This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Doctor Tran Thi Thu Huong - Department of General Surgery, Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
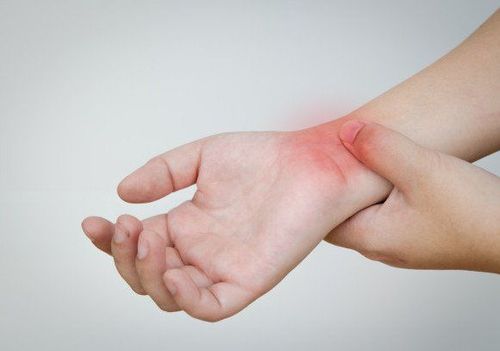
rotator cuff inflammation (De Quervain's syndrome) is inflammation of the tendon sheath of the long and short extensor of the thumb. The disease is common in people who have to use repetitive movements of holding, grasping, turning, and twisting such as teachers, surgeons, haircuts, etc., and is most common in women after childbirth and during pregnancy. lactation period
1. Symptoms of rotator cuff inflammation
Pain in the rotator cuff of the wrist, pain may increase with thumb movement, pain may be more at night, spreading along the thumb and up the forearm. Pain when doing some movements such as stretching the wrist, shaking, lifting a heavy object, opening the door... Reduced ability to stretch, rotate the wrist and grasp.
Swelling in the rotator cuff region. When pressed, there is a sharp pain
Feel the tendon sheath thickens, there may be heat and redness.
Thumb movement can hear the rubbing of tendons
Finkelstein's test: Flex the thumb and in the palm. Grasp the fingers over the thumb. Tilt your wrist towards the pillar. If the patient feels sharp pain in the long tendon of the thumb, it is a positive sign.
Subclinical:
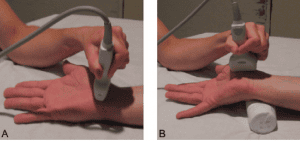
Ultrasound of the rotator cuff, can see the long tendon of the thumb, the tendon of the short extensor is thickened, the tendon sheath is thick, there may be fluid around.
Inflammatory tests and X-rays of the wrist joint .
Definitive diagnosis: based on clinical and subclinical

2. Physiotherapy methods and techniques
2.1. Rest and limit wrist and thumb movement
Rest and limitation of wrist and thumb movement play an important role in healing: Reduce or stop thumb wrist movement for 4 to 6 weeks. If there is a lot of pain and swelling, you can use a splint or an elastic band for your thumb (Elastic band should be worn 24/24 for 4-6 weeks). Limit stretching movements of the thumb and wrist. Doing exercises that strengthen the muscles and stretch the affected muscles can help with the disease (exercise intensity to a level where the tension does not cause pain.)
Avoid carrying heavy loads on painful hands
2.2. Heat treatment
- Hot compress: for chronic pain, no swelling, hot red wrist
- Cold compress: When pain is acute, when the wrist is swollen, hot, red
2.3. Electrolyte conduct drugs
Electrolysis leads drugs with anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving effects such as 3% Natrisalicylat placed in the rotator cuff region.
2.4 Ultrasound
Use high-rise ultrasound to help with local anti-inflammatory
2.5. Shock Shock
Shock is performed once a week
2.6 Laser
Use low-power laser for local anti-inflammatory pain relief
2.7. Soft tissue mobility engineering
3. Other treatments
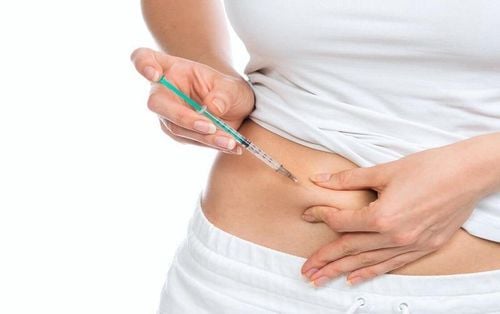
Acetaminophen (paracetamol) 500mg X 4 tablets/day. Can be combined with codeine (Efferalgan codeine) or tramadon (Ultracet), but only for short-term use. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Use low doses, short-term. Use with caution in elderly patients, with a history of gastrointestinal disease, cardiovascular disease or chronic renal failure. Can be used orally or topically. Local corticosteroid injection: Inject 0.3ml locally into the tendon sheath in case of severe or persistent pain. Inject no more than 3 times/time and not more than 3 times/year examination and treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.