This is an automatically translated article.
According to statistics, for every 100 pregnant mothers infected with HIV, 30 children will also be born with HIV transmission from the mother. However, this number will be significantly reduced if treatment is known to prevent mother-to-child transmission of HIV.HIV is a disease of the century, until now there has been no cure for this disease. For pregnant women with HIV, the most important thing is how to avoid HIV transmission from mother to child. This is very difficult but not impossible.
1. Can HIV be transmitted from mother to child?
The rate of HIV transmission from mother to child is very large, the way of transmission can be from the time the fetus is in the womb, during childbirth or during breastfeeding. If a pregnant woman is HIV-infected, treatment with a combination of anti-HIV drugs can help improve her health and prevent mother-to-child HIV transmission before, during or after delivery. The earlier the treatment, the more effective it is.
2. How to prevent mother-to-child HIV transmission?
If the pregnant woman's HIV test result is positive, the doctor will advise the pregnant woman to do some things to prevent mother-to-child transmission of HIV, which are:
2.1 Need for adequate drug treatment If If HIV infection is detected before pregnancy, the correct use of HIV drugs will help reduce the risk of HIV transmission to the baby and the infection rate is less than 1%.
In case a pregnant woman has not been treated for HIV before becoming pregnant, talk to her doctor about this to have an appropriate solution. If you are HIV-positive during pregnancy, start treatment immediately and take it every day.
After birth, the baby also needs to be treated for 4-6 weeks to help prevent HIV infection more effectively.
2.2 Use baby protection during birth

Sử dụng biện pháp bảo vệ bé trong khi sinh
If HIV treatment is effective and reduces the amount of HIV virus in the mother's body, then the doctor can plan for the mother to have a normal delivery (at this time, the risk of HIV transmission from mother to child) baby during birth will be extremely small).
However, if the test results show that the mother's viral load is still high, a cesarean section will be a safe measure to avoid mother-to-child HIV transmission. This procedure will help reduce the risk of transmitting HIV to the baby is higher than vaginal birth.
2.3 Using measures to protect the baby while breastfeeding Research results have shown that the breast milk of an HIV-infected mother also contains HIV virus, so the baby is also likely to be infected with HIV from the mother. during the lactation period. However, if mothers strictly follow the instructions on safe breastfeeding or can afford to buy formula for their babies, they will effectively avoid mother-to-child HIV transmission. Preventive measures are put in place in case the mother is infected with HIV.
In case the mother is not eligible for formula feeding, she can still breastfeed her baby but must comply with the full treatment and exclusively breastfeed the baby for at least the first 6 months of life. Do not give your baby any other foods with breast milk during this time. At the same time, the baby must also be on antiretroviral therapy to prevent mother-to-child transmission of HIV.
If HIV-positive pregnant women are treated with the right regimen during pregnancy and labor and the baby is born with antiretroviral drugs for about 6 weeks after birth, HIV infection from mother to child to the lowest extent.
In addition, a number of factors can help increase the effectiveness of measures to prevent mother-to-child HIV transmission including:
Get tested for HIV infection as early as possible before or during pregnancy good; When infected with HIV, it is necessary to actively discuss with the doctor and choose a surgical method to reduce the risk of mother-to-child transmission.
3. How to know if a child has HIV?
If you have absolutely applied measures to prevent mother-to-child transmission of HIV, but still want to have certain results whether the child is infected with HIV or not, you can conduct tests for the baby immediately after birth and for about 4 to 6 weeks afterwards.
If the test result is negative, it is still necessary to test the baby again after 18 months and after the end of the breastfeeding period to check if the baby has been infected during breastfeeding. If the result is positive, the child needs to be treated immediately.
Nothing is impossible, an HIV-infected mother can also give birth to a perfectly healthy baby if all measures are taken to avoid mother-to-child transmission of HIV according to the doctor's instructions.
4. When should pregnant women be tested for HIV?
To protect the health of the fetus and have a healthy and safe pregnancy, pregnant women should conduct an HIV screening test before becoming pregnant or as soon as they know they are pregnant. Testing and early diagnosis will help get a timely treatment regimen and reduce the severity of the disease as well as prevent HIV transmission from mother to child more effectively.
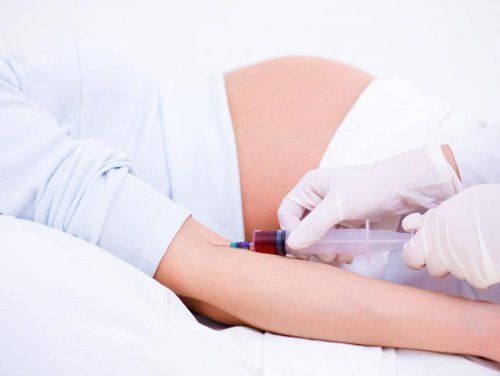
Phụ nữ mang thai cần xét nghiệm HIV chẩn đoán dự phòng lây truyền HIV từ mẹ sang con
The social disease screening package at Vinmec International Hospital has a rapid HIV Ab test, which accurately detects HIV virus, especially necessary for pregnant mothers to take early preventive measures. prevent mother-to-child transmission of HIV.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Synthesized source: Department of HIV/AIDS Prevention and Control - Ministry of Health