This is an automatically translated article.
Acute cholecystitis is an emergency disease, so it is necessary to detect and treat it early to avoid possible life-threatening complications.
1. What is acute cholecystitis?
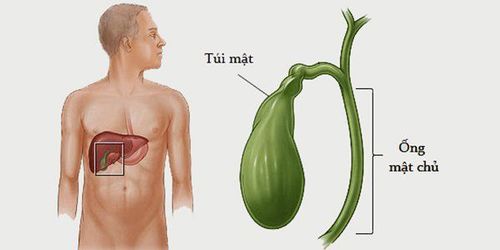
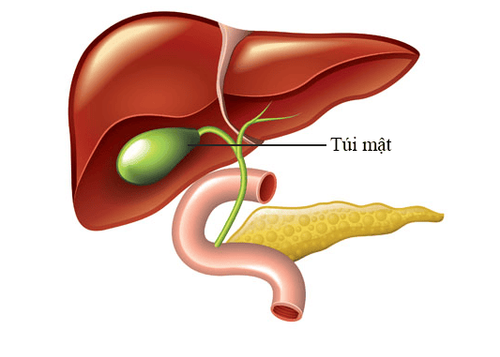
1.1 What is the function of the gallbladder?
The gallbladder is located close to the liver, about 8-10cm long, about 3-4cm wide. The gallbladder and cystic duct are responsible for storing bile produced by the liver. When we eat, bile will be excreted more. The gallbladder will contract, expelling bile into the common bile duct, emptying bile into the duodenum to go down the small intestine to digest food. At the same time, the gallbladder also coordinates the flow of bile into the duodenum in a rhythmic manner. When the gallbladder becomes inflamed, it blocks the passage of bile to the small intestine.
1.2 Causes of acute cholecystitis
The leading cause of cholecystitis is bile duct stones and gallstones (accounting for up to 90% of cases). Gallstones cause stagnation of bile, damage the gallbladder wall, cause bacterial infection leading to acute cholecystitis. If the acute attack passes, it will become chronic cholecystitis, causing atrophy of the gallbladder wall, making the gallbladder adhere to the stone. In the absence of bacterial infection, gallstones will persist for many years. However, if the gallstone rubs against the mucosa, or if the gallbladder becomes infected by bacteria, it will lead to pyelonephritis.
Other causes of acute cholecystitis are bacteria, worms in the bile ducts. The most common bacteria in acute cholecystitis are E.coli, Proteus, Salmonella or anaerobic bacteria. In addition, cholecystitis can also be the result of a coagulopathy or a complication of selective neurectomy, causing disturbances in gallbladder contractility, cholestasis, or trauma.
In other cases, acute cholecystitis may be caused by a tumor compressing the bile duct, blocking the outflow of bile, causing infection. In elderly patients, cholecystitis may be caused by a high-fat diet.
1.3 Symptoms of acute cholecystitis
Basic manifestations of acute cholecystitis include: Abdominal pain, fever and jaundice. Patients often have abdominal pain after eating, mainly pain in the right lower quadrant, penetrating the back or spreading to the right shoulder, but sometimes pain in the epigastrium (above the navel). A few hours after abdominal pain (or 6-12 hours), the patient may have a fever up to 39°C, accompanied by chills, sweating. Others, patients have jaundice, yellow eyes, tongue, palms, soles of the feet, ... if stones block the bile ducts causing accumulation of bile. In addition, the patient also has symptoms of nausea and vomiting, flatulence, abdominal distension, ...

Biểu hiện cơ bản của viêm túi mật cấp gồm đau bụng
2. Complications of acute cholecystitis
Acute cholecystitis, if not detected early and treated promptly, can cause some dangerous complications such as gallbladder necrosis or perforation or rupture of the gallbladder. Gallbladder perforation is a very dangerous complication because it can cause circulatory failure, internal bleeding, fistula into the gastrointestinal tract or peritonitis. Peritonitis due to gallbladder rupture can easily lead to adhesions of internal organs such as (stomach - duodenum, colon, pancreas, great omentum) or localized abscess in the abdomen, dangerous danger to the patient's life.
In other cases, acute cholecystitis may not cause perforation or rupture of the gallbladder, but causes the gallbladder to swell, the gallbladder wall to be dilated, weak, and causes bile to leak into the abdomen, leading to biliary peritonitis. Biliary peritonitis is a dangerous complication that can lead to septic shock, hypotension, cardiovascular collapse and even death.
In addition, acute cholecystitis can also cause bile duct abscess and pyelonephritis. In particular, acute cholangitis can cause sepsis, a condition that can be life-threatening.
Therefore, when there are symptoms of fever, abdominal pain, especially after eating fatty foods, people with pre-existing gallstone disease or chronic cholangitis should quickly go to the doctor for diagnosis and treatment. positive value. This will help the patient avoid dangerous complications of acute cholecystitis.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.