This is an automatically translated article.
Antinuclear antibodies and anti-double chain antibodies are autoantibodies that occur in autoimmune diseases. Accordingly, testing for the detection and quantification of these antibodies is aimed at diagnosing confusing dysfunctions of the immune system when clinical signs are suggestive.1. General principles of the quantitative test of antinuclear - double chain antibodies in the diagnosis of autoimmune diseases
Not only antinuclear and double chain antibodies, the test for detection and quantification of antibodies in general in the diagnosis of autoimmune diseases has the same principle.
Specifically, the tests are based on a sequence of immune responses that are triggered by complementary enzymes. First, a chemical containing antibodies against autoantibodies will be incubated with the patient's blood. In the event that the specimen does have autoantibodies of autoimmune diseases, they will bind to the antibodies in the chemical and form precipitated complexes. The next step is to wash away unbound and unspecifically bound molecules in the specimen. The added enzyme conjugate is then bound to the antigen-antibody complex immobilized with the chromogenic fluorescent agents. This color is only observed under an optical microscope and can be measured optically at 650 nm. The higher the coloration, the more proportional to the concentration of the antigen-antibody complex. From there, the antibody concentration in a unit of initial blood volume will be calculated and collectively estimated the circulating antibody concentration in the whole body of the patient.
Thus, the process of quantifying antinuclear - double chain antibodies in the diagnosis of autoimmune diseases needs to go through many stages, in the past it needed to be done completely manually, but now there are mechanical means to support a part. From there, the recorded results will be more accurate.
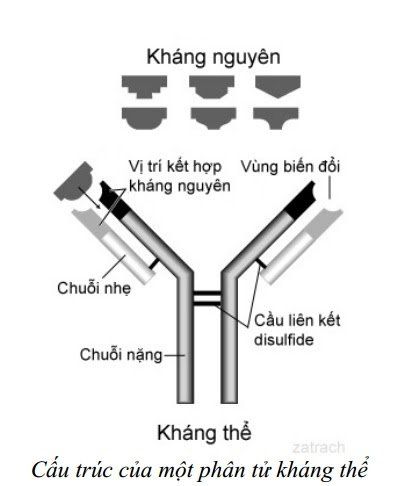
Kháng nguyên - kháng thể trong chẩn đoán và phát hiện bệnh tự miễn
2. Steps to prepare for quantitative testing of antinuclear - double chain antibodies
2.1. Human Resources Because this is an in-depth, highly sophisticated test; At the same time, the results of the test are also decisive in the diagnosis and treatment of the patient, the process of quantitative testing for antinuclear - double chain antibodies requires a doctor specializing in biochemical tests to perform. .
In other cases, it can be replaced by a professional laboratory technician, experienced and trained in testing for autoantibodies in the diagnosis of specific immune diseases and tests general principles of fluorescence.
2.2. Means and chemicals Immunochemistry analyzer can perform tests with the principle of fluorescence. ANA detection reagent kit: includes 8 wells containing the following components:
Well 1 and 2: Empty well, used to dilute samples. Wells 3 and 4: Reaction wells, used to coat antigens with specimens, to create antigen-antibody complexes if autoantibodies are present. Well 5: Control well, yellow, contains specific antibodies, PBS, BSA (Bovine serum albumin), detergent, preservative sodium azide 0.09% and proclin 300 0.05%. Well 6: The well contains the enzyme conjugate, light red, containing HRP-binding anti-human igg antibodies; PBS, BSA, bleach, preservative proclin 300 0.05%. Well 7: The well contains sample diluent, yellow, containing PBS, BSA, detergent, sodium azide preservative 0.09% and proclin 300 0.05%. Well 8: TMB substrate well, transparent, containing 3.3', 5.5'- Tetramethylbenzidin and ANA antibody pre-coated in microwells with the product codename ANAscreen
Xét nghiệm ANA có vai trò quan trọng trong chẩn đoán bệnh lý tự miễn
Anti-dsDNA detection reagent kit : includes 8 wells containing the following components:
Well 1 and 2: Empty well, used to dilute samples Well 3 and 4: Reactive well, used to coat antigen with specimen, to create an antigen-antibody complex if autoantibodies are present. Well 5: Control well, yellow, contains specific antibodies, PBS, BSA (Bovine serum albumin), detergent, preservative sodium azide 0.09% and proclin 300 0.05%. Well 6: The well contains the enzyme conjugate, light red, containing HRP-binding anti-human igg antibodies; PBS, BSA, bleach, preservative proclin 300 0.05%. Well 7: The well contains sample diluent, yellow, containing PBS, BSA, detergent, sodium azide preservative 0.09% and proclin 300 0.05%. Well 8: TMB substrate well, transparent, containing 3.3', 5.5'- Tetramethylbenzidin and recombinant double-stranded dsDNA antibody (human dsDNA) pre-coated in microwells with product coding names is dsDNA Screen. System solutions:
Wash (1x20ml): Washing solution, containing TRIS, detergent, sodium azide preservative 0.09% (50x). System fluid (1x2.5ml): System fluid containing acid (1000x). Other tools:
Vortex machine. Pipette 10 μl. 1000 ml and 2500 ml dosing cylinders. Distilled or deionized water. All test instruments and chemicals should be stored in the dark at 2 - 8 degrees Celsius. Do not expose to direct heat, sunlight or strong light during storage. and use.

Máy lắc Vortex được sử dụng trong phòng thí nghiệm phục vụ xét nghiệm định lượng kháng thể
2.3. Patient This is the same test as regular blood tests. Specimens to be analyzed are blood taken from a vein in the forearm or arm. The patient will not eat anything before the blood test.
Blood collection will be done by the nurse or laboratory technician after explaining to the family and the patient clearly the meaning and procedure of the test.
2.4. Order paper When a doctor orders a test, the order paper needs to clearly and fully record the patient's information and specifically the test target is the quantification of antinuclear antibodies (ANA) or anti-chain antibodies. double (anti-dsDNA).
On the laboratory side, information about the time of sampling, the way to preserve the sample and the expected time of returning the results should also be recorded.
3. Quantification of antinuclear - double chain antibodies
3.1. Sample collection The patient has a venous blood drawn from the forearm or arm to make a specimen for testing.
Blood samples need to be stored in test tubes and contain standard preservatives, and then need to be sent to the laboratory quickly.
Máu tĩnh mạch cẳng tay được sử dụng trong xét nghiệm định lượng kháng thể
3.2. Technical Procedure The reagents and reagents are pre-calibrated and ready to use.
Make the Anti-ANA test standard stable for 28 days and a calibration is required every time a reagent lot is changed.
Quality check is within allowable limits. It is common to run two levels of internal control per day, normal and abnormal. Compared with the law on quality control, if passed, samples will be analyzed.
Put the patient into analysis according to the machine's procedure. When the results are available, the doctor or technician will analyze and compare them with the test card, print and return the results to the patient at the scheduled time.
The remaining specimens and waste from the testing machine are treated as infectious medical waste before being discharged into the environment.
4. Determination of quantitative results of antinuclear - double chain antibodies
4.1. Reference value for quantification of antinuclear antibodies (ANA) Normal: negative result, quantification value less than 1.0 U/ml Suspicious result: quantitative value between 1.0 and 1.2 U/ml Positive result: quantitative value above 1.2 U/ml 4.2. Reference value for quantification of anti-double-stranded antibodies (anti-dsDNA) Normal: negative result, quantification value from less than 25 U/ml Positive result: quantification value above 25 U/ml The normal and pathological limits of reference depend on the type of antibody to be quantified and on the laboratory with the available equipment, instruments, chemicals, and standardization procedures.

Quy trình định lượng kháng thể cần được thực hiện tại cơ sở y tế được trang thiết bị máy móc hiện đại
5. Factors that may cause erroneous results of antinuclear - double chain antibody quantification
With the facilities, tools, chemicals as well as standardization procedures are available, so far, most laboratories have not reported on factors that can cause falsification of quantitative results antinuclear - double chain antibody.
Even, the results do not have a statistically significant difference if the sample is hemolytic, has abnormally high levels of triglycerides or bilirubin. At the same time, blood preservation with anticoagulants Citrate, EDTA or Heparine did not falsify the detection and measurement results of ANA and anti-dsDNA.
When a patient has suspicious signs, detecting and measuring the levels of antinuclear antibodies (ANA) and anti-double-stranded antibodies (anti-dsDNA) is an important step in the diagnosis process. self-exempt. Accordingly, the sooner the diagnosis is made, the more actively the patient can be treated from the beginning, which will limit the damage caused by the immune system and the long-term prognosis of the disease.
Customers who need medical examination and treatment at Vinmec can directly go to Vinmec Health System nationwide or contact information HERE.
Recommended video
Vinmec cord blood bank - solution for patients with critical diseases
MORE:
What is an autoimmune disease? Common autoimmune diseases in children Joint problems are common in autoimmune diseases