This is an automatically translated article.
Tenofovir 300 is the preferred drug class indicated for the treatment of HIV-1-infected patients in combination with other retroviral inhibitors; post-exposure prophylaxis against HIV. So what is Tenofovir 300? What points to pay attention to, and pay attention to when using? The following article will help you better understand the uses and possible side effects of Tenofovir 300.
1. What are the uses of Tenofovir 300mg?
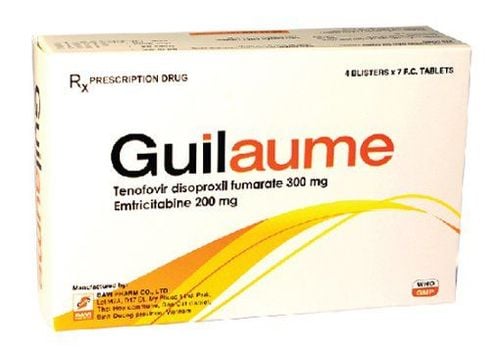
1.1. What is Tenofovir 300mg? Tenofovir 300mg medicine has the main ingredient Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate 300 mg
(Equivalent to tenofovir 136 mg), and excipients: Lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose M101, croscarmellose sodium, modified starch, magnesium stearate, colloidal silicon dioxide, opadry II blue.
Tenofovir 300mg is a product of US Pharma USA, with the main ingredient being Tenofovir in the form of Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, indicated for the treatment of HIV-1-infected patients in combination with other retroviral inhibitors; HIV post-exposure prophylaxis used in combination with other antiretroviral agents; chronic hepatitis B virus.
Tenofovir 300mg is prepared in the form of: Film-coated tablets, packed in boxes of 3 blisters, each blister has 10 tablets.
1.2. What are the uses of Tenofovir 300mg? Tenofovir is used to treat HIV-1 infection in adults over 18 years of age: Must be combined with other antiretroviral agents.
In addition, the drug is also used to prevent health workers who have to come into contact with samples (blood, body fluids, etc.) at risk of HIV infection: Must be combined with other antiretroviral drugs. In addition, the drug is also used to treat chronic hepatitis B in adults over 18 years of age with compensated liver function, evidence of active viral replication, persistent elevation of ALT, active hepatitis or tissue cirrhosis is demonstrated by histology. In this case, Tenofovir Alafenamide will be used.
2. Usage of Tenofovir 300
2.1. How to take Tenofovir 300 Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate tablets or tenofovir and emtricitabine combination tablets are taken once a day. Both tablets can be taken on an empty stomach or on an empty stomach.
With tenofovir, emtricitabine, and efavirenz combination tablets, it is best taken at night before going to bed to avoid side effects of efavirenz on the central nervous system.
If tenofovir tablets are used alone, do not use combination tablets containing tenofovir.
In case of concurrent use of tenofovir and delayed-release didanosine capsules, the drugs must be taken on an empty stomach or after a light meal; In addition, the dose of didanosine should be reduced.
Note, must take the medicine on time, the times of taking the medicine are evenly spaced.
2.2. Dosage of Tenofovir 300 Dosage: Adults with HIV - 1: Take 1 tablet x 1 time per day in combination with other antiretroviral drugs. Post-exposure HIV prophylaxis (best within a few hours and continued for the next 4 weeks if well tolerated): 1 tablet once daily in combination with another antiretroviral agent (lamivudine/emtricitabine) ). Prophylaxis of non-occupational HIV infection (best within 72 hours and continuing for 28 days): Take 1 tablet once daily in combination with at least 2 other antiretroviral agents. Chronic hepatitis B : Recommended dose: Take 1 tablet x 1 time per day. The optimal duration of drug discontinuation is currently unclear. Can be discontinued:
In patients with AgHBe (+), without cirrhosis: Treatment for at least 6 to 12 months after HBe seroconversion (AgHBe (-), undetectable inflammatory viral DNA) hepatitis B and resistant to -HBe) or until HBs seroconversion or when the drug becomes ineffective. The serum ALT and hepatitis B viral DNA ratios should be checked at regular intervals after treatment discontinuation to detect any late recurrence. In patients with AgHBe (-), without cirrhosis: Treatment must be continued until HBs seroconversion or until the drug is no longer effective. In the case of treatment lasting more than 2 years, it should be reassessed at regular intervals to determine whether pursuing such treatment is appropriate for the patient. If tenofovir disoproxil fumarate is discontinued in a patient with chronic hepatitis B co-infected with HIV, the patient should be monitored closely for all signs of worsening of hepatitis.
The drug has not been studied in children under 18 years of age and in elderly people over 65 years of age.
Handling missed dose: If you miss a dose, take it as soon as possible. However, if it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and take your next dose at the scheduled time. Note that double the prescribed dose should not be taken.
Treatment of overdose: There is limited clinical experience with doses higher than the therapeutic dose of 300 mg. In a study where an oral dose of 600 mg tenofovir disoproxil fumarate was administered to 8 patients for 28 days. RESULTS: No serious adverse events were reported. The consequences of higher doses are currently unknown.
If there is an overdose, the patient presents with evidence of toxicity, symptomatic treatment and necessary supportive measures should be instituted. Tenofovir is readily hemodialysis with an extraction coefficient close to 54%. With an oral dose of 300 mg tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, after 4 hours of hemodialysis, nearly 10% of the dose was eliminated.
If there are any symptoms of overdose, stop taking the drug immediately and notify the doctor immediately.
3. Contraindications of Tenofovir 300
3.1. Contraindications when using Tenofovir 300: Patients with hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients or excipients of the drug. The patient has severe renal failure. Patients with abnormal neutrophils less than 0.75 x 109 per liter or abnormal hemoglobin concentration less than 75g per liter. 3.2. Tenofovir 300 drug interactions with other drugs: Didanosin Atazanavir Liponavir + Ritonavir: Combination of Liponavir + Ritonavir increases tenofovir concentrations when co-administered. Patients treated on this regimen presented with an associated adverse event. Tenofovir should then be discontinued to avoid associated adverse effects. 3.3. Drugs Affecting Renal Function: As tenofovir is eliminated primarily by the renal route, co-administration with medicinal products that decrease renal function may increase serum concentrations of tenofovir and/or increase the concentrations of medicinal products. other renal excretion. In the treatment of hepatitis B, tenofovir must not be co-administered with adefovir dipivoxil.
3.4. Use of the drug during pregnancy and lactation. Pregnancy: Not recommended for pregnant women.
Lactation: It is not known whether tenofovir passes into breast milk. However, mothers taking tenofovir to treat HIV should not breastfeed to prevent transmission to their babies.
3.5. Effects of the drug on the ability to drive and use machines. There are no studies to show the effect of the drug on people who are operating machinery, driving vehicles, people working at height and other cases. However, patients should be informed of the potential for headache during treatment with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate.
4. Notes when taking Tenofovir 300
Caution when using the drug for:
Patients with lactic acidosis, severe hepatic edema due to steatosis Before taking tenofovir 300 patients should be tested first for lactic acidosis and severe hepatic edema due to steatosis.
Severe hepatitis when treatment is interrupted: Incontinent treatment of hepatitis B virus (HBV), including with tenofovir, is likely to result in severe, subclinical hepatitis. , on the test occurred showed at least 7 months after discontinuation. Treatment should be repeated as appropriate.
Use in combination with other antiretroviral/antiretroviral drugs): Do not take tenofovir with other drugs that contain tenofovir disoproxil fumarate or adefovir dipivoxil.
Use in HIV-1 and HBV coinfected patients: Due to the risk of increased HIV-1 resistance, tenofovir should only be given to HIV-1 and HBV coinfected patients as part of an appropriate ART regimen. . HIV-1 antibody testing should be performed in HBV-infected patients prior to tenofovir administration.
Use in patients with impaired renal function: It is recommended to vary the dosing interval of tenofovir according to the individual patient's creatinine clearance less than 50 ml/min or on hemodialysis (see Dosage and Administration). ).
5. Possible side effects of tenofovir 300mg
Common, ADR more than 1 in 100: Body as a whole: Muscle fatigue, headache. Gastrointestinal: Diarrhea, flatulence, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dyspepsia. Hematology: Neutropenia, hypophosphataemia. Biochemistry: Increases ALT, AST, and glucose test results. Uncommon, 1/1000 less than ADR less than 1/100: Abdominal pain, liver toxicity, kidney toxicity (especially at high doses).
Rare, ADR less than 1/1000: Liver toxicity, lactic acidosis (abdominal pain, loss of appetite, diarrhea, tachypnea, weakness, generalized malaise, muscle pain or cramps, nausea, somnolence) . Acute renal failure, proteinuria, Fanconi syndrome, tubular necrosis. Pancreatitis. Inform your doctor about any unwanted effects you may experience while using the drug.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.