This is an automatically translated article.
When the signs and symptoms of systemic anesthetic toxicity are noticed, the initial treatment is to stop the injection of local anesthetic immediately. Then ask someone to help, as well as control the patient's airway. After completing the initial treatment measures, specific treatment should be initiated immediately.
1. How dangerous is local anesthetic poisoning?
Anesthesia is the type that is now widely used in medicine. Cases of local anesthetic poisoning are rare, but cannot be guaranteed to happen. Local anesthetic poisoning can range from transient symptoms to severe symptoms on the central nervous system and heart. Therefore, if local anesthetic poisoning is not treated promptly and correctly, the mortality rate will be very high.
The cause of local anesthetic poisoning is due to the injection of local anesthetic into the blood vessels and the abnormal absorption of the anesthetic into the blood vessels due to the use of high concentrations of local anesthetics or the use of large quantities of drugs. or by releasing the garnet too soon. Besides, some risk factors for local anesthetic poisoning such as:
Local anesthetics such as Bupivacaine toxicity > Lidocaine anesthetic > Ropivacaine local anesthetic > Mixed local anesthetic > Levobupivacaine anesthetic. Anesthesia in areas with large blood vessels will increase the risk of vascular injection and increase the risk of absorption of local anesthetic; Anesthesia in the following areas will increase the risk of anesthetic toxicity compared to other areas: Intercostal anesthesia > sacral anesthesia > epidural anesthesia > brachial plexus anesthesia > subcutaneous anesthesia; 1 dose injection or continuous infusion of the drug; Patients with cardiovascular dysfunction, or kidney and liver diseases; The elderly, debilitated or children, pregnant women are at increased risk of anesthetic toxicity. When intoxicated with a general anesthetic, symptoms usually appear within 1-5 minutes, but can be as late as 60 minutes after the anesthetic is injected, or even after 12 hours. Symptoms will correspond to the area affected by the anesthetic. Specifically as follows:
For the central nervous system: The initial symptoms after being poisoned by local anesthetics are that the patient sees a metallic taste in the mouth, numbness in the mouth, double vision, ringing in the ears or dizziness, and speaking. difficult. In more severe cases, there may be muscle twitching or drowsiness, loss of consciousness. Cardiovascular manifestations: Cardiac toxicity is common due to bupivacaine poisoning, symptoms often appear as cardiac arrhythmias or conduction disturbances in the heart. There may be ventricular arrhythmias at first, followed by progressive hypotension. More severe can cause cardiac arrest, if not treated promptly, the patient can die soon after.
Thuốc tê là loại hiện được sử dụng rộng rãi trong y khoa
2. Treatment regimen for poisoning with general anesthetic
When the signs and symptoms of systemic anesthetic toxicity are noticed, the initial treatment is to stop the injection of local anesthetic immediately. Then ask someone to help, as well as control the patient's airway.
In necessary cases, to be sure, perform intubation for 100% oxygen and ensure adequate ventilation, add a secure intravenous line, and assess cardiovascular and take blood for testing, but this should not delay the treatment of poisoning with general anesthetic.
After completing the initial treatment of systemic anesthetic poisoning, it is necessary to immediately perform specific treatment according to the following methods:
In case of central nervous system poisoning:
Use Thiopental dose 150-300 mg IV or use Midazolam 0.1 - 0.2 mg/kg. Consider the use of intravenous lipid emulsion to reduce the concentration of local anesthetic in the patient's plasma. If the patient's condition is stable after taking measures to treat drug poisoning, the surgery can be continued. Cardiac poisoning cases:
Normally, the cardiovascular system is less likely to be poisoned with anesthetics than the central nervous system, but when it comes to cardiovascular poisoning, the treatment of anesthetic poisoning is more difficult and more dangerous. Therefore, it is necessary to quickly compensate for circulating volume by using Intralipid 20% (dose applied to 70kg patients) to create a lipid reservoir that precipitates local anesthetics, at the same time, activates Ca, K channels, increases myocardial activity as well as increases myocardial activity. such as increased ATP synthesis and decreased binding of local anesthetics to the myocardium. Intralipid 20% intravenous bolus injection 1.5 ml/kg over 1 min (100 ml. 2 bolus doses should be repeated 5 min apart) in case circulation has not recovered sufficiently. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation should be carried out for the patient.Intralipid 20% should be started intravenously at a rate of 0.25ml/kg/min, taking care to use 400ml within 20 minutes.In case of effective circulation. If not recovered, then after 5 minutes increase the intravenous dose to 0.5 ml/kg/min within 10 minutes with a dose of 400 ml until the patient's circulation is fully and stably restored. ventricles, vasopressors and cardiopulmonary resuscitation during Intralipid therapy.
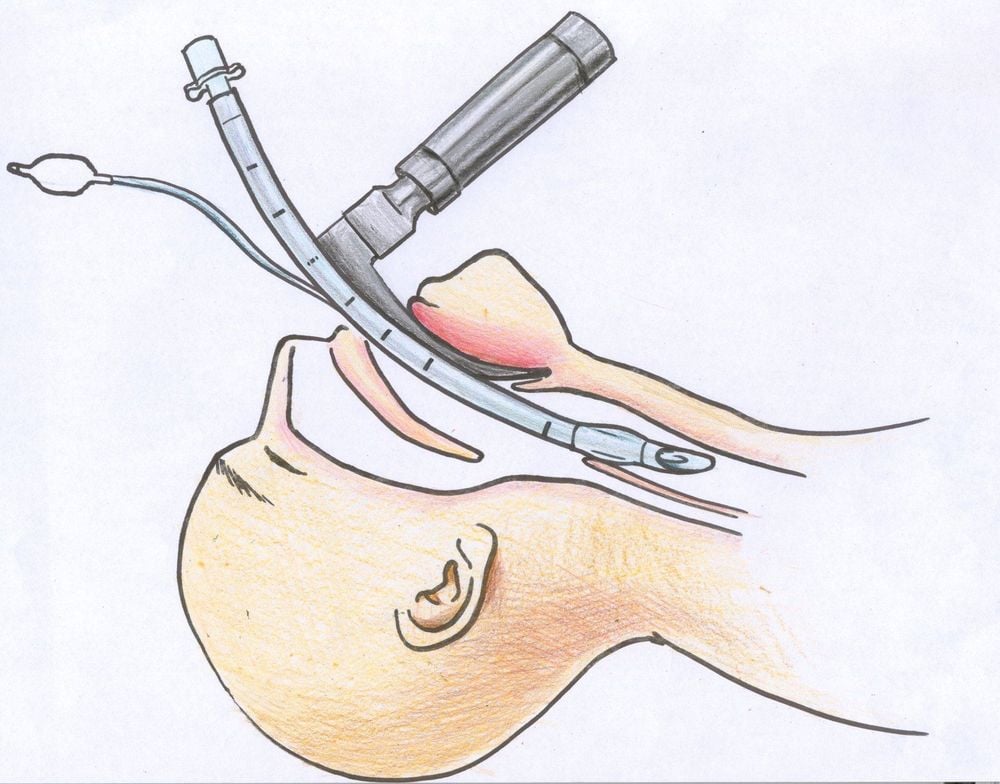
Thực hiện phương pháp đặt nội khí quản cho thở oxy 100% và đảm đảm thông khí đủ, đặt thêm đường truyền tĩnh mạch
3. Preventing and minimizing the risk of poisoning with general anesthetic
Poisoning by general anesthetic is very dangerous, so prevention of anesthetic poisoning is a method that should be noted. Methods of prevention of local anesthetic toxicity include:
When using local anesthetic, the smallest dose of local anesthetic should be used to achieve the desired level of anesthesia as well as the desired duration of anesthesia. At the same time, use devices to support anesthesia such as anesthesia under the guidance of ultrasound or nerve stimulator. Before giving anesthesia to the patient, it is necessary to know the patient's risk factors for anesthetic toxicity. Before each injection, the syringe should be aspirated to avoid injecting into the bloodstream. At the same time, when injecting, it is necessary to inject slowly, observe and ask the patient to detect signs of anesthetic poisoning from the very beginning. After injecting local anesthetic, it is necessary to monitor the patient continuously with Monitor for at least 30 minutes and talk and communicate regularly with the patient to detect symptoms of systemic anesthetic toxicity. When the patient has a change in mental status, neurological symptoms or abnormal cardiovascular signs after anesthesia, it is necessary to think of signs of toxicity from general anesthetic. Consider cases of poisoning with general anesthetic even when small doses of local anesthetic are injected, subcutaneous anesthesia, mucosal anesthesia, surgical anesthesia, and after removal of the garo. Also discuss the dose of anesthetic in the preoperative examination of the patient. Lipid 20% should be used at the first and obvious manifestation of systemic anesthetic toxicity due to any local anesthetic. However, adrenaline doses ≤ 1 mcg/kg/min should be used to be more effective in CPR and improve treatment in patients with cardiac arrest or hypotension due to anesthetic toxicity.

Ngộ độc thuốc tê toàn thân rất nguy hiểm
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that strictly applies safe surgical anesthesia practice standards according to international guidelines. Vinmec has a team of experienced anesthesiologists and nurses, modern equipment such as: nerve detectors, ultrasound machines, Karl Storz's difficult airway control system, comprehensive anesthesia monitoring system GE's AoA (Adequate of Anesthesia) including monitoring of anesthesia, pain and muscle relaxation will provide high quality and safety, helping patients to have adequate anesthesia, not wake up, and do not have residual muscle relaxants after surgery.
Vinmec Health System is also proud to be the first hospital in Vietnam to sign with the World Anesthesiology Association (WFSA) towards the goal of becoming the safest hospital for surgical anesthesia in Southeast Asia.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.