This is an automatically translated article.
Post by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Gastrointestinal Endoscopy - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
Gallbladder function plays an important role in the sphincter of Oddi mechanism and patients without a gallbladder are more likely to have sphincter of Oddi dysfunction. Other potential factors for sphincter of Oddi dysfunction include female sex, hypothyroidism, irritable bowel syndrome, pre-existing pancreatitis, and exogenous medications.
1. Cholecystectomy and the risk of sphincter of Oddi
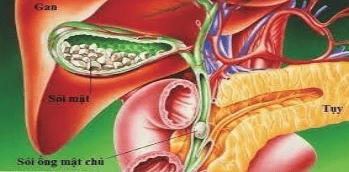
Certain populations, such as patients who have undergone cholecystectomy, have a predisposition to disorder of the sphincter of Oddi. In subjects with an intact gallbladder, CCK hormone inhibited sphincter phase wave activity of Oddi, but 6 months after cholecystectomy, CCK did not inhibit this activity. Overall, about 1.5% of patients develop sphincter of Oddi disorder after cholecystectomy.
2. Aging of the gallbladder, preoperative gallstones, gallstone lithotripsy, liver transplantation and alcoholism. Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction has also been associated with aging of the gallbladder, preoperative cholelithiasis, gallstone lithotripsy, liver transplantation, and alcoholism.
Delayed biliary emptying associated with hypothyroidism suggests another risk factor for sphincter of Oddi disorder. In addition, subjects with hypothyroidism have an increased risk of gallstones, which is thought to be secondary to the absence of a relaxing effect of thyroxine on the sphincter of Oddi.
Patients with irritable bowel syndrome may be at increased risk of sphincter of Oddi disorders. Evans and colleagues report that patients with irritable bowel syndrome after cholecystectomy were more likely to demonstrate a delayed response to the sphincter-relaxing properties of CCK compared with post-cholecystectomy patients. biliary tract without irritable bowel syndrome. The prevalence and incidence of sphincter of Oddi disorders in irritable bowel syndrome patients is unclear because of the difficulty of diagnosis due to the overlap of symptoms.
4. Drugs and risk of sphincter of Oddi Disorders Exogenous agents play an additional role in populations at risk for sphincter of Oddi. Opiates are known to alter flow through the sphincter of Oddi. In the absence of a gallbladder, morphine, meperidine, and pentazocine increase biliary pressure in the gallbladder.
Trials in cats showed that Leucine and methionine-enkephalin induce initial contraction followed by prolonged relaxation of the sphincter of Oddi in cats, suggesting that endogenous delta opioidism is involved in increased flow through the sphincter. Importantly, the naloxone antagonist does not increase the basal sphincter of Oddi pressure induced by morphine but reduces the effect of morphine on the frequency and amplitude of the sphincter of Oddi phase wave. The inhibitory effect of naloxone suggests that opioid receptors are involved, whereas the absence of naloxone antagonizes the sphincter basal pressure of Oddi possibly mediated by opioid receptors.
Thus, morphine increases the amplitude and frequency of the phase wave (via the opioid receptor) as well as the basal pressure (via the opioid receptor) of the sphincter of Oddi. These effects have also been demonstrated with fentanyl and codeine. Morphine showed limited effect on the sphincter of Oddi in pre-cholecystectomy patients, whereas it caused a significant increase in postoperative basal sphincter pressure. Because morphine can cause abdominal pain unrelated to the sphincter of Oddi, Holtzer and Hulst proposed a “morphin-enzyme-pain” stimulation test: The pain was associated with at least a doubling of alanine aminotransferase 8 hours after Drug administration showed sphincter of Oddi dyskinesia. Morphine-associated transaminase elevations have been reported to be 65-fold higher than normal in patients without gallbladder. Mousavi and colleagues demonstrated that chronic opiates induce sphincter of Oddi dysfunction compared with controls, and some authors have documented asymptomatic, dilated CBD in opiate-addicted patients.
Briefly, sphincter of Oddi disorder denotes impaired bile flow through the sphincter of Oddi due to fixed stenosis or disordered muscle control (dysmotility). Gallbladder function appears to play an important role in the sphincter of Oddi mechanism and patients without a gallbladder are more likely to have sphincter of Oddi dysfunction. Other potential contributing factors include female gender, hypothyroidism, irritable bowel syndrome, pre-existing pancreatitis, and exogenous medications.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References:
Elham Afghanistan. Sphincter of Oddi Function and Risk Factors for Dysfunction. Front Nutr. Year 2017; 4: