This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Internal Cardiologists and Interventional Cardiologists - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Atrial fibrillation is one of the most common cardiac arrhythmias worldwide. Good prevention or treatment of atrial fibrillation plays an important role in avoiding the serious complications that atrial fibrillation can cause, including stroke.
1. What is atrial fibrillation?
In the normal person, the heart consists of four chambers, two atria above and two larger ventricles located below. The right atrium receives oxygen-poor blood from organs in the body, and sends it to the right ventricle to pump blood to the lungs, where gas exchange occurs to become oxygen-rich blood. The left atrium receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs and sends it down to the left ventricle to carry blood throughout the body.
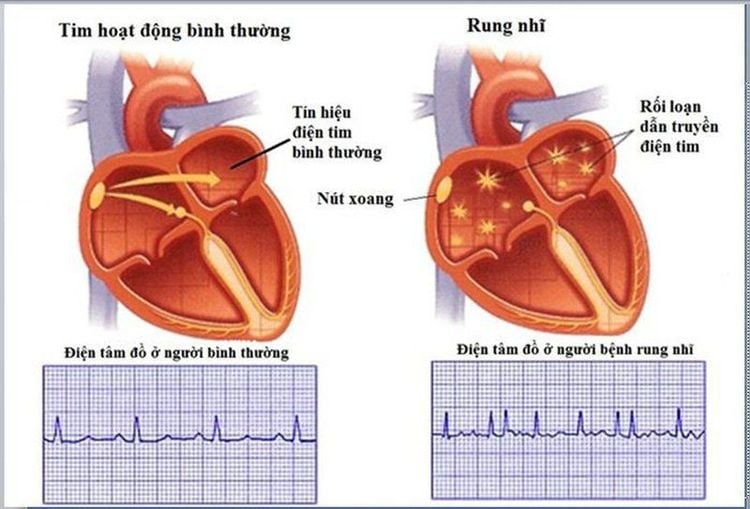
The reason for the color flow to circulate the heart is due to the synchronized and rhythmic contractions of the heart chambers. The heart is capable of spontaneous impulses thanks to the aortic sinus node located in the right atrium, close to the point where it empties into the right atrium chamber of the superior vena cava. The impulses generated by the sinus node have an average frequency of about 60-100 beats per minute and are transmitted to other parts of the heart through a conduction system that reaches to the individual cardiac muscle cells. It is thanks to this impulse generation and impulse conduction system that the chambers of the heart contract regularly and perform well the task of pumping blood to feed their body.
When there is an abnormality in the impulse generation and/or impulse conduction system, an arrhythmia occurs. Atrial fibrillation is a very common clinical arrhythmia. In atrial fibrillation, the sinus node loses its ability to control the rhythm, and instead, different locations in the atrial chamber take turns sending out continuous pulses that stimulate the muscle fibers of the atria to vibrate. The pulse frequency at points in the two atrial chambers is very large but irregular, about 350-600 beats/min. The two atria do not contract, but only vibrate, thereby reducing blood flow to the ventricles and increasing the amount of blood pooling in the atria, stimulating blood clotting leading to the formation of small clots in the chambers. atrium. In addition, if these fast-frequency impulses spread down the two ventricles, the heart rate will increase, in case the heart rate is too fast, it will create ineffective strokes (empty beats), causing the heart rate to increase. reduced blood flow to the body, the patient may have low blood pressure or faint.
Many statistics show that in the population, the number of people with atrial fibrillation is very high. Atrial fibrillation also increases the risk of stroke by up to 5 times compared with the general population and is the cause of more than 25% of clinical strokes. Atrial fibrillation does not go away on its own and often gets worse if not detected and treated promptly.
Bệnh rung nhĩ còn làm tăng nguy cơ mắc đột quỵ lên đến 5 lần so với những người bình thường
2. Risk factors for atrial fibrillation
The direct cause and mechanism of atrial fibrillation are not fully understood. However, experts have identified many risk factors for atrial fibrillation. Risk factors are not the cause of the disease, everyone is at risk for atrial fibrillation, especially those who have risk factors, are more likely to develop atrial fibrillation, or if the disease is present, the risk of developing atrial fibrillation is higher. The risk of severe progression and complications is also increased. Some risk factors have been recognized such as:
Age: the elderly, especially those over 60 years old, account for a higher proportion of patients with atrial fibrillation compared with young people. Cardiovascular disease: Atrial fibrillation is closely related to hypertension. Diseases related to the coronary artery system, heart valve disease, pericarditis, myocarditis, or after cardiac surgery, congenital heart disease are also factors that increase the risk of disease. atrial fibrillation. Metabolic diseases such as diabetes and substance abuse increase the likelihood of atrial fibrillation. Certain systemic diseases such as undetected and well-controlled hyperthyroidism also increase the risk of atrial fibrillation. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: can lead to atrial arrhythmias such as multifocal atrial tachycardia, atrial fibrillation.

Rung nhĩ có mối liên quan chặt chẽ tới bệnh tăng huyết áp
3. Diagnosis of atrial fibrillation
Diagnosis of atrial fibrillation is based on clinical and laboratory findings, although many patients with atrial fibrillation may not have any symptoms. Atrial fibrillation often causes patients to feel nervous, palpitations because the heart beats at a very fast rate, often >100 beats/min.
Patients with atrial fibrillation because the heart does not pump blood effectively, so it is easy to fall into a state of shortness of breath, shortness of breath, even fainting or a very dangerous drop in blood pressure. Chest pain, sweating, and dizziness may also occur when the ventricles beat at a rapid rate, especially in patients with concomitant coronary artery disease.
Prolonged atrial fibrillation left untreated and detected early can lead to congestive heart failure. When the heart failure stage, the patient easily feels tired when exercising or at rest, reducing the ability to work, appearing edema, swollen neck veins.
In clinical practice, atrial fibrillation is diagnosed based on the electrocardiogram. Monitoring of heart rate and conduction characteristics helps to evaluate abnormal arrhythmias in more detail.
To protect heart health in general and detect early signs of myocardial infarction and stroke, customers can sign up for Cardiovascular Screening Package - Basic Cardiovascular Examination of Vinmec International General Hospital . The examination package helps to detect cardiovascular problems at the earliest through tests and modern imaging methods. The package is for all ages, genders and is especially essential for people with risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.