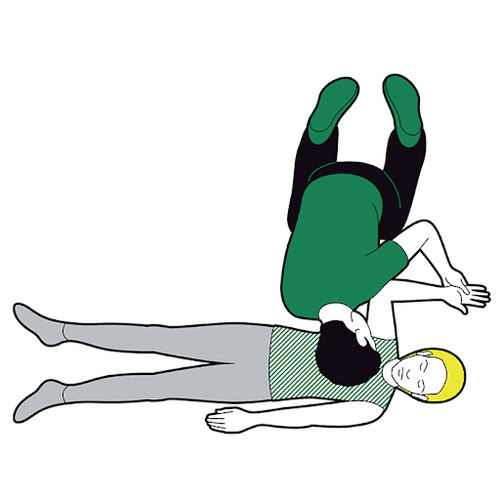
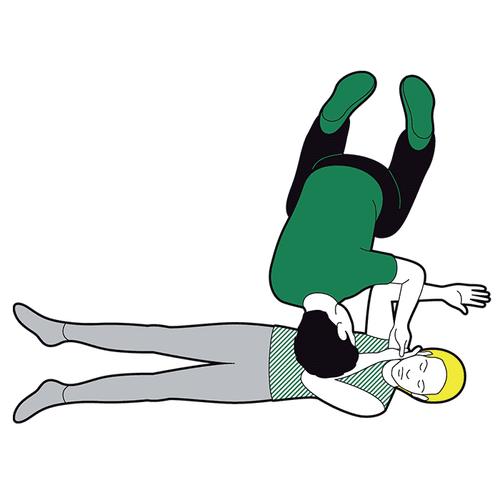
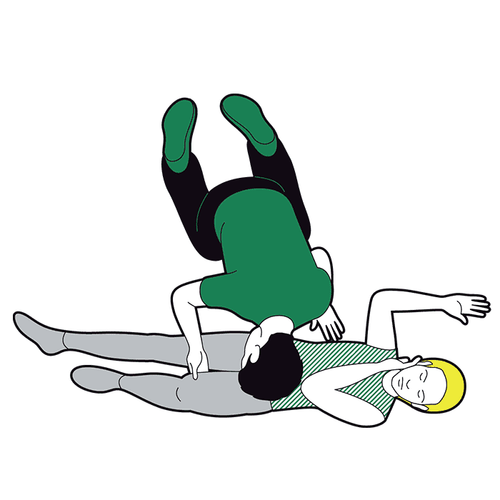

Call 911 for emergency help if you haven't already. Monitor victim response while waiting for help to arrive. If the casualty remains in the recovery position for more than 30 minutes, place the victim in a safe position on the opposite side.
3. Introduce some other safe positions in first aid
Supine position The victim is placed supine on a hard surface, with the head in a natural position. The supine position is applied to patients with suspected hypotension, cervical spine injury and who are undergoing emergency respiratory arrest.Supine position with head elevated The victim lies on his or her back with the head elevated no more than 30 degrees. The supine position is high to limit cerebral edema and reduce the risk of aspiration of vomit into the lungs, suitable for cases of suspected cerebrovascular accident or traumatic brain injury with hemodynamic values in the normal range. often. Victims with low blood pressure or conditions that reduce cerebral perfusion should not be placed in this position.
Supine position with high legs The victim is placed on his back with his legs elevated using a chair, soft pillow, or any other item available at the scene. The supine position with high legs is suitable for victims with edema of the two extremities, a lot of blood loss due to trauma to enhance blood circulation from the lower extremities to the heart.
prone position This is the least used position in clinical practice because it creates many difficulties for first aid and patient monitoring. Patients who are placed in the prone position also experience discomfort and breathing difficulties. However, the prone position is suitable for patients with back and chest injuries that need to be exposed and examined or applied to patients with severe acute respiratory failure with indications for prone ventilation.
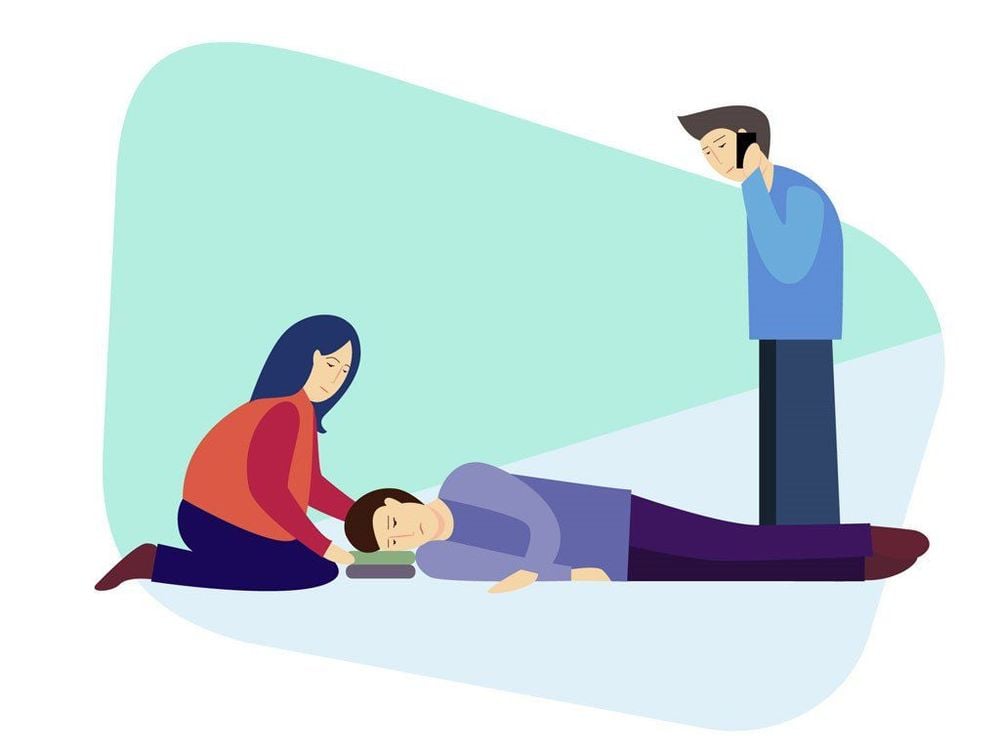

Nằm nghiêng an toàn là một tư thế được hầu hết các hiệp hội cấp cứu hồi sức khuyến cáo trong hầu hết các trường hợp
Master Phan Ngoc Toan used to work as a Internal Medicine Doctor at Quang Tri General Hospital, Emergency and Intensive Care Doctor - Hoan My Da Nang Hospital before working at Vinmec International General Hospital. Da Nang as it is today. Doctor Math has a lot of experience in the treatment of Resuscitation – Adult Emergency, Pediatric Emergency.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
SEE MORE
Emergency myocardial infarction Emergency heat stroke emergency Pneumothorax emergency