This is an automatically translated article.
Rhesus factor (Rh) is an inherited protein found on the surface of red blood cells. If your blood has this protein it is considered Rh positive and if it is not, it is negative.1. What is Rh blood group?
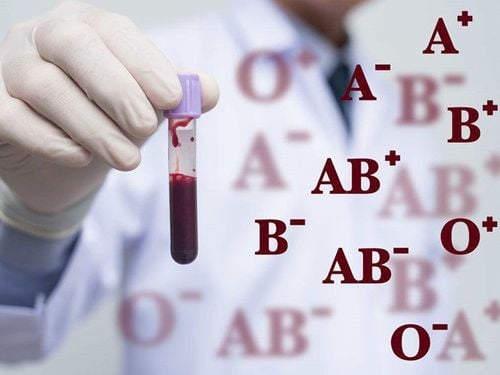
In addition to the ABO blood group system, the blood group is also classified according to the Rh blood group, also known as the rhesus factor. This is another type of antigen found on red blood cells. If the cells have antigens, they will be considered Rh positive. If they don't, then they are considered Rh negative. Depending on whether Rh antigens are present or not, each blood type is written after the name with a positive or negative symbol, for example A positive blood group is written as A+.Rh positive is the most common blood group. Having Rh negative blood type is not a disease and usually does not affect your health. However, it can affect the pregnancy of the mother and the fetus, for example, the mother is Rh negative but the fetus is Rh positive, during pregnancy, the pregnant woman needs to be monitored and taken care of. difference between mother and fetus are Rh incompatibility. The fetus can inherit the Rh factor from either parent.
2. Why is a Rh factor blood test needed?
Rh blood group system antigens are inherited, and anti-Rh antibodies only appear in the Rh- body when immune with red blood cells containing the D (Rh+) antigen. This antibody is usually IgG. If an Rh(-) person has never received an Rh+ blood transfusion, there will be no immediate reaction to their Rh+ transfusion. However, after 2-4 weeks of Rh+ blood transfusion, the amount of anti-Rh antibodies was relatively high enough to cause agglutination of the donor Rh(+) red blood cells to persist in the recipient's blood. This reaction is slow and very mild. After 2-4 months of Rh transfusion, the anti-Rh antibody concentration in Rh- human blood reaches the maximum. If Rh + blood is given to these people for the second time, it can cause a serious blood transfusion accident, no less than a transfusion accident of the ABO system. After several transfusions of Rh(+) blood to an Rh(-), Rh(-) person becomes very sensitive to Rh(+) antigens, blood transfusion complications are extremely dangerous. That's why health care workers need to pay attention to people who have received blood transfusions many times. And healthy people and healthy people both need to determine the Rh blood group to classify it as negative or positive, from which to have an appropriate treatment plan in case a blood transfusion is necessary.
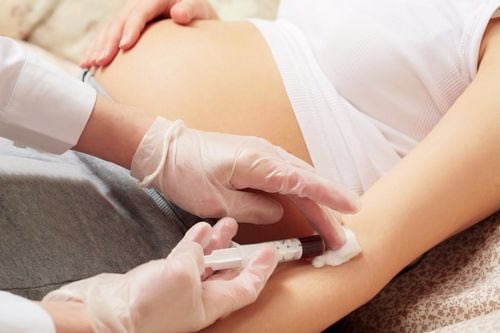
Xét nghiệm máu yếu tố Rh
3. What is the importance of rhesus blood group test?
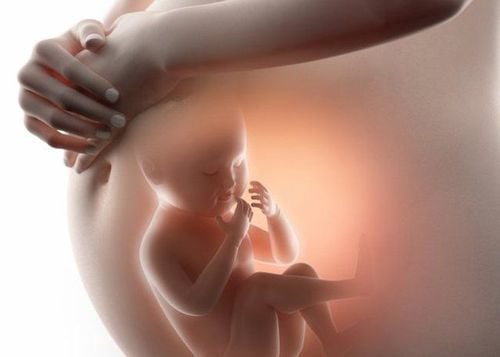
During pregnancy, problems can occur if the mother is Rh(+) and the fetus is Rh(-). Normally, the mother's blood does not mix with the fetal blood during pregnancy. However, a small amount of your baby's blood can come into contact with your blood during delivery or if you have bleeding or abdominal trauma during pregnancy. If you are Rh(-) and your baby is Rh(-), your body may make proteins called Rh antibodies after coming into contact with your baby's red blood cells.The antibodies produced are not a problem in the first pregnancy. The bigger concern is with subsequent pregnancies of the same woman. If the next fetus is Rh(+), these Rh antibodies can cross the placenta and destroy the baby's red blood cells. This can lead to life-threatening anemia in the fetus, a condition in which red blood cells are destroyed faster than the baby's body can produce red, while red blood cells Demand plays an extremely important role to carry oxygen throughout the body and nourish the fetus.
Therefore, Rh(-) pregnant women are advised to have some other blood tests such as antibody screening tests during the first trimester of pregnancy, during the 28th week of pregnancy and at delivery. Antibody screening tests are used to detect antibodies against Rh(+) blood. If you have not started producing Rh antibodies, you may need an injection of a blood product called Rh immune globulin. Immunoglobulins prevent the mother's body from producing Rh antibodies during pregnancy. If the baby is born with Rh(-) blood type, no additional treatment is needed, and if the baby is born Rh(+), you will need another shot soon after birth.
If the woman is Rh(-) and the fetus may be Rh(+), the doctor may recommend Rh immune globulin injections in situations where the mother's blood may come into contact with fetal blood, including:
Miscarriage Abortion Ectopic pregnancy - when a fertilized egg implants and implants outside the uterus, usually in a fallopian tube Molar pregnancy, which is a non-cancerous (benign) tumor development in the uterus Amniocentesis - a prenatal test in which a sample of the fluid that surrounds and protects the baby in the uterus (amniotic fluid) is removed for testing or treatment Sampling for a chorionic villus sampling Test prenatal genetic testing (English name is Codocentesis), also known as percutaneous umbilical cord blood sampling (PUBS). Blood is taken from a vein in the umbilical cord to check for chromosomal abnormalities. Doctors usually perform this test when the fetus is 18 weeks old. This test carries a higher risk of miscarriage than amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling. In general, this test is only done when the results of other tests are not clear. Bleeding during pregnancy Abdominal trauma during pregnancy The doctor or midwife performs manual fetal rotation before labor During childbirth bleeding and contact between mother and baby's blood If the antibody screening test shows that the mother has produced antibodies, the injection of Rh immune globulin will not be effective. The fetus and the mother will be carefully and closely monitored. The person can receive a blood transfusion through the umbilical cord during pregnancy, if necessary, the fetus can receive a blood transfusion through the umbilical cord or shortly after birth.
4. What should pregnant women do to prevent complications caused by Rh factor incompatibility?

Đối với các sản phụ lần đầu mang thai nên thực hiện xét nghiệm nhóm máu để phân loại Rh(-) hay Rh(+)
If the woman has Rh(+) blood group, no treatment is needed. However, if a woman has Rh (-) blood group and her baby is Rh (+), there is a chance that her body will create resistance to harm the next pregnancy. If you experience vaginal bleeding at any point during your pregnancy, see an obstetrician immediately. Ask your doctor about scheduling your Rh Immune Globulin injection during pregnancy and remind the health care professionals who will be taking care of you about your Rh status during labor.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: Mayoclinic.org