This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by BSCICI, MSc Nguyen Thi Huong Linh - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.Ovulation is an abnormal pregnancy in which part or all of the placenta degenerates into small and large fluid-filled sacs that stick together in clusters like frog eggs. Most egg pregnancies are benign, but if not properly monitored and treated, it will lead to unpredictable consequences: About 10-30% of egg pregnancies can cause dangerous complications, even malignant cancer. culture cells. So what are the signs to recognize this abnormal pregnancy?
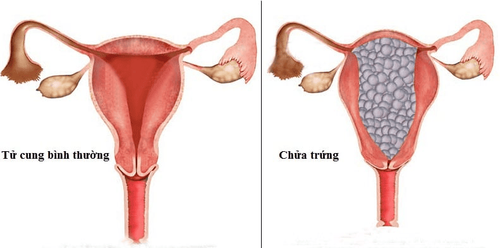
1. What is egg pregnancy? Ovulation is a pathological condition of the placenta. In which part or all of the placenta is degenerated into large and small sacs of fluid that stick together into bunches like grapes, occupying the entire area of the uterus, overwhelming the development of the fetus.
Egg pregnancy is divided into 2 types:
Complete egg pregnancy: No fetal organization. The vegetable spines swell, the hairy blood vessels disappear, and the cell layer grows rapidly. Partial pregnancy : There is a fetus or a part of the fetus. Most of the vegetable spikes turn into water sacs, and a part of the vegetable spines is normal. Ovarian pregnancy can also be distinguished by the following properties:
Benign ovum: The syncytial layer is not disrupted, the unicellular layer does not enter the uterine muscle. Malignant ovum (infiltrating oocyte) : The syncytial layer thins and there are areas of disruption. The inner layer of protozoa invades outside and spills into the lining of the uterus, penetrates deeply into the uterine muscle layer, and sometimes perforates the uterine muscle layer, causing intra-abdominal bleeding.
Trắc nghiệm: Bạn có hiểu đúng về dấu hiệu mang thai sớm?
Các dấu hiệu mang thai sớm không phải chỉ mỗi trễ kinh mà còn có rất nhiều dấu hiệu khác như xuất huyết âm đạo, ngực căng tức,… Điểm xem bạn biết được bao nhiêu dấu hiệu mang thai sớm thông qua bài trắc nghiệm này nhé!
2 . Causes and consequences of pregnancy
Until now, medicine has not found the exact cause of pregnancy. Only a few influencing factors have been given, such as:
Errors of genetic factors during fertilization have led to abnormalities in chromosomes. About 90% of cases of ectopic pregnancy originate from the father and 10% from the mother. Common in women over 40 years old or under 20 years old Women who have had multiple births, or have a history of abnormal first pregnancy, or have had abnormalities in the uterus, is one of the high risk factors for pregnancy. Lack of nutrition: Inadequate nutrition such as lack of nutrients such as protein, folic acid, vitamin A, etc. Therefore, the incidence in developing countries is higher than in developed countries. Most of the pregnancies are benign, but during the progression of the pregnancy, very dangerous complications can appear:
Hemorrhage: Due to a miscarriage, it causes bleeding, which is dangerous to the life of the pregnant woman. Invasion causing uterine perforation: Because the egg penetrates deeply into the uterine muscle, perforating the uterine muscle layer, causing abdominal bleeding. Cancer : Cancer of the culture cells invades the mother's body through the blood and metastasizes to distant organs. This is also known as mesothelioma, which accounts for about 10 to 30% of all egg pregnancies.
The patient has a delay in menstruation. Bleeding: This is the first important symptom, accounting for over 90% of pregnancies. Natural vaginal bleeding, dark black or thin red blood, prolonged discharge. Severe morning sickness: Seen in 25-30% of cases, manifesting with vomiting, sometimes edema, with proteinuria. Abdomen grow fast. The machine is not seen. Physical symptoms:
Whole body fatigue, showing anemia. Possible pregnancy toxicity. Sometimes there is jaundice, yellow urine. The uterus is soft, the size of the uterus is larger than the gestational age (except in the case of a retrograde pregnancy). The fetal part is not palpable. The fetal heart cannot be heard. Thyroid cysts occur in 25-50%, often bilateral. Vaginal examination may reveal vaginal metastases, fingertip-sized, dark purple, often anterior, friable, may bleed May have signs of pre-eclampsia (10%) May have symptoms of hyperextension thyroid (10%): Tachycardia, hot and moist skin, shaking hands, enlarged thyroid
4. How to detect early pregnancy The safest and fastest way to detect pregnancy is to have regular antenatal check-ups as recommended and when there are any unusual symptoms. Patients should go to a trusted medical facility to see a doctor to examine and do the necessary tests for early diagnosis and timely treatment to avoid unfortunate complications. There are 2 groups of measures to detect pregnancy: Imaging and Testing:
Imaging: With ultrasound, it is possible to diagnose an ovulatory pregnancy that can be detected very early and easily, usually in babies < 9 the week.
Quantitative Beta-hCG : Is the basic test to diagnose and monitor pregnancy. The amount of E-hCG is elevated above 100,000 mUI/ml. Estrogen quantification: In the urine, estrogen in the form of estrone, estradiol or estriol is lower than in normal pregnancy, due to the disorder of vegetable secretion and because there is no change in estradiol. and estriol occurs in the fetal adrenal glands. However, this index has little significance and is not used in practice because this difference is only evident when gestational age is 14 weeks or more. Quantification of HPL: (Human placental lactogen), is usually high in normal pregnancy, but very low in ovulatory pregnancy. In summary, the diagnosis of ovulatory pregnancy is mainly based on ultrasound and testing of Beta-hCG
.
5. Treatment of egg pregnancy Aspiration abortion
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, proceed with dilatation or aspiration of eggs as soon as possible. Infusion of uterotonic oxytocin during and after the procedure and antibiotics to prevent infection. Send pathological anatomy of the curettage tissue. Scheduled Postprocedure Follow-up Beta hCG and scheduled ultrasound Contraceptive for 2 years Prophylactic hysterectomy
Total hysterectomy or total hysterectomy after curettage is usually used in women who do not want to have children anymore or are over 40 years old and in case of an invasive pregnancy, the uterus is perforated.
Follow up after curettage
It is necessary to monitor the whole body, morning symptoms, symptoms of vaginal bleeding, the shrinking of the thyroid cysts and uterine contractions.
After curettage, it is necessary to continue monitoring the Beta-HCG index once a week until this index returns to normal. After returning to normal - in the next 2 years it is necessary to monitor this indicator to ensure that the pregnancy has been completely eliminated. The frequency of Beta-HCG test during this period is as follows:
First 3 months: Beta-HCG test once every 2 weeks. - Next 6 months: Beta-HCG test once a month (if the previous results are negative).- In the following year: Quantify Beta-HCG 1 time every 2 months (monitoring continuously for 2 years) Ultrasound: find nodules for metastases, monitor follicular cysts line.
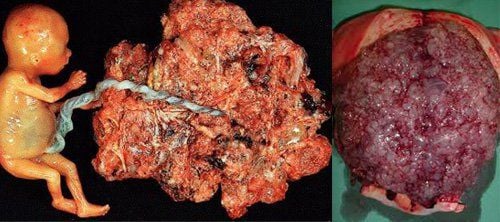
6. Monitoring progress after treatment of pregnancy After treatment, the following manifestations are considered unfavorable progress. Including:
The uterus is still large, the thyroid cyst does not disappear or metastasize appears. Beta-hCG: the main means of monitoring and diagnosing complications after removal of the ovum (including cases of prophylactic hysterectomy). Beta-hCG concentration after test was higher than previous test Beta-hCG concentration after 3 consecutive tests did not decrease (less than 10%): Beta-hCG concentration >20,000 UI/L 4 weeks after curettage Concentration Beta-hCG >500 UI/L 8 weeks after curettage- E-hCG concentration >5 UI/L after 6 months Post-pregnancy follow-up period: Women need to closely monitor their health for the next 2 years during pregnancy treatment, at least 12-18 months. During this time, it is necessary to take appropriate birth control methods to ensure health and readiness for the next pregnancy.
Proper and sufficient first and regular prenatal check-ups are considered as one of the measures to prevent pregnancy. Vinmec International General Hospital currently has many maternity packages (12-27-36 weeks), in which the 12-week maternity package helps monitor the health of mother and baby right from the beginning of pregnancy, early detection. and timely intervention in health problems. In addition to the usual services, the maternity monitoring program from 12 weeks has special services that other maternity packages do not have such as: Double Test or Triple Test to screen for fetal malformations; Quantitative angiogenesis factor test for preeclampsia; thyroid screening test; Rubella test; Testing for parasites transmitted from mother to child seriously affects the baby's brain and physical development after birth.
For detailed information about the 12-week maternity package and registration, you can contact the clinics and hospitals of the Vinmec health system nationwide or register online on the website.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.