This is an automatically translated article.
The article was consulted with Specialist Doctor I Tran Quoc Vinh - Emergency Doctor - Department of Resuscitation - Emergency - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Immune system deficiencies are defects in the body's natural immune response mechanism that can be caused by impaired spleen function or splenectomy. This will make the spleen unable to eliminate bacteria in the blood leading to an increased risk of sepsis by shell bacteria.
1. How to diagnose infection due to immunodeficiency?
The following factors can be used to diagnose immunodeficiency in a patient:Fever and unexplained symptoms due to immunosuppression Have a bacterial strain considered superinfection in an immune individual fully immunocompromised but etiologically immunocompromised person Duration of organ transplantation and degree of immunosuppression Broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy is effective in high-risk or asymptomatic patients Localized However, it should be noted that not all cases of fever are caused by infection. Other issues such as rejection, tissue ischemia and necrosis, thrombophlebitis, and lymphoma should be considered for diagnosis. distinguish.
If the patient is still febrile without finding a source of infection, it is possible to monitor the direction of viral infection, look for abscesses, look for systemic candidiasis or problems related to the liver or spleen or infection with aspergillus.
Patients should be monitored for all local signs carefully and do tests consistent with local findings such as urine culture, sputum culture, blood culture in addition to routine tests such as complete blood count, X-ray - Optical, ultrasound. Other procedures such as biopsies of the liver, skin, and bone marrow can help confirm the diagnosis.
In transplant patients, most infections occur in the first 2 to 4 weeks after transplantation, related to the procedure and inpatient hospital stay or to the organ transplant.
After lung transplant, especially pneumonia and mediastinitis, liver transplant is prone to intra-abdominal abscess, cholangitis, peritonitis, kidney transplant or urinary tract infection, perirenal abscess and infected lymph node cyst. In contrast, in bone marrow transplant patients, the cause of fever is unknown in 60-70%.
2. Possible causes of immunodeficiency
Humoral immunodeficiency: usually congenital, although hypogammaglobulinemia may be present in patients with multiple myeloma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia and in splenectomy patients Granulocytopenia: common after hematopoietic cell transplantation (stem cell transplantation), after myelosuppressive chemotherapy in patients with tumors or in acute leukemia Immunodeficiency Cells: is a large and heterogeneous group that includes HIV, Hodgkin's lymphoma, immunosuppressive corticosteroids, and cytotoxic agents. hematopoietic: patients are at risk of infectious complications from the first post-transplant period to 3 months after, especially in allogeneic transplant patients and are taking immunosuppressive drugs to treat graft disease chronic hostility Organ transplant recipients : infections may be due to the transplanted organ or the type of surgery and length of hospital stay Deficient states Other immunocompromised: is a group of patients who are not separately immunodeficient but are at increased risk of infection due to the use of immunosuppressive drugs, asthenia, trauma, invasive procedures, nervous system disorders Central or obstructive lesions of the lungs, ureters, or pyelonephritis
3. How to prevent infection in immunocompromised patients?
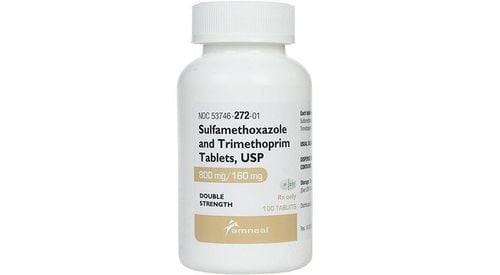
Trimethoprim: Prophylaxis of peumocytsis in organ transplant patients, reduction of the incidence of bacterial pneumonia, urinary tract infections due to nocarida and toxoplasmosis Acyclovir: prophylaxis of infections herpes simplex virus and chickenpox in organ transplant patients Gancyclovir : prophylaxis of cytomegalovirus infection in organ transplant or bone marrow transplant patients Oral non-absorbable antibiotics and quinolones : avoid gastrointestinal bacterial infection , reduces the risk of sepsis in patients with leukopenia In addition, hand washing remains the simplest and most effective measure to reduce nosocomial infections in all patients, especially those immunocompromised.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space. Customers when choosing to perform tests here can be completely assured of the accuracy of test results.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.