This is an automatically translated article.
Monthly menstruation occurs when girls reach puberty. To monitor and control the health of our body, we need to know our menstrual cycle. This article is intended to provide information about the menstrual cycle.
1. Menstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle is a series of monthly changes a woman's body makes in preparation for the possibility of pregnancy. Each month, one of the ovaries releases an egg. This process is called ovulation. At the same time, hormonal changes are also preparing the uterus for pregnancy. If ovulation occurs and the egg is not fertilized, the lining of the uterus sheds through the vagina. This is the menstrual period.
2. Normal menstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle, calculated from the first day of one period to the first day of the next, is not the same for all women. Menstruation can occur after 21 to 35 days and lasts for two to seven days. During the first few years after menstruation begins, long cycles are common. However, menstrual cycles tend to shorten and become more regular as you age.
Your menstrual cycle may be regular, of the same length every month, or your menstrual cycle may be irregular, and your period may be light or heavy, painful or painless, long or short, and still considered normal often. To a large extent, "normal" is normal to you.
When using certain types of birth control, such as the birth control pill and an intrauterine device (IUD), will change your menstrual cycle and possibly even your menstrual cycle. disorders.
As you near menopause, your periods may return to being irregular. However, because the risk of uterine cancer increases as you get older, talk to your doctor about any unusual bleeding around menopause with your healthcare provider. yours.
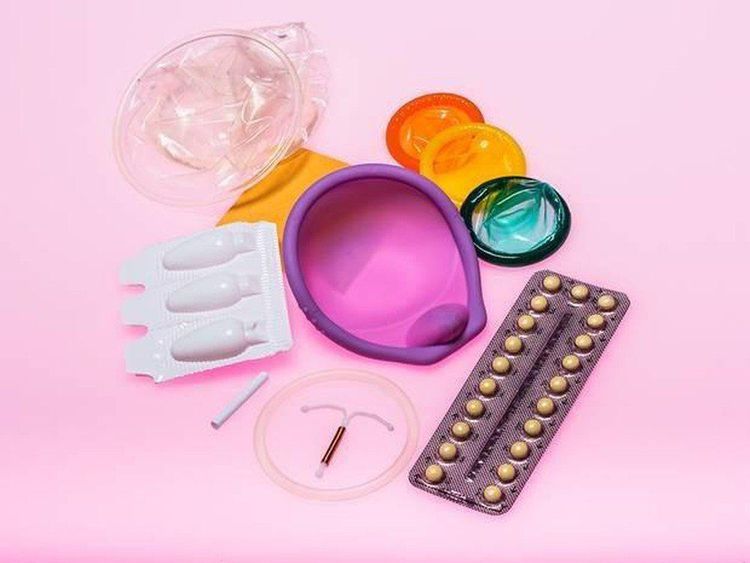
Một số biện pháp tránh thai có thể làm thay đổi chu kỳ kinh nguyệt
3. Menstrual Cycle Tracking
To find out if you're normal, start recording your menstrual cycle on a calendar. Start by tracking your start date monthly for several months in a row to determine the regularity of your periods.
If you are worried about your period, make a note of the following every month:
Last day. How long does your period usually last? Is it longer or shorter than usual? Flow. Record how heavy your menstrual flow is. Does it seem lighter or heavier than usual? How often do you need to change the guard or clean it? Have you ever had a blood clot? Abnormal bleeding. Do you bleed between periods? Pain. Describe any pain associated with your period. Is the pain worse than usual? Other changes. Have you experienced any changes in mood or behavior? Is there anything new happening around the timing of your period changes?
4. Causes of Irregular Menstrual Cycle
Irregular menstrual cycles can have many different causes, including:
Pregnancy or breastfeeding. A missed period can be an early sign of pregnancy. Breastfeeding often delays the return of menstruation after pregnancy. Eating disorders, excessive weight loss, or excessive exercise. Eating disorders - such as anorexia nervosa - excessive weight loss and increased physical activity can disrupt menstruation. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Women with this common endocrine system disorder may have irregular periods as well as enlarged ovaries that contain small fluid - called cysts - in each ovary on ultrasound examination.
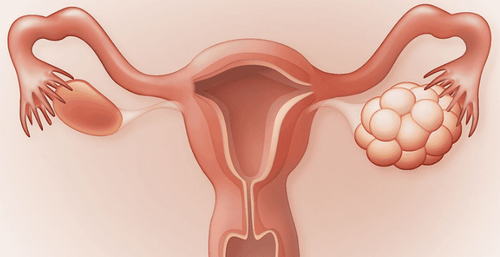
Một số phụ nữ mắc hội chứng buồng trứng đa nang có thể có kinh nguyệt không đều
Premature ovarian failure. Premature ovarian failure is the loss of normal ovarian function before the age of 40. Women with premature ovarian failure – also known as primary ovarian failure – may have irregular or irregular periods for many years. five. Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). This reproductive organ infection can cause irregular menstrual bleeding. Fibroids . Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths of the uterus. They can make your period heavier and longer. Some methods of preventing irregular periods
For some women, using birth control pills can help regulate the menstrual cycle. Treatment for any underlying problems, such as an eating disorder, can also help. However, some menstrual irregularities cannot be prevented.
Also, consult your healthcare provider if:
Your periods suddenly stop for more than 90 days and are not pregnant Your periods become irregular after regularly You bleed for more than seven days You bleed more than usual or soak through multiple pads or tampons every hour or two Your periods are less than 21 days apart or more than 35 days bleeding between periods You have severe pain during your period You suddenly have a fever and feel nauseous after using a tampon
5. Some multiple choice questions about menstruation
How long is the typical period? While 3-5 days is the most common, anywhere from 2 to 7 days is considered normal. See your doctor if your period lasts longer than a week or suddenly changes from your period. How much blood does the average woman lose during each period? Although you can't easily measure blood loss, most women know when their periods are heavy. If the bleeding seems excessive, is soaking tampons or tampons every hour for several hours, or you notice large blood clots, let your doctor know.

Nếu thấy lượng máu chảy ra quá nhiều trong kỳ kinh bạn nên thông báo cho bác sĩ
Late periods are common in young women, especially in the first few years of menstruation, and things like stress, weight loss, and too much exercise can cause irregular periods. Additionally, some birth control methods can stop periods and may even be designed for that purpose. Talk to your doctor if you're fine but start to miss your period. It's normal to feel pain when your period begins: But you should notify your doctor of very severe or persistent pain. Persistent pain in the pelvic area can be a symptom of more serious problems, such as endometriosis - a growth outside the uterus, often into the pelvic cavity, of the tissue that normally lines the uterus. In fact, women who live together all menstruate at the same time. Although many of us believe it, research results on "menstrual synchronicity" are varied and there is no scientific consensus on it. How long is a normal menstrual cycle? For most women, periods occur between 21 and 35 days apart. In young girls and adolescents, menstruation is often irregular and has a cycle that ranges from 21 to 45 days. Keeping track of your periods on a calendar can help you and your doctor figure out your normal pattern. What could make your period worse? A 2010 study found that women who reported feeling high levels of stress were more than twice as likely to experience at least five moderate to severe symptoms during their period than women with lower stress. . How many periods will you have in your life? That's a menstrual cycle for about 35 years, with an average of 13 menstrual cycles a year. Bleeding between periods is always a sign that something is wrong. But you should see your doctor promptly so he can find the cause. Bleeding between periods can have a number of causes, some of which are serious. It is normal for menstrual blood to clot or clot. Many women have occasional bleeding or clots, especially on heavy bleeding days. If the blood clots are large or you need to change your tampon every 2 or 3 hours, call your doctor. At Vinmec International General Hospital, there is a basic gynecological examination and screening package to help customers detect gynecological diseases early for timely treatment. If you have a need for consultation and examination at the Hospitals of the national health system, please book an appointment on the website for service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: webmd.com