This is an automatically translated article.
Cholecystitis is one of the common diseases of the gallbladder. One of the serious complications of this pathology is perforation, rupture of the gallbladder, which can be life-threatening.
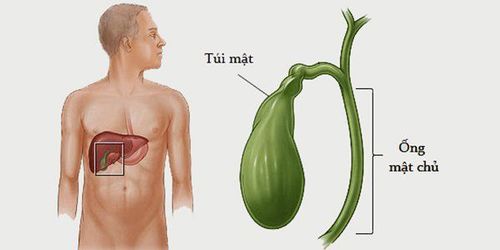
1. Location and role of gallbladder
The gallbladder is pear-shaped, green, small in size, located on the underside of the right lobe of the liver (right hypochondrium). When fully distended, the gallbladder is about 6-8cm long and 3cm wide. The gallbladder belongs to the extrahepatic biliary tract and consists of three parts: neck, body, and fundus. The gallbladder is responsible for storing bile produced by the liver. Bile is responsible for helping digest fats and assisting the body in absorbing fat-soluble vitamins and nutrients. In the process of breaking down fat, the gallbladder is responsible for pushing and regulating the amount of bile that passes through the duodenum into the small intestine to digest food.
2. An overview of cholecystitis
Cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder (with or without gallstones). Gallstone cholecystitis accounts for 90% of cases. As the stones move and rub against each other, they can damage the gallbladder wall or block the bile ducts. This condition causes bile to stagnate in the gallbladder, causing active substances or bacteria in the bile to cause cholecystitis.
In addition, cholecystitis can also be caused by bacteria, viruses or parasites. Besides, another cause of cholecystitis is a tumor that compresses the bile ducts, stagnates the outflow of bile, and easily causes infection. In the elderly, cholecystitis can be caused by a high-fat diet.
When the gallbladder is inflamed, the typical manifestation is pain in the right lower quadrant, penetrating the back or right shoulder, sometimes epigastric pain, so it is easy to confuse with the symptoms of stomach pain - duodenum. When in pain, if the patient eats or drinks, the pain will increase due to irritation of the biliary tract. The patient may also develop a fever several hours after the pain. Other symptoms are jaundice, yellow eyes, palms, feet, ... The degree of jaundice more or less depends on the degree of obstruction of bile. Besides, patients may have symptoms of digestive disorders such as loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting,...
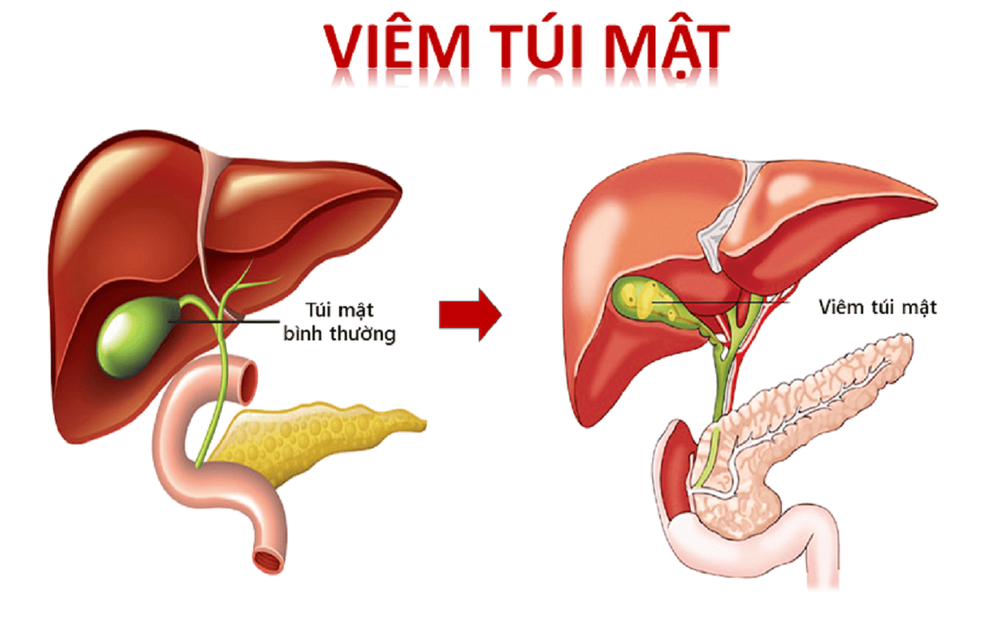
Hình ảnh mô phỏng tình trạng viêm túi mật
3. Perforation, rupture of gallbladder due to cholecystitis
Cholecystitis, if left untreated for a long time, can cause the gallbladder to be damaged, not work effectively, even leading to dangerous complications such as:
Gallbladder distention: If cholecystitis forms due to the accumulation of bile, the gallbladder can stretch and swell beyond its normal size, causing pain, increasing the risk of gallbladder rupture, infection, and gallbladder necrosis; Bacterial infection: Excessive accumulation of bile in the gallbladder, causing cholecystitis, increases the risk of bleeding into the gallbladder, which can cause infection in the blood or other parts of the body; Necrosis: If left untreated, cholecystitis can cause tissue death in the gallbladder; Perforation of the gallbladder (broken gallbladder): This is the result of an enlarged gallbladder or necrosis of the gallbladder. In case the perforation is not detected early, the abdomen is prone to infection, which can directly threaten the patient's life.
4. Doctor's advice
Depending on the condition of cholecystitis, the doctor will recommend specific treatment to prevent gallbladder rupture complications. Treatment options for patients with cholecystitis are as follows:
Medical treatment: Rest, fluids to balance electrolytes. Then, use pain relievers, smooth muscle relaxants and appropriate antibiotics as prescribed by the doctor; Surgical treatment: Only perform emergency surgery if the patient does not respond to medical treatment, accompanied by severe toxic infection or surgical complications such as gallbladder necrosis, peritoneal bile infiltration and peritonitis . Currently, doctors often apply laparoscopic gallbladder surgery technique. Most cases of cholecystitis are caused by gallstones. Therefore, in order to reduce the risk of cholecystitis leading to perforation and rupture of the gallbladder, each person should take measures to prevent gallstone formation as follows:
Do not skip meals or improperly fast; Only eat white meat, limit red meat, fat and animal organs. With vegetable protein such as beans, beans, you should eat in crushed or simmered form; Exercise regularly, at least 30 minutes/day to improve health and avoid the risk of gallstones; If you must lose weight, you should lose weight slowly (about 0.5 - 1kg/week) because losing weight too quickly can increase the risk of gallstone formation; Maintain a healthy weight because being overweight or obese increases the risk of gallstones. Therefore, you should reduce the number of calories you eat daily, combined with increased physical activity; Periodic health check and deworming as directed by the doctor.

Người bệnh nên thăm khám với bác sĩ khi có bất thường tránh tình trạng vỡ túi mật
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.