This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Nguyen Quoc Viet - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital and Master, Doctor Cao Thanh Tam - Cardiologist - Cardiologist - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
Master - Doctor Cao Thanh Tam has many years of experience in the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Dyslipidemia or dyslipidemia is a common disease today. Dyslipidemia causes dangerous complications on cardiovascular such as cerebrovascular accident, stroke, even leading to death or disability. The following article will give you the recommendations of the Vietnam Heart Association to control blood lipids.
1. What is dyslipidemia?
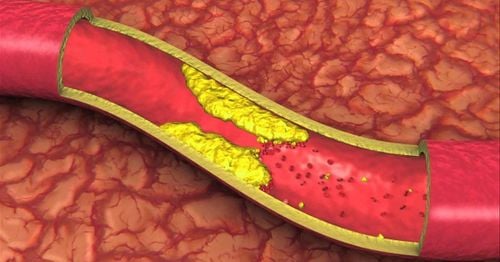
Dyslipidemia is a medical condition when there is a disturbance in the concentration of lipid components such as: increased cholesterol or increased triglycerides, or increased LDL-C (bad cholesterol), or decreased HDL-C (good cholesterol), .. As a result, the formation of atherosclerotic plaques causes embolism, increasing the risk of cardiovascular complications and stroke, and increasing other vascular complications. The most serious consequences are death or disability.2. Hyperlipidemia causes what diseases?
Complications caused by dyslipidemia include:Peripheral symptoms of hyperlipidemia: Erythema in eyelids, jaundice in tendons of elbows, knees, hands, heels, periosteum. Some visceral signs of hyperlipidemia: Lipemia retinalis, fatty liver, can cause acute pancreatitis. Atherosclerosis: Injury to medium and large diameter arteries such as coronary artery damage causing myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular injury causing stroke, injury to lower extremity arteries causing ischemic inflammation. foot necrosis blood.
3. Recommendations for blood lipid control
3.1. Principles of treatment
Treatment of dyslipidemia requires a combination of lifestyle changes and medication. In which, lifestyle change is the first indication; including increasing exercise, physical activity and adjusting a reasonable diet for each condition and nature of work.In order to choose an appropriate blood lipid control plan, people are based on the following Dyslipidemia Assessment Table:
| Thông số lipid | Nồng độ | Đánh giá nguy cơ |
| CT (mg/dL) | < 200 | Bình thường |
| 200 - 239 | Cao giới hạn | |
| ≥ 240 | Cao | |
| TG (mg/dL) | < 150 | Bình thường |
| 150-199 | Cao giới hạn | |
| 200-499 | Cao | |
| ≥ 500 | Rất cao | |
| LDL-c (mg/dL) | < 100 | Tối ưu |
| 100-129 | Gần tối ưu | |
| 130-159 | Cao giới hạn | |
| 160-189 | Cao | |
| ≥ 190 | Rất cao | |
| HDL-c (mg/dL) | < 40 | Thấp |
| ≥ 60 | Cao |
However, in some cardiovascular and metabolic diseases, these indicators may vary depending on the goal of treatment.
3.2. Lifestyle interventions on blood lipid levels
Exercise: Increasing physical activity helps to lose weight, maintain an ideal weight, and contribute to good control of blood sugar and blood pressure. Exercise time - physical activity is about 30 to 45 minutes a day, 5 days a week, the intensity and duration of exercise depends on the health status, especially those with blood pressure, coronary artery disease, heart failure ... Diet: Losing weight if overweight, losing weight starts with reducing the amount of calories you eat. Eat a variety of foods. It is necessary to regulate energy consumption to prevent overweight and obesity. Encourage consumption of fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, breads, fish (especially oily fish). Saturated fat should be replaced with unsaturated fats of plant origin and from the above foods to reduce energy intake from fat to < 35% of total energy, saturated fat to < 7% total energy, trans fat < 1% of total energy and cholesterol < 300 mg/day. Salt should be reduced to less than 5g/day by avoiding powdered salt, limiting the use of salt in cooking by choosing fresh foods, and avoiding processed and canned foods. Limit alcohol consumption to <10-20 g/day for women and < 20-30 g/day for men and should be avoided in patients with hypertriglyceridemia. Limit the use of drinks and foods containing sugar, especially soft drinks. Avoid smoking or exposure to tobacco.3.3. Treatment of dyslipidemia with drugs
Lifestyle changes after 2-3 months that do not bring the desired effect, are indicated for treatment with lipid-lowering drugs:statins (HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors). Fibrate group. Nicotinic acid group (Niacin, vitamin PP). Resin group (Bile acid sequestrants). Ezetimibe. Omega 3 (Fish Oils) can be added. In order to well control blood lipids, patients need to adhere to a reasonable diet regimen, increase exercise, and exercise. Periodic blood lipid testing is recommended, especially for those with risk factors such as diabetes mellitus. diabetes, overweight, obesity, ... Once detected dyslipidemia should be treated early to achieve the best effect.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.