This is an automatically translated article.
The more scientists dig into psoriasis, the more treatment options there are for patients with this dermatological disease. Because then they will know more about what specific factors to target in order to develop effective treatments. Treatments will become more and more personalized as drugs are being developed that target different aspects of the immune system.
1. What is psoriasis?
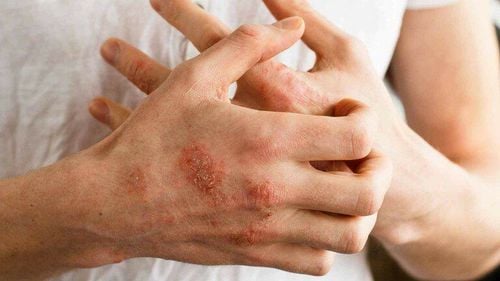
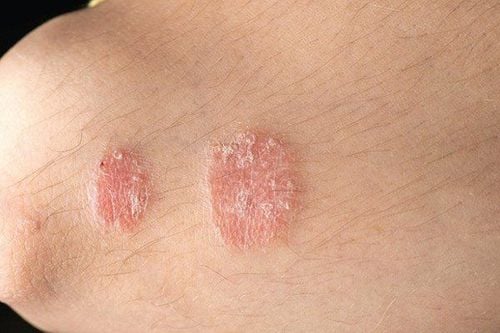
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that causes a rapid buildup of skin cells. This accumulation of cells causes scabs on the surface of the skin. There may be inflammation and redness around the scab. Typical psoriasis is white and develops into thick red patches. Sometimes, these patches will crack and bleed.
Psoriasis is the result of a rapid skin cell production. Normally, skin cells grow deep inside and slowly rise to the surface, the old cells will fall off. The normal life cycle of skin cells is one month.
In people with psoriasis, skin cell production can happen in just a few days. So the skin cells don't have time to fall off. This rapid overproduction leads to a build-up of skin cells.
Psoriasis often develops on joints, like elbows and knees. However, they can develop anywhere on the body, including:
Hands Feet Neck Scalp Face Psoriasis rarely affects the nails, mouth, and the area around the genitals.
Psoriasis is often associated with a number of other conditions, including:
Type 2 diabetes Inflammatory bowel disease Heart disease Psoriatic arthritis Anxiety Depression
2. What causes psoriasis?
Doctors don't know what causes psoriasis. However, thanks to decades of research, they have a general idea of the two main factors that cause disease: genetics and the immune system.
Immune system: Psoriasis is an autoimmune condition. An autoimmune condition is the result of the body attacking itself. In people with psoriasis, T-lymphocytes mistakenly attack skin cells. Normally, white blood cells are responsible for attacking and destroying invading bacteria and fighting infections. This mistaken attack overwhelms the production of skin cells. Skin cell production accelerates causing new skin cells to grow too quickly. They are pushed to the surface of the skin, where they pile up. This leads to the patches commonly associated with psoriasis. Attacks on skin cells also cause areas of the skin to become inflamed and red. Genetics: Some people inherit genes that make them more likely to develop psoriasis. If you have a family member with dermatophytosis, your risk of developing psoriasis is higher. However, the percentage of people with psoriasis and genetic factors is small. According to the National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF), about 2 to 3 percent of people with the gene develop the condition. SEE ALSO: Causes of psoriasis
Hệ thống miễn dịch và di truyền học là hai nguyên nhân chủ yếu của bệnh vảy nến
3. Personalized Psoriasis Medicine
Psoriasis is an immune system disorder characterized by inflammation and rapid overproduction of skin cells, producing scabs, pain, swelling, heat, and redness. A skin condition that can cause significant physical and emotional discomfort.
Therapies for psoriasis include:
Topical drugs (topical treatment) Light therapy (phototherapy) Oral or injectable drugs (systemic therapy) So far, we have not There is a cure for psoriasis, so the main goal of treatment is to reduce inflammation and prevent skin cells from growing too quickly.
In the past, doctors treated psoriasis using a “wise approach”. Patients with mild to moderate psoriasis will start with topical therapies, and if they don't respond well to that, will move on to other treatments, such as systemic therapy or physical therapy. phototherapy.
This approach calls for treating people with moderate to severe psoriasis with phototherapy or traditional systemic therapies such as drugs such as methotrexate and cyclosporin, before providing them with therapies biologics, is a treatment that works with your immune system.
Psoriasis treatment strategies have changed to a more patient-specific approach. Today, patients and their doctors can choose their treatment based on:
The effectiveness of the treatment. Severity of the disease. Lifestyle considerations Risk factors Associated diseases (co-morbidities) The most recent biologic product approved by the FDA for the treatment of psoriasis is Stelara (ustekinumab). Ustekinumab contains an antibody that is produced in a laboratory and designed to bind to a specific target in the immune system. When given to patients, this antibody blocks the action of two proteins (interleukin 12 and 23) that contribute to inflammation and overproduction of skin cells. By targeting these proteins, Ustekinumab can disrupt inflammatory pathways.
Drugs under development are targeting different pathways in the immune system that lead to inflammation. Researchers are exploring the importance of interleukin 17. They are also looking at proteins and molecules that can disrupt cell signaling, which could increase the spread of inflammation.
As scientists learn more about the immune pathways that lead to the development of psoriasis, they can target specific molecules to treat and provide more treatment options for psoriasis. patient.

Sử dụng thuốc bôi ngoài da để điều trị bệnh vảy nến
4. A long-term strategy in the treatment of psoriasis
Doctors are recommending a team approach to psoriasis treatment. Patients, families, and their healthcare providers need to work together to address the many possible conditions associated with psoriasis, including:
Risk of developing metabolic syndrome : Occurrence of obesity, high blood pressure, high cholesterol and diabetes in one patient. Lymphoma Heart disease Depression. Currently, doctors do not fully understand the relationship of these comorbidities to psoriasis, but it is an area of active research.
Because psoriasis is a chronic disease with no cure, the patient may have to use treatments for a long time. Many FDA-approved therapies have been evaluated over extended periods of time.
The good news is that some of the signs and symptoms of psoriasis can be treated with simple measures such as:
Regular use of a moisturizer can improve itching and scaling. Reducing or limiting tobacco use and alcohol intake can reduce the number of psoriasis flares. Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight and being physically active can help reduce or prevent the development of related diseases. Doctors advise patients to seek early treatment from a doctor experienced with the disease. Dermatologists can provide patients with an accurate diagnosis and information to manage the disease. If you are diagnosed and treated early, you can avoid the risks of ineffective and inappropriate therapy.
Some patients get bored easily with treatments, but newer therapies can make them more comfortable. That's why experts advise patients to explore treatment options early and educate themselves about their condition. Even when patients have mild psoriasis and decide they don't want a particular treatment, there are ways they can relieve their symptoms.
At Vinmec International General Hospital, there is a package of examination and advice on treatment of atopic dermatitis for all customers of all ages. Customers are at risk such as allergies, being affected by ambient conditions such as weather, climate, and humidity. There are symptoms such as: There are vesicles concentrated in clusters, red raised bumps above the skin surface or thick, lichenified, cracked, scaly skin patches, concentrated in clusters, patches or scattered; Lesions are common on the cheeks, chin, forehead, elbow folds, and can be scattered all over the body; At the lesion site, there is itchy skin, intense itching, especially at night, there may be bacterial infection at the itch...
When signing up for the package of examination and consultation for treatment of atopic dermatitis, customers will be examined and performed tests including:
Gynecological examination. Perform tests such as: Quantitative IgE, fresh mycobacteria, specific IgE quantification with respiratory allergens - food (Panel 1 Viet), test Rida Allergy Screen (panel 1).
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: fda.gov, healthline.com