This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Ngoc Phu - ICU Doctor - Intensive Care Department - Vinmec Times City International General HospitalDrug-resistant tuberculosis is a dangerous form of TB disease with side effects that seriously affect the patient's health. The treatment of drug-resistant TB is not only costly, but also lasts longer than with normal TB. Therefore, patients need to strictly adhere to the principles of treatment as directed by the doctor.
1. What is drug-resistant TB?
Patient is suspected of drug resistance while being treated for TB but the symptoms of fever, cough, sputum production do not improve or subside for some time and then reappear with increasing symptoms, the patient continues weight loss.
However, drug-resistant TB can be diagnosed in people who have never had TB, and the clinical symptoms of MDR-TB may not be that different from that of regular TB.
Based on the results of antibiogram or WHO-certified rapid diagnostic tests (Hain test, Xpert MTB/RIF...), diagnostic criteria for drug-resistant tuberculosis are determined as follows:
Drug-resistant TB: Resistant to only one other first-line anti-TB drug Rifampicin Multi-drug resistant TB: Resistance to two or more first-line anti-TB drugs but not to Rifampicin

Người bị bệnh lao kháng thuốc gặp nhiều khó khăn trong việc điều trị bệnh
Multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB): Concomitant resistance to at least two anti-TB drugs, Isoniazid and Rifampicin Pre-Super resistant: MDR-TB has additional resistance to any drug in the Fluoroquinolone class or to at least one of the three second-line injection of Capreomycin, Kanamycin, Amikacin, (but not both at the same time). Super-resistant (XDR-TB): MDR-TB has additional resistance to any of the fluoroquinolones and any of the three second-line injections (Capreomycin, Kanamycin, Amikacin).
2. Classification of drug-resistant TB
2.1. Classification of patients with MDR-TB according to treatment history
New MDR TB: Patients with MDR TB who have no history of TB treatment or have been treated for less than 1 month (also called primary MDR TB). Recurrence: A patient with a history of previous TB treatment, concluded to be cured or completed, and is now diagnosed with MDR-TB. Formula I failure: Patients with MDR TB have a history of TB patients who have failed formula I in the past. Formula II failure: Patients with MDR-TB with a history of prior failure of formula II. Re-treatment after abandonment: A patient who has had a history of TB treatment before, was concluded to be abandoned, and is now diagnosed with MDR-TB. Other MDR-TB: A patient with MDR TB with unknown previous treatment results.

Người bệnh có tiền sử bệnh lao được phân loại là bệnh nhân lao đa kháng
2.2. Classification of patients with MDR-TB according to pre-treatment test
Multi-resistant TB with positive direct smear, positive culture (S+, C+). MDR-TB was negative, culture was positive (S-, C+). MDR-TB was positive by direct smear, culture was negative (S+, C-).
3. What are the methods of testing for drug-resistant TB?
3.1. Xpert MTB/RIF . Test
This is a test that gives results in about 2 hours with high sensitivity and specificity. AFB(+) cases should be tested for Xpert for resistance to rifampicin before giving first line anti-tuberculosis drug regimens.

Máy xét nghiệm Xpert MTB/RIF
3.2. Direct sputum smear for AFB
All people with suspected TB symptoms must have a sputum test for pulmonary TB . In order to facilitate the patient's diagnosis on the day of visit, the test of 2 sputum samples on the spot should be applied instead of the 3 sputum sample test as before. The local sputum sample needs to be carefully instructed so that the patient can collect it properly, the time of sampling 1 and 2 should be at least 2 hours apart.
Hình ảnh nhuộm soi đờm trực tiếp tìm AFB
3.3. Culture for TB bacteria
Culture on solid medium gives positive results after 3-4 weeks. Culture in liquid medium (MGIT - BACTEC) gave positive results after 2 weeks. Cases detected at provincial hospitals should be encouraged for culture testing when possible.
3.4. Routine chest x-ray
Pictures on chest X-ray suggestive of advanced pulmonary TB are infiltrates, nodules, caverns, can see images of traction in the upper half of the lung field, which can be unilateral or bilateral.
Chest X-ray has a high screening value with a sensitivity of over 90% for AFB (+) TB cases.
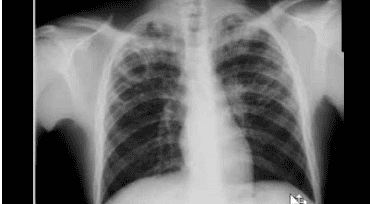
Chụp Xquang phổi là một phương pháp xét nghiệm lao kháng thuốc
4. How to treat drug-resistant TB?
4.1. Principles of formulating
“The regimen should have at least 5 effective drugs, including 4 main second-line TB drugs (1 class A drug, 1 class B drug, at least 2 class C drugs) and pyrazinamide. In case there are not enough effective drugs to develop the above regimen, drugs of groups D2, D3 can be used to ensure enough 5 drugs. When a patient is resistant to FQs (group A) or second-line injections (group B), another drug should be substituted, but still following the same principles as for R/MDR-TB resistant patients. Using injectable drugs is still sensitive and can be used for a long time (12 months or during the course of treatment). If resistance to all injectable drugs is present, the use of drugs that the patient has never used or has not used injections is recommended. Using new generation Fluoroquinolone. Consider using new drugs according to World Health Organization recommendations and guidelines (Bedaquiline, Delamanid). Consider high-dose Isoniazid if anti-KAT results or low H-antibody results.

Bệnh nhân cần hoàn toàn tuân thủ nguyên tắc xây dựng phác đồ của bác sĩ
4.2 Some treatment regimens for drug-resistant TB
4.2.1. Standard short-term regimen for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis
4-6 Km Lfx Pto Cfz Z H High Dose E / 5 Lfx Cfz Z E
4.2.2. Standard 20-month regimen
8 Km (Cm) Lfx Pto Cs Z/12 Lfx Pto Cs Z
4.2.3. Pre-super resistance regimen
Principle: Replace resistant drugs with effective drugs (listed in the classification of drug-resistant TB drugs – WHO 2016) and still adhere to the general principle (at least 5 effective drugs, including 4 drugs). second-line TB drugs and pyrazinamide. D2, D3 drugs can be used to ensure all 5 drugs are effective)
4.2.4. Super resistance regimen
Principle of protocol development: similar to pre-super resistant NB. However, because patients are already resistant to both FQs and second-line drugs, it is more difficult to choose an effective drug, especially for patients who have used most of the second-line drugs in the past. long-term availability or recurrence, failure of multidrug regimens. Priority should be given to the use of new drugs with the highest effectiveness, and at the same time, further strengthen the monitoring of treatment, management of adverse reactions, careful counseling for patients and family members to ensure compliance with the guidelines. 57 to achieve the best treatment outcome because this is the patient's last chance for treatment.
4.2.5. Personal sketches
Enrolled subjects: R/MDR-TB resistant TB not eligible for standard regimens, including:
Meningococcal TB (depending on age, treatment history) Pregnant or lactating women Tuberculosis Severe multidrug-resistant lung: Intolerance, hypersensitivity, risk of drug toxicity (drug interactions) to any drug in the regimen. Some special cases need to adjust the dose of drugs or should not use some drugs: Patients with QT interval >=500 ms on electrocardiogram, liver failure, kidney failure, diabetes mellitus, epilepsy, neuritis optic nerve and peripheral nerve.
Principle: Replace intolerant or unsuitable drugs with other drugs and ensure “at least 5 effective drugs, including 4 effective second-line TB drugs (1 class A drug, 1 B, at least 2 class C drugs) and pyrazinamide. In case there are not enough effective drugs to develop the above regimen, drugs of groups D2, D3 can be used to ensure enough 5 drugs.
Bệnh nhân suy thận cần tham khảo ý kiến bác sĩ để có sự điều chỉnh thuốc phù hợp
4.3. Anti-tuberculosis drugs
50 The TB Program is responsible for an adequate, ongoing supply of quality anti-TB drugs. Specifically:Essential anti-TB drugs (row 1):
Essential anti-TB drugs (row 1) are: isoniazid (H), rifampicin (R), pyrazinamide (Z), streptomycin (S), ethambutol (E). ). Currently, WHO has recommended the addition of two first-line anti-TB drugs, rifabutin (Rfb) and rifapentine (Rpt). First-line essential anti-tuberculosis drugs should be stored at a cool temperature, away from moisture. Second-line anti-TB drugs:
Second-line anti-TB drugs mainly include the following drug classes:
A-Fluoroquinolones (FQs): Levofloxacin, Moxifloxacin, Gatifloxacin Group B-Second-line injection: Amikacin, Capreomycin, Kanamycin, Streptomycin(*) Group C-Other second-line drugs: Ethionamide, Prothionamide, Cycloserine, Terizidone Linezolid, Clofazimine. Group D - Complementary drugs (not in the main group): Bedaquiline, Delamanid, p-aminosalicylic acid, Imipenem-cilastatin, Meropenem, Amoxicillin-clavulanate, Thioacetazone. The situation of drug-resistant TB, especially multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis, is increasing rapidly in our country as well as in other countries around the world. Therefore, in addition to diagnosing the disease to have a timely treatment plan, adherence to the regimen and principles of drug-resistant TB is also extremely important. To do this requires close cooperation between the patient and the doctor, along with relatives and the social community to help the patient feel secure and strictly adhere to the treatment regimen to bring the best treatment effect. .
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.