This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Thi Thanh Binh - Rehabilitation Doctor - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Da Nang International General Hospital.Rehabilitation to avoid recurrence after hip dislocation surgery plays an important role in helping patients know how to protect their new hip, and be able to be independent in daily activities.
1. Dislocation of the hip
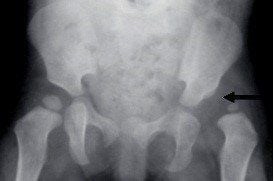
Hip dislocation is a condition in which the femoral head pops out of the socket, which is relatively uncommon, accounting for only about 5% of all dislocations. Hip dislocations are usually caused by severe trauma that occurs due to an indirect force applied to the lower femoral head and knee area when the thigh is flexed, the knee joint is internally rotated and adducted in the flexed position. The force transmitted from the femoral body pushes into the posterior capsule and into the articular socket, causing the capsule to tear. The femoral head protrudes and ruptures the round ligament.Hip dislocation can cause fatal complications of femoral head, sciatic nerve injury, hip arthritis...
There are many ways to classify hip dislocation such as:
By type of dislocation: posterior dislocation, Displaced forward, dislocated downward. Central dislocation According to severity: including 4 degrees The treatment method for hip dislocation depends on the severity and accompanying complications. Non-surgical conservative treatment in the elderly cases of osteoporosis, non-displaced hip fractures, mild protrusion of the femoral head into the pelvis, patients with medical diseases being treated that cannot be operated on... Surgery when orthopedic surgery fails, the fracture line is displaced through the joint, there is a piece stuck in the joint, the head is deviated into the pelvis...
Hip replacement is a modern surgical method for patients who have lost function hip function due to hip injury. The risk of hip dislocation after surgery accounts for about 0.5-4% depending on the surgical technique and concomitant disease. Because rehabilitation after surgery is very important, it is a process from before surgery, after surgery and until discharge from the hospital. Rehabilitation helps patients know how to prevent recurrent hip dislocation.

2. Rehabilitation of hip dislocation
2.1 Principles of rehabilitation The principles of rehabilitation and treatment of hip dislocation include:Protecting the repair tissue, preventing recurrence of hip dislocation Pain relief, reducing inflammation Anti-venous thrombosis Restore Restoring hip range of motion Strengthening hip, pelvic and gluteal muscle groups Restoring gait 2.2 Rehabilitation methods 2.2.1 Rehabilitation after hip dislocation During the patient's time lying motionless:
Keep hip joint immobilized after 3 weeks in bed Breathing exercises to prevent lung complications buttock to maintain muscle strength Resistant movement to the rest of the extremities After a period of immobility
Actively assist with hip movements to maintain range of motion: flexion, extension, abduction, pressure, internal and external rotation by the technician's hand or by the pulley sling. For hip flexion and internal rotation, exercise should be done in a neutral 0-degree position to avoid re-dislocation of the hip. Resistance exercise for quadriceps and scrotum muscles Usually patients walk without supporting their painful feet to the ground from the 3rd to the 6th week. After 6 weeks, the patient can be allowed to walk with partial weight. 2.2.2 Rehabilitation after surgery to replace dislocated hip Stage 1: rehabilitation from 0-6 weeks after surgery. The goal is to help patients practice manual movement of the joints, protect the surgical tissue and prevent muscle contractions and abnormal gait, reduce pain and inflammation. Exercises include:
Passive exercise allowing the groin to flex 70 degrees and fully extend Passive exercise allowing the groin to rotate 70 degrees when the groin is flexed 30 degrees for 6 weeks Passive exercise allowing the groin to rotate 70 degrees while hip extension 0 degrees within 6 weeks Static contraction of glutes, quadriceps After 6 weeks of scaring, massaging hamstrings, quads, paraspinal muscles Cycling in place without resistance after 6 weeks Lying on side, change posture for back pain.
Gently strengthen muscles, restore joint range of motion Cycling in place without resistance, add resistance for about 10-12 weeks Lying on your side, actively practicing internal rotation, external rotation, Lying on your side with elbows with glutes, hip stretchers Lying on your side, doing hip flexion for about 30-60 degrees, hip flexion with legs straight Practice lying on your back with your legs raised to raise your whole hips and spine Balance exercise: practice standing with 2 legs then 1 leg Strengthening glutes Walking uphill, stairs: in 6-8 weeks Practice standing up and squatting Practice flexing, adduction, extension, internal rotation, external rotation of the hip. Do not flex the hip and stop exercising when the patient is in pain Continue to avoid any pelvic muscle contractions Stage 3: rehabilitation 13-16 weeks after surgery. The goal is to help the patient recover full strength and endurance, strengthen the mid gluteal muscles with weight bearing. Exercises include:
No treadmill until 16 weeks Cycling, walking One-legged squats Continue the exercises in phase 2 Stage 4: 16-18 weeks post-surgery. Patients return to sports when the hip is pain-free, back to daily activities.. Strength training exercises and flexible program based on the patient's sport or job.
2.2.3 Rehabilitation after surgery due to hip fracture, central hip dislocation Stage 1: 0 to 4 weeks after surgery
Breathing exercises to prevent lung complications especially for the elderly Neck mobility Legs and feet of painful extremities to increase circulation Tension of quadriceps, calves, and glutes to maintain muscle Strength Increase muscle strength with resistance to remaining extremities Passive motion of painful hip joints: flexion, extension, flexion, adduction Stage 2: 4-7 weeks after surgery
Continue exercises like phase I Walk with crutches without weights Strongly train quadriceps, triceps, glutes gradually increasing resistance Increases range of hip range of motion Cycling in place Stage 3: 7-12 weeks post-surgery
Give some weight-bearing leg support Exercises to increase strength and range of motion hip joint. Return to normal activities after 12 weeks. After 6 months of sports activities. In summary, rehabilitation after surgery is very important, is a process before surgery, after surgery and after discharge from the hospital. Rehabilitation helps patients prevent recurrence after hip surgery, and recovery time, return to normal activities faster. In addition, patients need to be periodically re-examined after 1 and 4 months of discharge. After that, every 6 months to 1 year, the hip joint must be re-examined by X-ray to detect hip degeneration in time.
In addition, the system of facilities here is very modern. The machines are all imported, new and high quality, effectively supporting the doctor's diagnosis and treatment process faster and more effectively.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.