This is an automatically translated article.
Syphilis is one of the most dangerous sexually transmitted diseases. If not treated in time, it can invade the viscera, skin, heart, and central nervous system of the patient and cause many complications, even lifelong disability or death.
1. What is syphilis?
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. Syphilis spirochetes were discovered by Schaudinn and Hoffmann in 1905 and are one of the slow growing but persistent and difficult to treat spirochetes. They enter the bloodstream and gradually spread to all organs in the body. Syphilis is usually transmitted through unprotected sex, through blood, or from a mother with syphilis to her baby during pregnancy.
Syphilis develops slowly over many years (10 - 30 years), sometimes lasts a lifetime, sometimes it is rampant, but there are also periods of silence with no symptoms, making the patient think that he has recovered and can be passed on to the next generation. The clinical picture of syphilis is very diverse, depending on the stage of disease development.
Bệnh giang mai diễn biến chậm rãi qua nhiều năm
2. Path of transmission and infection
2.1. Infectious source Treponema pallidum occurs in many lesions (syphilis chancre, mucosal plaques, lymph nodes, ...) so it is easy to spread if normal people have unprotected sex without taking measures. protect the sick. The incubation period of syphilis is relatively long from 10 days to 100 days, an average of about 3 weeks, the patient will gradually see signs of the disease. Period of transmission: Syphilis is most contagious during the first (I) and second (II) periods when the skin and mucosal lesions contain many syphilis spirochetes. 2.2. Mode of transmission Syphilis is spread mainly through sexual contact. When normal people have unprotected sex with an infected person, spirochetes will pass through the wound during sexual intercourse, enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body. Factors that increase the risk of disease transmission are being infected with HIV/AIDS, having diseases that cause damage to the genital organs, having unprotected sex (oral sex, having sex). homosexuality,...). In addition, syphilis can also be spread by blood transfusion (injecting blood or injecting drugs without disinfecting syringes) or indirectly through contaminated utensils and items. If a pregnant mother has untreated syphilis, she can also pass it on to her baby (congenital syphilis).
Xét nghiệm chẩn đoán bệnh giang mai
3. Measures to diagnose syphilis
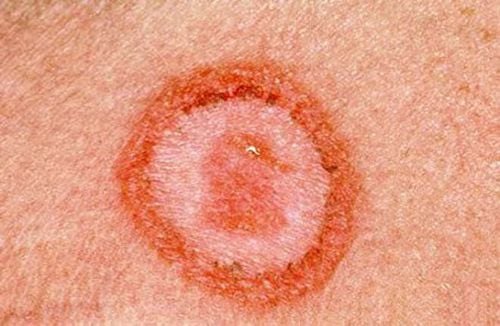
When detecting sores on the genitals or any location with intimate sexual contact, the patient should go to the hospital for examination and screening tests for timely treatment. To diagnose syphilis, doctors can rely on:3.1 Clinical signs After the incubation period (from 10 to 100 days) in the genitals, the patient may appear syphilis chancre, rash, mucosal plaques, syphilis papules, wet papules, hair loss, swollen lymph nodes in the whole body (neck, armpits), pharyngitis...
3.2 Diagnostic tests for syphilis Looking for spirochetes The doctor will take samples from the wound. Ulcers or in syphilis papules, mucosal plaques, lymph node aspiration, remove secretions on the background of syphilis papules, mucosal patches or ulcers, and then examine them directly on a black background microscope. If the syphilis test results show the spirochete Treponema pallidum in the form of a moving spring, the patient has syphilis.
Blood test to diagnose syphilis After 2 weeks of detecting syphilis, the patient can have a blood test to check again to see if the body has syphilis antibodies.
In addition, if the patient is assessed to be at risk of neurosyphilis or cardiovascular syphilis, additional cerebrospinal fluid should be obtained for the above tests.
Diagnosis of syphilis is difficult, but treatment of syphilis is not too complicated, except in cases of syphilis with complications in the nervous system. If syphilis is detected early and treated early, the chances of cure are very high. Most of the time, if a patient is infected with syphilis and is detected at stage I and stage II syphilis, only 1 dose of intramuscular injection is needed to treat the disease. Therefore, education about prevention or early detection of syphilis is essential.
Chẩn đoán giang mai thì khó nhưng điều trị giang mai không quá phức tạp
4. Precautionary measures
Propaganda, medical education, sex health: Propagating a healthy lifestyle, being faithful to one wife and one husband. Educate on safe sex behavior, have a method of protection when having sex (using condoms). When the patient detects the signs of the disease, it is necessary to overcome the guilt and immediately go to the specialized and reputable medical centers for examination and treatment. Do not self-medicate and self-medicate. Attention to hygiene and prevention: To prevent congenital syphilis in children, it is necessary to timely detect and treat the mother if she is unfortunately infected during pregnancy. Systematic serological tests should be performed in all pregnant women. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital offers a package of Examination and Screening for social diseases to help customers detect diseases early and have effective treatment and prevention of dangerous complications. The screening package for social diseases at Vinmec is for all ages, both men and women.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
MORE:
Where does syphilis lesions in women usually occur? Syphilis "preferred" sites Syphilis warning symptoms