This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Thi Thanh Binh - Rehabilitation Doctor - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Da Nang International General Hospital.1. Scoliosis
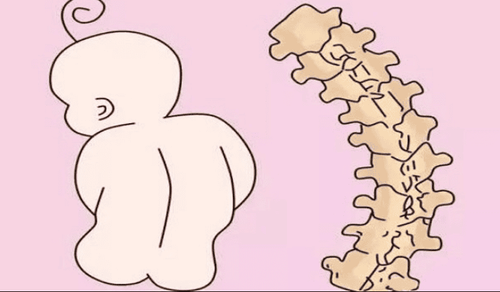
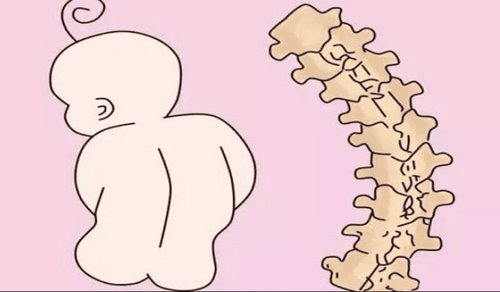
Scoliosis is a condition in which the spine is abnormally curved to the right or left side of the spine. This is a malformation in the spine accounting for 2-3% of the population and causes anatomical distortions, dangerously affecting the respiratory, circulatory, and motor organs, affecting the development of the body. , height and long-term complications.Scoliosis is divided into two main groups: structural and non-structural scoliosis. Nonstructural scoliosis is a curvature of the spine with no structural change and no rotation of the vertebrae, the deformity disappears when the patient bends over. Structural scoliosis is a scoliosis with a deformed spine and rotated vertebral bodies, the deformity persisting when the patient bends over.
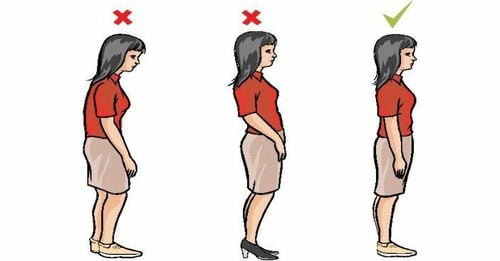
The most common causes of scoliosis are congenital, inherited from parents or have risk factors during pregnancy. In addition, for children with scoliosis, it may be caused by incorrect sitting posture, inappropriate size of the desk. Carrying heavy objects for a long time for scoliosis in adults,...
2. Rehabilitation for scoliosis patients
Rehabilitation exercises aim to stretch the muscles and ligaments on the concave side of the spine and strengthen the muscles on the convex side of the spine, helping to correct the spinal posture. Scoliosis exercises include:2.1 Exercises in the supine position There are 5 exercises in the supine position:
Exercise 1: The patient lies on his back, hands interlaced and placed behind the neck. The technician bends the patient's right knee, brings the opposite knee and elbow together, and then switches sides. Left knee touches right elbow, right knee touches left elbow. Each movement needs to be repeated 10 times. Exercise 2: The patient lies on his back, bends his legs, rests his heels and shoulders on the bed, lifts his buttocks, brings his buttocks to the curved spine, puts him on the bed, then lifts his buttocks to return to the original position. Bring your butt towards the curvilinear spine twice, then bring your butt toward the curvilinear spine once. Repeat this movement 10 times. Exercise 3: The patient lies on his back, bends his knees, lifts his buttocks up to a rainbow shape, holds for 5-10 seconds, and then puts his buttocks down on the bed. Repeat the movement 10 times. Exercise 4: The patient lies on his back, bends his knees, lifts his buttocks up, then brings his butt to the right, put it on the bed, then lifts his butt to bring his butt to the left. Repeat the movement 10 times. Lesson 5: The patient lies on his back, knees bent, fingers of both hands interlaced, arms straight, bends forward, hands to the right and then lies down, repeat and bring both hands to the left. Repeat each movement 10 times. 2.2 Exercises in the lying position Lesson 6: The patient lies on the side of the spine with concave curvature, the spine convex angle is above. Support the lower hand to support the hand on the head while the body is still in a straight position, the lower leg is extended, the upper leg is bent, hold for 5 - 10 seconds and then lie down again. Repeat the movement 10 times.


3. Prevention of scoliosis
To prevent scoliosis, first of all, it is necessary to improve the general health of the body by exercising regularly, strengthening the muscles, connective tissues, ligaments, joints, increasing resilience and balanced development. Especially for young children:Need to prevent malnutrition, rickets. The diet should have enough protein, minerals, calcium and vitamin D. The study table and chair must be appropriate for the age group and the sitting posture must be correct, paying attention to the correct sitting posture. Learning places at school need to ensure enough light, natural lighting and artificial lighting. At home, in addition to the general lighting system, the family also needs to equip a lamp in the study corner for the students, to ensure better lighting. There should be breaks between classes. Students should not carry too heavy a bag, the weight of the bag should not exceed 15% of the body weight. The backpack needs to have two straps, when using it, students wear it on both shoulders, avoiding wearing it on one side. Students, especially primary school students, need to have periodic spine exams to detect early cases of scoliosis so that they can have timely treatment. In summary, scoliosis is an abnormal malformation of the anatomical structure of the spine, and leaves long-term malformed complications, affecting surrounding organs. Therefore, people with scoliosis need to be treated and rehabilitated to improve the curvature. Moreover, for the age of students, it is necessary to have periodic spine examination to detect and intervene in time.
Vinmec International General Hospital is a high-quality medical facility in Vietnam with a team of highly qualified medical professionals, well-trained, domestic and foreign, and experienced.
A system of modern and advanced medical equipment, possessing many of the best machines in the world, helping to detect many difficult and dangerous diseases in a short time, supporting the diagnosis and treatment of doctors the most effective. The hospital space is designed according to 5-star hotel standards, giving patients comfort, friendliness and peace of mind.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.