This is an automatically translated article.
The phenomenon of increased sweating is quite common in the community. This is a disease that occurs when the sympathetic system is overactive, causing the patient to experience excessive sweating in the palms, feet, armpits, groin area, ... which are the areas where sweat glands are very concentrated. The drug treatment does not seem to bring about the expected effect; Meanwhile, laparoscopic sympathectomy initially gave quite satisfactory results.
1. What is sympathetic hyperhidrosis?
Excessive sweating is a disorder in the control of the sympathetic nervous system on the sweat glands, leading to excessive sweating and discomfort for the patient. The thoracic sympathetic chain is involved in nerve control of the sweat glands of the upper extremities, located anterior to the neck of the thoracic rib and below the pleura. In addition, the location of sweating can also be in the armpits, soles of the feet, on the face or the whole upper body. As a result, these symptoms affect important aspects of quality of life including physical, psychological, and social ones.
Symptoms of excessive sweating in a person usually begin in childhood or adolescence and continue throughout life. Anxiety and irritation can cause or worsen this condition. Sweating can also be promoted when ambient temperature is high and stress, negative emotions in thought and action or sometimes can appear without any obvious reason. However, people with the disease will tend to increase sweating more in the summer and improve in the winter or in a cool, comfortable environment.
Regarding the causes of increased sweating, so far there is no clear explanation. Most hypotheses are put forward because the sympathetic nervous system is overstimulated, not only by some factors such as anxiety and agitation, but also by consuming stimulant foods and drinks such as coffee. , tea or smoking and also the outside environment. However, some chronic diseases that cause metabolic disorders such as diabetes, heart failure, Parkinson's disease, thyroiditis,... also cause excessive sweating that has no relation to the system. sympathetic.
Tăng tiết mồ hôi khiến người bệnh khó chịu
The treatment of increased sweating with drugs does not seem to bring about the expected effect. The drug groups mainly focus on limiting stimulant factors with sympathomimetic antagonists, anti-depressants, and anxiety-reducing drugs... Meanwhile, endoscopic sympathectomy is the first step for patients with quite positive results. Details of laparoscopic sympathectomy are presented in the following sections.
2. What is endoscopic sympathectomy?
Laparoscopic intrathoracic sympathectomy is surgery to treat hyperhidrosis caused by sympathetic hyperhidrosis.
In clinical practice, this type of surgery is preferred to treat sweating of the palms or face, in the upper half of the body in general. In which, the sympathetic ganglia are located in the thorax and let the sympathetic nerves go out, to the sweat glands located under the epidermis to control the sweat secretion function in body regulation. heat. This surgery will target the sympathetic ganglia in the chest and destroy them, inhibiting the secretion of sweat.
Vị trí hạch giao cảm
3. Indications for endoscopic sympathectomy
Laparoscopic sympathectomy is only considered in people whose palms, armpits, face... are excessively sweaty than usual. At the same time, this phenomenon affects the patient's life, reduces concentration, limits manipulation in study, work and even normal activities.
In addition, the indications of endoscopic sympathectomy will be considered until other treatments to reduce sweating completely do not bring any effect to the patient.
4. Endoscopic sympathectomy procedure
4.1. Before surgery You need to tell the surgeon or anesthesiologist about your health status:
Current or past medical conditions, medications you are taking Are you pregnant or likely to be pregnant? pregnancy Any other medicines, vitamins, herbs and supplements you are taking, even those you bought without a prescription 4.2. In the days leading up to surgery You may be asked to stop taking medications that affect blood clotting, such as aspirin, ibuprofen, and warfarin. Ask your surgeon what medications you can still take on the day of surgery. If you smoke, stop smoking. Smoking not only aggravates this condition, but also increases the risk for anesthesia-resuscitation problems and slower wound healing.
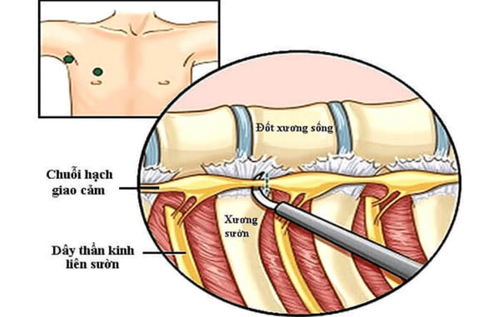
Cắt hạch giao cảm điều trị chứng tăng tiết mồ hôi
4.3. On the day of surgery Follow the instructions for fasting and drinking. Take the medication as directed by your surgeon with a small sip of water. Cleaning and changing clothes according to operating room regulations 4.4. Surgical procedure The patient is under general anesthesia and mechanical ventilation through an endotracheal tube. The patient is placed supine with both arms outstretched on the table so that the arms and torso are in a 30° Fowler position. Surgeons perform aseptic surgery that covers the neck, armpits, and upper arms down to the sides of the ribs. A small knife incision is made in the underarm area and the laparoscope is inserted into the chest. Another thoracoscope was also inserted through an incision between the clavicle and the second intercostal space. A volume of CO2 is pumped into the thorax with high pressure to actively deflate the lungs, in order to increase space for the surgical field. By monitoring on the screen, the sympathetic chain in the thorax is easily identified. They are covered by the thin membrane of the pleura, located behind the chest wall. Anatomically corresponding to the ribs, the nodes in the sympathetic chain will be excised or destroyed in turn. After terminating this side, the surgeon will repeat the same steps to intervene in the contralateral sympathetic chain. Finally, the CO2 will be released. Withdraw the instrument and close the wound.
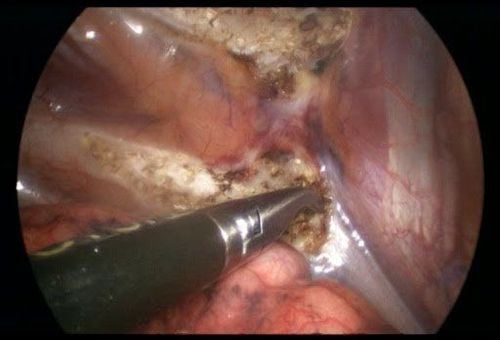
Hình ảnh phẫu thuật nội soi cắt hạch giao cảm
4.5. After surgery Most patients after laparoscopic sympathectomy only need to be observed in the hospital for one night and can go home the next day. Although you may still feel some pain, this should subside after about a week or two and you can take pain relievers as prescribed by your doctor. You need to follow your surgeon's instructions for wound care such as keeping the incision area clean and dry and changing the wound dressing every day. Continue to follow up with the surgeon. At future visits, the doctor will examine the incision and see if the surgery was a success.
5. Risks and long-term prognosis of laparoscopic sympathectomy
Like other surgeries, laparoscopic sympathectomy also cannot avoid certain risks such as:
Allergic reactions to drugs Respiratory problems Hemostasis disorders Post-operative infections For laparoscopic intrathoracic sympathectomy alone, although the rate is very small, some of the following complications may be encountered:
Intrathoracic hemorrhage Pneumothorax Arterial or nerve damage Increased sweating in other areas of the body to compensate for bradycardia Pneumonia In the long term, this surgery can improve quality of life for most patients. However, the effectiveness is sometimes limited in people with very severe disease. Some people after surgery notice sweat reappearing in new places on the body but this may go away on its own.
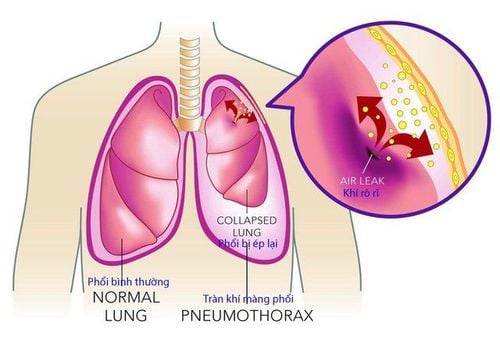
Tràn khí màng phổi có thể gặp sau phẫu thuật
In conclusion, laparoscopic intrathoracic sympathectomy is a lifesaver in the treatment of hyperhidrosis. By understanding the above information, patients can proactively visit early and plan timely intervention, soon regain confidence in life.
SEE ALSO:
Get rid of hand sweat disease 30 years after laparoscopic surgery 30 minutes Sweating heavily: Good or bad? How to reduce underarm sweating can be done at home