This is an automatically translated article.
Article written by MSc Nguyen Thuc Vy - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital
Epilepsy is a common disorder of the nervous system. It is important to distinguish between seizures (seizures) and epilepsy (epilepsy). Approximately 4% of the population has at least one seizure during their lifetime. In patients with first-time seizures, cranial MRI is mostly normal because seizures can be triggered by fever, medication, dehydration, or insomnia. The term epilepsy is used for cases of spontaneous and recurrent seizures.
1. Epilepsy can be divided into 2 groups
Partial seizures: include simple partial seizures when the patient does not lose consciousness when a convulsion occurs and complex partial seizures when the patient loses consciousness when a muscle convulsion occurs. Complicated partial seizures can progress to generalized seizures. Generalized Seizures: Seizures that are obvious in all regions of the brain are called generalized epilepsy, the person loses consciousness and the convulsions cause muscle spasticity. About 60% of patients with epilepsy can be controlled with antiepileptic drugs. In many patients with epilepsy, the use of antiepileptic drugs does not control the seizure symptoms. Using MRI in epilepsy with seizure-specific pulse sequences can detect seizure causes in 80% of these patients.
Excision of the epileptic brain regions detected on MRI is the only effective treatment for these patients.
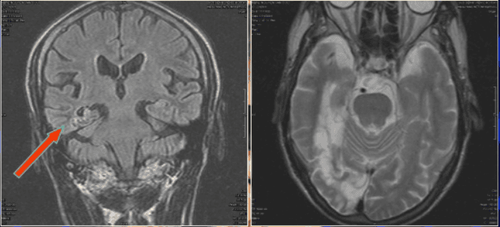
2. Role of MRI in Epilepsy
MRI helps detect and interpret epileptic lesions. Contributing to treatment and prognosis. Selection of patients for surgery.
3. When to order MRI in epilepsy
Cranial MRI is indicated in secondary generalized partial or focal epilepsy whose diagnosis is based on clinical and EEG, epilepsy unresponsive to medical therapy, or epilepsy with neurological deficits. evolution.4. Common causes of seizures not controlled by medication
Mesial temporal sclerosis is the most common cause. Cortical developmental malformations: focal cortical dysplasia, microcephaly, gray matter ectopic,... Brain tumor Vascular abnormalities: arterial venous malformation (gliosis) due to sequelae of trauma, infarction,... Nerve skin syndrome (phakomatosis) and other mixed abnormalities.

5. Seizure-specific pulse sequences in cranial MRI
In addition to the basic pulse sequences in cranial MRI for epilepsy patients, special pulses such as 3D T1W Gradient echo IR with a thin slice thickness of 1mm have high white matter - gray matter resolution (BRAVO pulse sequence). for GE machines), 3D FLAIR, FLAIR oblique assessment of the hippocampus, other techniques such as MR-spectroscopy.
Vinmec Nha Trang Hospital with GE Healthcare's 3.0 Tesla Silent Resonator, the current generation of optimal machines in detecting birth defects of the brain as well as the causes of epilepsy. quality and assist in the selection of treatment options for the patient.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.