This is an automatically translated article.
Sea fish is a favorite and very healthy food. However, many people after eating sea fish often suffer from histamine poisoning, if not handled, it can lead to serious allergies, even life-threatening.
1. How does histamine poisoning happen?
Histamine is an irreplaceable biological amino acid that is hydrophilic, can withstand high heat without destruction and is involved in the local immune system, or maintains the physiological function of the intestines and it acts as a transmitter. In the human body, histamine is found most abundantly in mast cells or basophils, at sites such as the nose, mouth, body endothelial surfaces, gastric mucosa, blood vessel walls, brain,...
In nature, histamine is formed from the conversion of histidine to histamine by histidine decarboxylase. This is also the cause of histamine poisoning in foods from cooked foods. When combined with histamine receptors on specific cells, the biological effects of histamine will manifest. There are 4 types of Histamine receptors that are H1, H2, H3, H4, but currently only fully know about H1 and H2 receptors:
H1 receptor: Located in smooth muscle organization, endothelium and nervous system central nervous system. Histamine acts on the H1-receptor, causing constriction of intestinal smooth muscle and relaxation of vascular smooth muscle, increasing capillary permeability leading to edema. Irritation of nerve endings causes pain, itching and allergic rhinitis syndromes, diarrhea. H2 receptors: appear in the parietal cells of the stomach wall. Histamine increases gastric acid secretion and leads to gastric and duodenal ulcers. Histamine poisoning is caused by ingesting a large amount of food containing a high concentration of histamine beyond the body's acceptable level. In particular, for people with allergies, just eating a small amount of food containing a small amount of histamine can cause an allergic reaction.
MORE: What foods cause allergies?
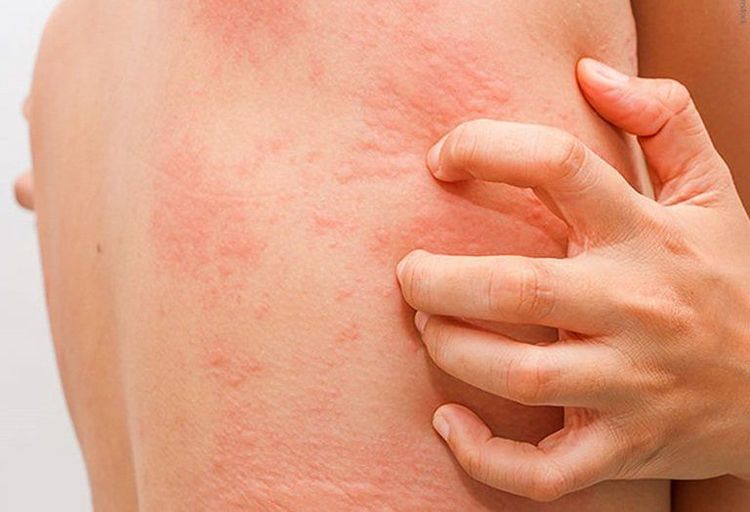
Dị ứng là một trong những biểu hiện đầu tiên của ngộ độc histamine
2. Histamine poisoning after eating sea fish
2.1 Where does Histamine form in marine fish?
Histamine is an irreplaceable amino acid, because the human body cannot synthesize it, but must be absorbed through food. Normally, fish contains the amino acid histamine, which is necessary for the growth and maintenance of healthy tissues in all parts of the body, especially red meat fish such as salmon, trout, and fish. tuna,...
When the fish is alive, bacteria always exist on the body such as gills and intestines of saltwater fish and are not harmful to the fish. But when the fish dies, fast-growing bacteria (such as Morganella morgani, enterobacteriaceae, ...) spread to the fish meat and produce the enzyme Histidine decarboxylase that converts Histidine into Histamine in the fish meat. This conversion process usually takes place quickly at a temperature of about 20-30oC. Moreover, fish meat has poor mechanical strength, so it is susceptible to microbial contamination.
The human body does not cause any reaction due to histamine but is broken down by enzymes when ingesting a certain amount of histamine. Only when the level of histamine in food is too high or the enzyme that breaks down histamine in the body is inhibited can histamine cause toxicity. According to the Food Safety Authority, histamine poisoning after eating sea fish depends on the total amount of histamine ingested, specifically as follows:
The amount of histamine ingested from 8mg-40mg: the patient feels salivation, tears. The amount of histamine ingested from 1500mg-4000mg: the patient has abdominal pain, diarrhea, headache, shortness of breath, rapid pulse, rash,... MORE: How to treat sea fish allergy

Histamine hình thành trong cá biển như thế nào?
2.2 Symptoms of histamine poisoning after eating sea fish
Symptoms of histamine poisoning after eating sea fish usually occur quickly from one to several hours after eating. People who eat poisoned sea fish will have the following clinical manifestations:
Red face, red eyes Difficulty breathing due to edema and tracheal spasms Redness, itching or skin rash Burning sensation in the mouth Increased secretions saliva. Stimulates gastric secretion, causing nausea, vomiting, diarrhea,... Rapid pulse, low blood pressure due to vasodilation Hangover, dizziness, headache due to histamine directly affects the nervous system.
2.3 Measures to handle and prevent Histamine poisoning
When you see that someone who eats sea fish has symptoms of a sea fish allergy, relatives should quickly handle it as follows:
Mild cases: only symptoms of skin allergies and digestive disorders need to be used antibiotics. histamine such as chlorpheniramine or claritin,... Severe cases: patients with clinical manifestations such as rapid pulse, low blood pressure, shortness of breath,... need to be quickly taken to the nearest medical facility for emergency treatment. and get timely treatment.
3. Measures to prevent histamine poisoning from marine fish
Histamine poisoning from marine fish can leave dangerous complications, but to limit this situation, you can take some measures to prevent histamine poisoning from marine fish by choosing fish as follows:
Fish eye : Observing fish eyes can distinguish fresh fish or rotten fish. Fresh fish eyes slightly convex and transparent cornea, bright black pupils. In contrast, for a flat or concave fish eye, the cornea is cloudy, the pupil is opaque. If the fish is severely poisoned, the fish's eyes can bulge out completely. Fish mouth: fresh fish's mouth will close tightly, in contrast, rancid fish will open wide. Fish gills: For fresh fish, the gills are bright red or dark red, the viscous fluid is translucent, odorless, and the gill cap is tightly closed. In the case of rotten fish, the gills are dark red-brown to light brown in color, with light gray or opaque viscous fluid, on the gills with dirt attached, damaged or fibrous, worn on the gills. Fins: Fresh fish have natural light colored scales, iridescent, clinging to the body of the fish, not peeling or falling off. On the contrary, for rotten fish, the scales on the fish will be peeled and pale, the color of the scales is no longer iridescent, has a rancid smell. Fish meat: Use your hand to gently press on the flesh of the fish, especially the part near the belly of the fish to distinguish whether the fish is fresh or rotten. Fresh fish flesh has the characteristics of good elasticity, firmness, and does not leave finger marks on the flesh of the fish. As for rotten fish, the fish meat is softer, sometimes soft, and has no elasticity when pressed. Even if the fish is rotten for a long time, when pressed on the fish meat, it will be concave and not elastic. Abdomen: Fresh fish belly is not swollen, still flat. In the case of rotten fish, the intestines of the fish are decomposed, creating gas, leading to a bloated abdomen. Anal: Fresh fish has a pale white anus and is deeply recessed inside. In contrast, rotten fish, the anus is red and protruding. It can be distinguished by holding the fish in your hand near the anus and gently squeezing it. If the fish is fresh, the anus is very firm, when squeezed, no intestinal juices come out. If the fish is rotten, you will see a lot of fluid coming out, even when you squeeze the belly and the anus may break.

Lựa chọn cá biển tươi sống giúp phòng ngừa ngộ độc histamine
In addition, to ensure quality, we need to preserve marine fish at the right temperature before processing. Besides, to avoid poisoning, you need to know how to prepare and prepare food from sea fish in hygienic and food safe manner.
In summary, sea fish is a favorite food and very good for health, but if the fish is not preserved well, it will lead to fish poisoning, and people who use fish will have histamine poisoning after eating. Therefore, it is necessary to know how to choose fish when buying and processing in accordance with food hygiene and safety. After eating sea fish, if there are signs of an allergy, the patient should be taken to a medical facility immediately for emergency treatment and prompt treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: rimf.org.vn













