This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Bui Minh Phuc - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital. Doctor has more than 18 years working in the field of obstetrics and gynecology.An ectopic pregnancy is an abnormal pregnancy, most of which are benign. However, if not diagnosed and treated early, it can lead to dangerous complications.
1. What is egg pregnancy?
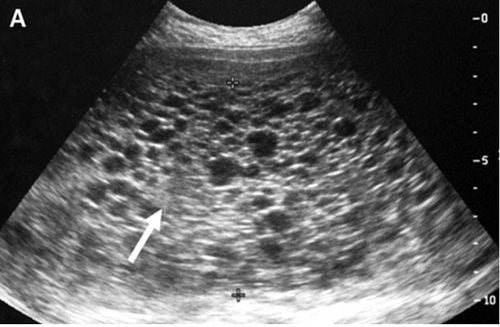
An ovum, also known as an ovum, is a rare complication of pregnancy that is characterized by the abnormal growth of trophoblasts, the cells that normally develop into the placenta.Ovulation may seem like a normal pregnancy at first, but most ovulatory pregnancies cause specific signs and symptoms, including:
Vaginal bleeding that is dark brown to red fresh in the first trimester Nausea and vomiting a lot Rapidly enlarged abdomen, uterus too large for normal pregnancy Pelvic pressure or pain.

Bụng to nhanh, tử cung quá lớn so với giai đoạn mang thai bình thường là dấu hiệu thường thấy của hiện tượng chửa trứng
2. Causes of pregnancy
The cause of this phenomenon is that part or all of the chorion (the chorion surrounding the embryo) has degenerated into fluid sacs of many sizes. They clump together and invade the uterine cavity. There are two types of ovum, full ovum and partial ovum.When the pregnant woman's uterus contains only fluid sacs, there is no formation of fetal tissue, it is called a total ovum. With a partial ovum, there may be normal placental tissue along with a sac of fluid. Fetal formation is also possible, but the fetus cannot survive and is often miscarried early in the pregnancy.
Pregnancy is caused by an abnormally fertilized egg. Human cells normally contain 23 pairs of chromosomes. One chromosome in each pair comes from the father, the other from the mother.
In complete ovum: An egg is fertilized by one or two sperm, and all the genetic material comes from the father. In this situation, chromosomes from the mother's egg are lost or inactivated and the father's chromosomes are duplicated. It is the defect in the genetic system that it cannot develop into a normal fetus, but instead develops a fetus without an embryo. In a partial pregnancy: The mother's chromosomes are still there, but the father provides two sets of chromosomes. As a result, the embryo has 69 chromosomes instead of 46. This usually happens when two sperm fertilize an egg, resulting in an extra copy of the father's genetic material.
3. Complications of pregnancy
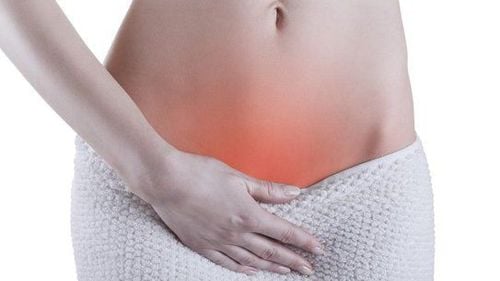
Trong một số trường hợp, chửa trứng xâm lấn sâu vào lớp giữa của thành tử cung, gây chảy máu âm đạo
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.