This is an automatically translated article.
Respiratory rehabilitation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is recommended as an effective treatment. This method helps patients improve breathing difficulties, improve quality of life.
1. Purpose of rehabilitation in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Respiratory rehabilitation helps relieve symptoms of dyspnea, improve quality of life, increase exercise capacity, stabilize or improve disease, reduce the number of exacerbs requiring hospitalization, and reduce the number of days hospital stay, saving treatment costs.
Rehabilitation of respiratory function includes:
Counseling: Patients are advised to quit smoking, advise on nutrition, guide to use medicine, how to use inhaler, inhaler, nebulizer, and oxygen properly, methods of coughing and expectoration, breathing exercises. Respiratory physiotherapy: instructing and practicing techniques to improve ventilation, how to cough up sputum, practice exercises to strengthen physical fitness. Psychological support and social reintegration to improve depression common in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.

Người bệnh được tư vấn về hướng dẫn sử dụng thuốc đúng cách đúng liều
2. Rehabilitation of respiratory function in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
2.1. Method of clearing phlegm to clear the airway The purpose is to help patients know how to remove sputum and bronchial secretions to make the airway open. Includes: controlled cough and forceful exhalation.
Controlled cough A controlled cough helps expel phlegm, clears the airways without making the patient tired, difficult to breathe... Controlled cough technique Step 1: Sit on a comfortable, comfortable bed or chair roof.
Step 2: Inhale slowly and deeply.
Step 3: Hold your breath for a few seconds.
Step 4: Cough twice, the first time to loosen the phlegm, the next time to push the phlegm out.
Step 5: Inhale slowly and gently. Pinch-lip breath a few times before repeating the cough.
Strong exhalation technique Exhale forcefully to replace controlled coughing in cases where the patient is weak, tired, and unable to cough. Strong Exhalation Technique Step 1: Inhale slowly and deeply.
Step 2: Hold your breath for a few seconds.
Step 3: Exhale forcefully and lengthen.
Step 4: Inhale gently. Breathe evenly a few times before repeating.

Người bệnh tập hít thở để làm thông đờm sạch đường hô hấp
2.2. Breathing exercises The purpose is to preserve and maintain respiratory function, overcome air stasis in the lungs
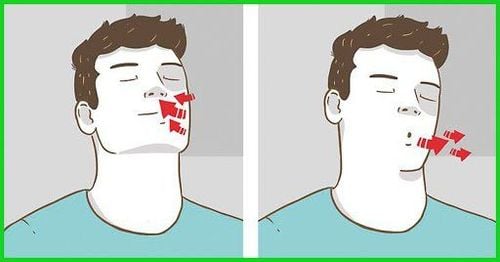
Pinch-lip breathing exercises
Purpose: To push out the stagnant air in the lungs to be able to breathe out. fresh air. Pinch-lip breathing is a method to help the airways not collapse when exhaling, so air can escape more easily, reducing shortness of breath. Perform pursed-lip breathing several times when breathing is difficult until the shortness of breath stops. Pinch-lip breathing technique Step 1: Sit comfortably, relax your neck and shoulders, inhale slowly through your nose.
Step 2: Pinch your lips together as if you are whistling, exhale through your mouth slowly so that the time to exhale is twice as long as the time to inhale.
Diaphragm breathing exercise
Diaphragm breathing exercise will help increase the efficiency of breathing movements and save energy. You should practice diaphragmatic breathing several times a day until it becomes a habit, you should practice diaphragmatic breathing while standing, walking and even doing housework. Horizontal breathing technique Step 1: Place one hand on your stomach and the other hand on your chest.
Step 2: Inhale slowly through the nose so that the hand on the abdomen feels the abdomen rising. The chest does not move.
Step 3: Pull in your stomach and exhale slowly through your mouth with the exhalation time being twice as long as inhaling and the hand on the abdomen feeling the abdomen go down.
Tập thở cơ hoành giúp tăng cường hiệu quả của hô hấp
3. Other respiratory rehabilitation measures
3.1 Exercise and exercise Exercise and movement therapy are a way to promote health and longevity. Exercise helps blood circulation, stronger muscles, stronger respiratory muscles, suitable for each person's ability and is gradually increased in intensity to achieve the necessary effect. Simple movements, from light to severe, when the patient feels short of breath, stop.
3.2 Upper limb movement exercises Upper limb movement exercises aim to strengthen upper extremity muscles, respiratory muscles. Strong shoulder, chest and arm muscles will provide good support for breathing and daily activities such as cooking, cleaning, personal hygiene, etc. Activities include weight lifting, exercise machines. Versatile upper extremity...
3.3 Leg movement exercises The purpose is to help the body gain strength and flexibility and the patient will be tired longer when exerted. Exercises are used such as: bicycle dynamometer, walking on flat ground, climbing stairs...
3.4 Instruct the patient to practice activities in daily activities Walking. Instruct the patient to walk on a flat surface, giving oxygen if necessary. When you feel short of breath, you must stop immediately. Advise the patient to walk at a pace appropriate to the patient's exertion. While walking, it is necessary to combine with diaphragmatic breathing exercises, when breathing in, the abdomen expands, when breathing out, the abdomen collapses. Set reasonable goals to achieve, do not try everything to achieve that goal. Climbing stairs. The patient needs to take one step at a time, holding onto the handrail of the stairs to avoid falling. Climbing is suitable for ability, tired can rest, need to combine with diaphragmatic breathing and pursed-lip breathing, oxygen to reduce shortness of breath and increase exercise capacity.
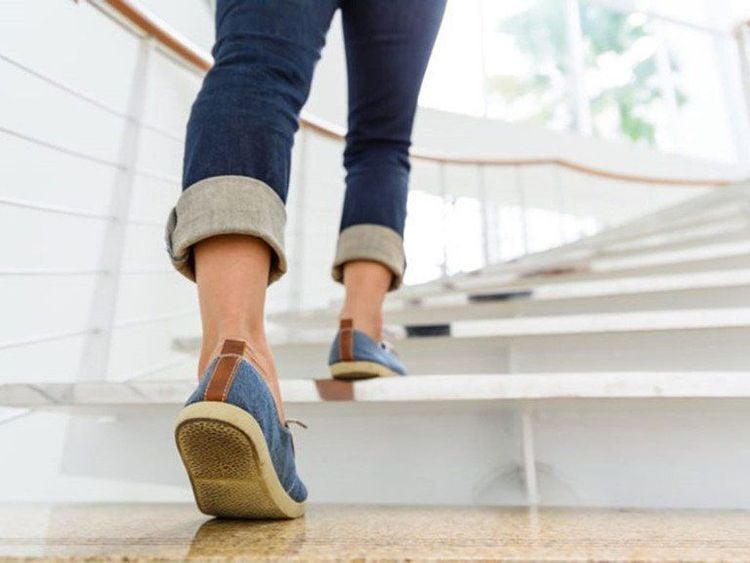

Leo cầu thang kết hợp với kĩ thuật hít thở để có hiệu quả cao nhất
Bathing, personal hygiene. To avoid breathing difficulties, it is recommended to use a chair to sit in the shower, appropriate height, with support or not at will. If you take a hot bath, the humid air is very tiring, so you need to open the door or use a ventilation fan. Strenuous movements that cause shortness of breath should be limited. Cooking. Arrange kitchen tools within easy reach, easy to get, avoid going back and forth. Sit while preparing food. Absolutely avoid stoves with a lot of smoke or grilled dishes. Prefer to use electric stove or microwave. The kitchen needs ventilation, so there should be a ventilation fan or a small fan. Vaccination. A flu vaccine is recommended every year and a pneumococcal vaccine every 3 to 5 years. Vinmec International General Hospital has been deploying immunization services with a variety of vaccines for different audiences, from infants, young children, adults, and women before and during pregnancy. . This includes vaccines against influenza and pneumococcal disease. The advantages of vaccination at Vinmec include:
Patients will be examined by specialist doctors, fully screened for physical and health problems, and advised on preventive vaccines and regimens. injecting equipment, monitoring and post-vaccination care before giving an indication to vaccinate according to the latest recommendations of the Ministry of Health & World Health Organization to ensure the best effectiveness and safety for children. . A team of experienced and professional pediatric doctors and nurses, understand children's psychology and apply effective pain relief methods for children during the vaccination process. 100% of vaccinated patients were monitored 30 minutes after injection and reassessed before leaving. Undertake medical supervision before, during and after vaccination at Vinmec Health System and always have an emergency team ready to coordinate with the vaccination department to handle cases of anaphylaxis, respiratory failure - circulatory arrest, ensuring Ensure timely and correct handling when incidents occur. Vaccines are imported and stored in a modern cold storage system, with a cold chain that meets GSP standards, keeping vaccines in the best conditions to ensure quality. To register for vaccination, please contact directly to Vinmec Health System nationwide or make an appointment HERE.