This is an automatically translated article.
Foot pedal wheelchairs are used not only to assist patients in moving but also in rehabilitation. This is a useful and highly effective means of helping patients move safely and independently in daily activities as well as integrate more easily with the community.1. What is a foot pedal wheelchair?
Foot pedal wheelchair is a type of wheelchair with three wheels, composed of 2 front wheels and 1 rear wheel. The front wheel is a wheel with the function of transmitting motion (force from the pedal drives the right front wheel, not the left front wheel), the rear wheel acts as a steering wheel.The foot pedal wheelchair will move forward if the user presses the pedal forward and will move backward if the pedal is depressed backward. Using a wheelchair will help people with disabilities move comfortably without the help of others.
Foot pedal wheelchair is also of great significance in supporting effective rehabilitation for patients with lower limb mobility impairments such as hemiplegia, sequelae of cerebrovascular accident, accidents such as trauma. spine , polyneuritis, ...
There are many patients with partial paralysis of the lower extremities, it is difficult to move and walk as before, but after using the wheelchair, pedal the foot to exercise. From 3 to 6 months, the patient was able to stand up and walk on his own. Therefore, this is a motor rehabilitation device that helps support patients with independent mobility and improves quality of life.
2. When is wheelchair foot pedal rehabilitation indicated?
2.1 Rehabilitation by foot pedal wheelchair is used when: Incomplete paralysis of 2 lower extremities. Hemiplegia. Cerebral palsy. Have Parkinson's disease. Diseases of the plexus, roots, nerves. Joint disease (acute or chronic stage): arthritis, gout,... Trauma: the stage of inability to bear weight such as after fracture, after rupture of tendons, muscles, ligaments,... Chronic medical conditions that limit mobility: Heart disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), elderly, ...2.2 Not applicable in cases where Patients with cognitive disorders will making it difficult to control the wheelchair. Ulcers in the buttocks, ulcers in the sacrum due to many factors. Patients after hip replacement surgery.

Phục hồi chức năng bằng xe lăn đạp chân
3. Carrying out rehabilitation exercises with a foot pedal wheelchair
Training time: each session is 20-30 minutes.3.1 Step 1: Get on the wheelchair Proceed to remove the pedals from the left and right axles. Lock the brake (the brake mounted on the front wheel of the vehicle can be used if using a vehicle with a brake lever under the seat). Get on the bus with people with weak legs who can't stand for a long time, so someone should help.
3.1.1 Patient is able to self-board. Place the wheelchair as close to the body as possible, and slowly raise the handrail opposite the control arm upwards. Get on the car from the side of the handrail to have the force to lift the body, adjust the body slowly so that the person is facing forward. Sit in the wheelchair seat.
3.1.2. Move the patient in a chair or bed into the wheelchair with the foot pedal Place the vehicle at an angle of about 45 degrees relative to the bed, locking the wheels. Raise the handrail on the side you want to transfer the patient up (opposite the side of the joystick). The patient is seated in the wheelchair from the armrest side to be lifted from the chair or bed. Raise the buttocks slightly so that the buttocks can be moved in the wheelchair. Sit in the wheelchair seat
3.1.3. Transfer patient from wheelchair to wheelchair with foot pedals Slowly stand up from wheelchair, stand still, feet shoulder width apart. To avoid falling, hold onto the armrests of the car, or the furniture. Put the foot pedal wheelchair to the back, so that the axis of rotation of the wheelchair is between the patient's legs. Gently lower your butt into the wheelchair seat.
3.1.4.Transfer patient from bed or high chair to foot pedal wheelchair Place foot pedal wheelchair next to bed or chair in which patient is sitting. Lock the wheels to keep the car fixed, not moving. Stand up from a bed or chair, with your back turned, feet shoulder-width apart so you can easily sit on the wheelchair. Keep your body balance by holding your hands on fixed hard objects such as handrails, tables, chairs, ... Put the wheelchair in from behind, the axle of the wheelchair is between the patient's legs. Slowly lower your hips back into the wheelchair seat.
3.2 Step 2: install pedals, fix 2 feet to 2 pedals. Have the patient wear soft shoes, not barefoot to avoid causing pain.
3.2.1 Standard form (fixes all 2 feet to 2 pedals) In case the caregiver installs the pedals. Push the wheelchair forward and backward to make the shaft rotate, bringing one side of the shaft forward. Place the pedal in turn on the forward rotating shaft.
Put 2 feet into 2 pedals. Adjust and fix the length of the belt to suit the user. Push the wheelchair back and forth, bringing the other axle forward. Similarly, install the pedals, put your feet on the pedals, secure with straps. The case of installing pedals when the patient is still in a wheelchair. Push the wheelchair back and forth to rotate the shaft, leaving the side of the shaft to prevent weak or paralyzed legs from facing downwards. Lock the wheelchair and install the pedals on the shaft that rotates downwards. Put your feet in the pedals, adjust the belt length and secure the right foot, release the brake, push the wheelchair back and forth and bring the other axle forward. Lock the brake, attach the other side pedal, put your foot on the pedal and secure the foot with a belt.
3.2.2 Bicycle mode (only 2 feet on the pedals) Push the wheelchair back and forth to rotate the shaft. The two sides of the shaft rotate in the state of one up, one down. Insert the left and right pedals, put your foot on the pedal.
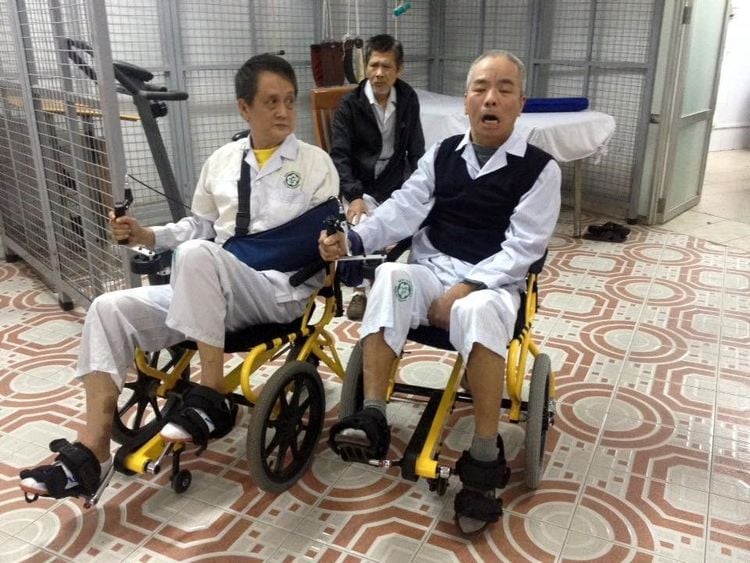

Trong quá trình phục hồi chức năng bằng xe lăn đạp chân cần theo dõi bệnh nhân thường xuyên
Note: It is necessary to have someone monitor the patient during the movement in a straight line, brake and lock the vehicle for timely assistance.
3.3.2 Redirecting the wheelchair After the patient has mastered the technique of moving the wheelchair, pedaling on a straight line, how to brake and lock the car, continue to practice turning the wheelchair. The technician instructs the patient to use the joystick to steer the wheelchair to the right or to the left. To turn right, rotate the joystick to the right. To turn left, rotate the joystick to the left.
In order for the patient to gradually become independent, with less help, a technician or a relative will only follow the patient's car to supervise until the patient can master and operate the vehicle independently. Practical exercises to rotate the pedal wheelchair around a point.
3.3.3 Go around the obstacles Exercise 1: Set landmarks at the beginning and end of the training point (place 2 landmarks 10m apart) and have the patient move around the landmark in a certain direction, then move direction.
Exercise 2: Practice pedaling in a yard with a circumference of about 50m, placing landmarks on the field for the patient to move according to those landmarks. Follow different directions as required.
3.4 Step 4: Getting out The patient must lock the brake before getting off the vehicle, place the pedal wheelchair next to the bed, chair, or other wheelchair (the position where the patient will get out of the pedal wheelchair) and lock brake again. Take your feet off the pedals, remove the left and right pedals.
3.4.1 When the patient gets off the vehicle to transfer to a chair or bed of wheelchair height pedal Raise the handrail on the side wanting to get off (opposite the steering wheel). Lift your butt up a little, move back and forth to sit on a chair or bed.
3.4.2 Getting off and moving to another wheelchair Stand up from the wheelchair, stand still, feet shoulder-width apart. Keep your hands on the table and chair, the armrests for support, to avoid falling. Move the wheelchair, bring the wheelchair from behind. Gently put your butt down and sit in the wheelchair seat.
3.4.3 In case of getting off the vehicle so that the patient is on a bed or high chair Stand up from the wheelchair, stand still, feet shoulder width apart. Keep your hands on the table and chair, the armrests for support, to avoid falling. Push the wheelchair away and turn to sit in bed or chair.
Besides, you need to monitor the patient's exercise, if there are symptoms of fatigue due to overtraining, you need to stop exercising immediately, notify the doctor about abnormal signs. Track progress through measurements of walking speed, speed and distance traveled by patient, muscle force, independent of the patient's activities.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the few hospitals with a modern Rehabilitation Department following the comprehensive healthcare model of major hospitals in the world. There are many treatment and exercise equipments here, including exercise aids for patients, ultrasound machines, electrical pulses, etc. In addition to the current treatment, Vinmec's rehabilitation department also directs Instruct patients to practice at home for preventive treatment, to avoid recurrence in the future.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Source: Ministry of Health