This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Master, Doctor Vu Huu Thang - Resuscitation - Emergency Doctor - Emergency Resuscitation Department - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital.Patients are at high risk of venous thromboembolism during and after major surgery, especially lower extremity orthopedic surgery. Venous thromboembolism causes many serious health complications and reduces the quality of life of patients. Therefore, doctors need to carefully consider a patient's risk factors and take precautions before each surgery.
1. Risk of venous thromboembolism during and after surgery
Venous thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot in a vein. Venous thrombosis can occur in any vein, but is most common in the veins of the lower extremities. Patients who undergo surgery, especially major orthopedic surgeries such as knee replacement, hip replacement, acetabular surgery, upper femoral head,... will have a high risk of developing blood clots. vein. This is the reason why many patients are hospitalized after performing orthopedic surgery.The rate of venous thromboembolism in surgery and after surgery has been shown through many different studies such as:
In 1973, Johnson and Charnley reviewed 7,959 hip replacement surgeries from 1962-1973. The results showed that the rate of pulmonary embolism in these patients was 7.9%, the mortality rate was 1.04%. In 1974, Coventry reported that in 2012 hip replacements, without anticoagulation, the mortality rate from pulmonary embolism was 3.4%. If warfarin is used for 5 days after surgery, the rate of pulmonary embolism is 2.2%. Several factors can increase the risk of venous thrombosis after surgery such as: The patient is immobile for more than 72 hours after surgery; pregnant or obese patients; the surgery lasted more than 2 hours,...
2. Why does surgery increase the risk of venous thrombosis during and after surgery?
Many factors during surgery increase the risk of venous thromboembolism such as:Intravascular injury due to surgical position and manipulation, thermal injury, use of bone cement, use of tourniquets during surgery ,... Circulatory stagnation due to the patient being motionless at the time of surgery; anesthesia ; Restriction of movement in the postoperative period,... Along with that, the surgical process can increase coagulation by increasing the release of coagulation factors in tissues, activating coagulation enzymes and inhibiting the system. endogenous fibrinolysis after surgery.
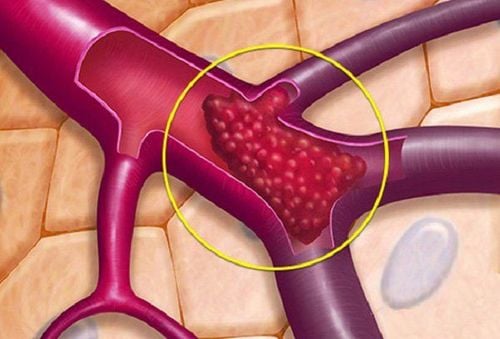
3. Consequences of venous thrombosis during and after surgery
Venous thrombosis usually forms in the legs and gets stuck in the leg veins. However, the thrombus can travel to the pulmonary blood vessels, causing a pulmonary embolism. Symptoms of a pulmonary embolism are shortness of breath, severe chest pain, and a high risk of sudden death. This is the most dangerous complication of venous thromboembolism during and after surgery, seriously threatening the patient's life.Besides, venous thromboembolism also causes many other dangerous complications such as:
Chronic post-embolism syndrome such as leg pain, leg edema, chronic leg skin ulcer,... Risk of venous thrombosis Pulmonary revascularization Chronic pulmonary arterial hypertension after embolism makes it difficult for patients to breathe during exertion, fatigue, exhaustion, and reduced working capacity.
4. Prophylaxis of venous thrombosis during and after surgery
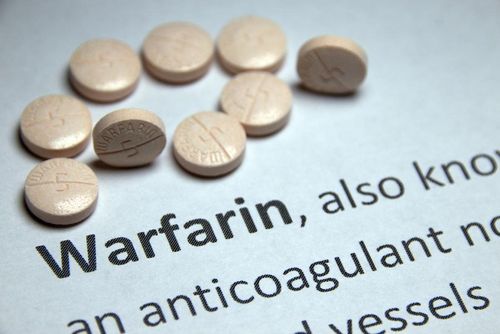
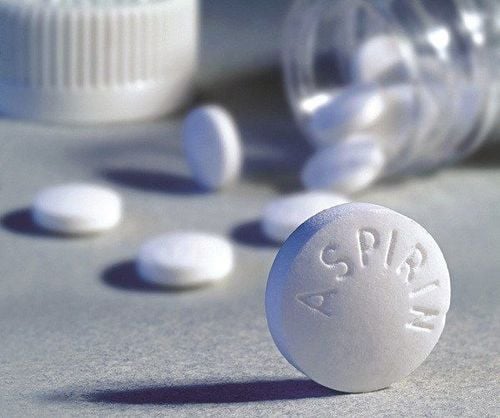
To prevent the risk of venous thrombosis during and after surgery, depending on each specific surgical case, the following measures can be applied:Using anticoagulants such as Warfarin, Heparin, Aspirin; direct thrombin inhibitors such as melagatran, ximelagatran, rivaroxaban,... However, before using anticoagulants, it is necessary to carefully assess the risk factors of each patient because taking anticoagulants can cause bleeding risks serious blood. Mechanical measures such as post-operative thigh and foot compression bandages, slightly spaced compression bandages,... These measures will increase blood circulation and reduce venous stasis but do not increase the risk of bleeding. . Mechanical measures are often indicated for patients in need of VTE prophylaxis but at high bleeding risk or in whom anticoagulation is contraindicated. Anesthesia: The use of epidural or spinal anesthesia can reduce the risk of venous thrombosis by 40-50%, as these methods increase blood flow to the lower extremities during surgery. Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consulting services. and comprehensive, professional medical treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.