This is an automatically translated article.
Thyroid surgery usually has few complications. However, like other types of surgery, surgical treatment of thyroid cancer still carries certain risks. The following information will help people have more knowledge about thyroid cancer treatment to make the right decision for their disease.
1. Thyroid Cancer Overview
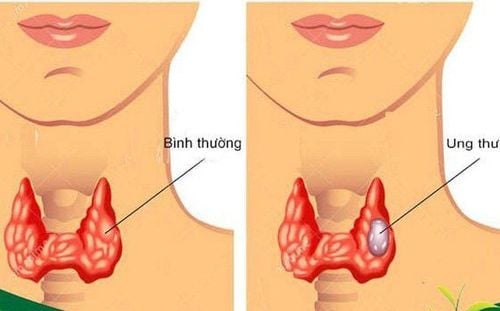
The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped gland located at the bottom of the neck that produces hormones that regulate most of the body's metabolism. Accordingly, the role of the thyroid gland has a direct influence on heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature and weight.Thyroid cancer is when the uncontrolled formation of malignant cells occurs in the cells of the thyroid gland. This disease may not cause any symptoms at first. However, in an advanced stage, thyroid tumors in the neck area can cause pain and swelling with lymphadenopathy.
The nature of thyroid cancer has many types, some are very slow growing and some are fast growing. Fortunately, if detected early, most thyroid cancers can be completely cured.
2. Surgical methods for thyroid cancer
2.1. Lobectomy
Surgical treatment of thyroid cancer by lobectomy is an intervention to remove the thyroid lobe containing the cancerous tumor. In particular, the tumor can be located in the right lobe, left lobe or right at the isthmus, the part connecting the two lobes.
The indication for lobectomy is for the treatment of papillary or follicular differentiated thyroid cancer that is small in size and has not shown signs of spreading beyond the thyroid gland. Sometimes this intervention is also used to diagnose thyroid cancer if fine-needle aspiration biopsy results do not provide a clear diagnosis.
An advantage of this surgery is that the patient does not need to take long-term thyroid hormone medication because part of the thyroid gland is preserved. However, the limitation of the method is that the tumor may still have the risk of recurrence on the remaining thyroid parenchyma. Therefore, after lobectomy, patients still have to periodically visit and screen for cancer with thyroid scans as well as measure thyroid hormone levels regularly in the blood.
2.2. Thyroidectomy
Unlike lobectomy, interventional thyroidectomy is a surgical removal of the thyroid parenchyma completely. This is the most common surgery for thyroid cancer with high radicality, limiting the risk of recurrence compared to lobectomy.
However, as with lobectomy, total thyroidectomy still has a not significantly longer incision. The downside is that you will need to take thyroid hormone medication (levothyroxine) daily for the rest of your life.
Để điều trị ung thư tuyến giáp, người bệnh có thể được chỉ định cắt tuyến giáp
2.3. Lymph node removal
If the thyroid cancer has metastasized to the lymph nodes in the neck area, they will also be dredged along with surgery on the thyroid gland.
However, surgeons can only recognize and intervene on prominently large lymph nodes, usually only one or two lymph nodes that are thought to contain cancer. The rest will be treated with additional radioactive iodine afterwards.
3. Possible complications in thyroid cancer surgery
In the hands of an experienced thyroid surgeon, thyroid surgery is generally a safe intervention with few complications. However, no different from other surgeries, thyroid surgery in general, thyroid cancer surgery in particular, cannot avoid certain complications.
3.1. Bleeding in the neck area
Any surgical intervention always carries a risk of bleeding. Fortunately, the average blood loss for thyroid surgery is usually small and the need for a revascularization is extremely rare. The problem, however, is that bleeding in the neck area is potentially life-threatening when the hematoma causes displacement or compression of the trachea, the patient becomes short of breath, and lacks oxygen in the blood. Therefore, after surgery, patients are often closely monitored for this complication. If there are any suspicious signs of postoperative bleeding, accompanied by the patient's difficulty in breathing, the neck area continues to swell, etc., the patient will need surgical intervention to stop the bleeding.
3.2. Hoarseness or change in voice
There are two nerves near the thyroid gland that control movement of the vocal cords. Damage to the laryngeal nerve from thyroid surgery can cause you to lose your voice or develop hoarseness.
Fortunately, this complication usually gets better within a few weeks of surgery but it can take up to 6 months to resolve. Even if a person has permanent hoarseness, although very rare, it is possible to improve the quality of the voice with the otolaryngologist later on.
3.3. Low blood calcium
Hypocalcemia due to low blood calcium levels can occur after thyroid and parathyroid surgery because the parathyroid glands may not work properly immediately after surgery. In the majority of cases, hypocalcemia due to hypoparathyroidism is quite common and only temporary.
The parathyroid glands are four small glands, about the size of a grain of rice. They are located near or attached to the thyroid gland and control blood calcium levels. Each thyroid lobe has two parathyroid glands. After thyroid surgery and before being discharged home, your blood calcium levels will be checked. At the same time, patients are also instructed about calcium supplements for the first week or two weeks after thyroid surgery.
When acute hypocalcemia occurs with symptoms such as numbness and tingling, especially around the lips and in the arms and legs, as well as muscle cramps, the patient needs to be hospitalized to receive calcium supplements through venous line.
3.4. Accumulation of fluid in the incision
Accumulation of fluid in the thyroid incision is serological or inflammatory in nature. If the amount is small, the fluid will be absorbed by itself, the patient does not need any intervention.
On the contrary, if fluid builds up continuously, the incision site feels fuller or swollen. At this point, the incision may need minor surgical drainage.
3.5. Infection
Like any other surgical intervention, thyroid surgery still carries the risk of infection. Infection can occur at the incision site due to poor postoperative care or infection below the wound.
These cases need to be treated with antibiotics combined with local antiseptic hygiene. Moreover, if the neck area is red, swollen, purulent, the patient has a high fever, it is necessary to consider surgical drainage of the infection.

Có thể dùng kháng sinh để điều trị nhiễm trùng khi phẫu thuật tuyến giáp
4. Patients at high risk for thyroid cancer surgery
Thyroid surgeons have identified three groups of subjects at high risk for complications of surgery in general and thyroid cancer surgery in particular:
Patients over 65 years old: Older patients with three times more likely to have complications than those under the age of 65. 10% of older patients had postoperative complications in general and 19% had complications related to thyroid surgery. For patients younger than 65 years, only 3% had general complications and 6% had complications related to thyroid surgery.
Patients with advanced thyroid cancer: When the thyroid cancer is advanced with clinical signs of hyperthyroidism syndrome, the indication for thyroid surgery will be very cautious. Any error in the intervention can promote metastasis to develop and be more difficult to control than the decision to treat chemotherapy alone.
Patients with many medical comorbidities: Chronic medical diseases on the cardiovascular system, respiratory system or metabolic disorders such as diabetes, chronic kidney disease will make the ability to tolerate surgery poor. increase the risk of complications during surgery as well as in the postoperative period.
Thyroid cancer surgery is the preferred method of first choice to thoroughly treat this pathology. Although this is a relatively simple surgical intervention because of the easily accessible location of the thyroid gland, surgery for thyroid cancer may not be without complications. Therefore, in order for the treatment to be effective, it is advisable to consider performing it in highly qualified and experienced medical facilities, especially for high-risk subjects.
Vinmec Health System is a hospital system with 02 hospitals that meet international standards for service and quality with JCI certification to ensure maximum patient safety. The hospital has full facilities for diagnosis and surgical treatment of thyroid cancer pathologies.
The most important thing is the dedicated medical staff, with many years of experience oncologists specializing in head, neck and thyroid surgery.
For common thyroid cancer surgery cases, the patient only needs to stay in the hospital for one night, the patient quickly recovers to be able to be discharged home safely.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, a system of modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its medical examination and treatment services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
In April & May 2021, when there is a need for thyroid cancer examination and treatment at Vinmec Times City International General Hospital, customers will enjoy double incentives:
- Free specialist examination and 50% off Thyroid Cancer Screening Packages such as:
+ Standard Thyroid Screening Package
+ Advanced Thyroid Screening Package
+ Special Thyroid Screening Package
- 50% off cost for customers with only post-examination treatment. The program is limited to the corresponding technique of each hospital and to customers who perform this treatment technique for the first time at Vinmec.