This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Specialist Doctor II Pham Thieu Trung - Anesthesiologist - General Surgery Department - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General HospitalPerioperative aspiration is the reflux of gastric juice into the airway before, during and after surgery. If perioperative aspiration is food particles, foreign objects, especially stomach acid can cause burns, thickening, and hindering the conduction and exchange of oxygen in the respiratory tract. Therefore, precautions should be taken to prevent perioperative aspiration.
1. What is perioperative aspiration?
Aspiration is the inhalation of foreign bodies into the airways, accordingly, aspiration can be classified into 2 types: Lung damage due to aspiration and aspiration pneumonia.Lung injury due to aspiration: Is damage caused by chemicals after inhaling substances in the stomach that are refluxed into the patient's airway. Aspiration pneumonia: An infection secondary to aspiration of stomach contents containing bacteria. Therefore, perioperative aspiration is the reflux of gastric juice into the airway before, during and after surgery.
Hít sặc chu phẫu chính là hiện tượng trào ngược dịch dạ dày vào đường thở trước, trong và sau phẫu thuật
In particular, if perioperative aspiration is food, foreign objects, especially gastric acid can cause burns, thickening, and hindering the conduction and exchange of oxygen in the respiratory tract.
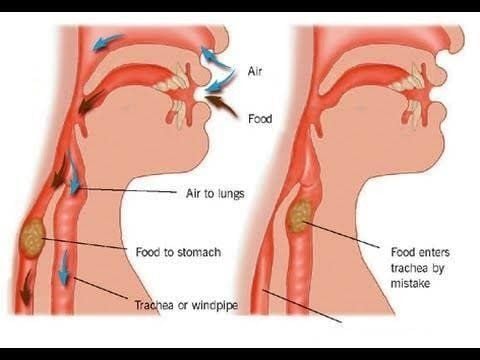
Nếu hít sặc chu phẫu là thức ăn, dị vật, nhất là dịch acid của dạ dày có thể làm bỏng,, dày dính cản trở sự dẫn, trao đổi oxy trong đường hô hấp
2. Risk factors for perioperative aspiration
Emergency surgery for a patient with a full stomach. Excessive gastric ventilation prior to endotracheal intubation. Pregnant women cesarean section. Obese patients. In the induction phase, the anesthesia is not enough, the patient has a vomiting reflex. Recovery period, especially after extubation. During the recovery period, the patient still has residual sedatives, Opioid drugs, and muscle relaxants that cause decreased reflexes to protect the airways.3. Clinical signs of perioperative aspiration
Inhaling stomach contents is often a disaster. Depends on the nature and quantity of substances contained in the inhaled stomach. The more acidic the inhaler is, the more likely the chemical pneumonia will be. Inhalation of pure gastric acid (pH < 2.5) causes extensive desquamation of the bronchial epithelium, lung, bleeding, and pulmonary edema.If aspiration of acute gastric juice is one of the most common causes of respiratory distress syndrome in adults. The clinical picture is acute-onset respiratory distress: cough, wheezing, fever, and tachypnea. Clinical examination will find:
At the bottom of the lung, there are many moist, crackles. Hypoxia can be noticed immediately after inhalation. Chest radiograph showing areas of intraluminal alveolar infiltrates in the aspirated lung region. If food particles are inhaled along with stomach acid, the picture shows bronchial obstruction. Although there is no superinfection, there is still fever and leukocytosis. Later collapse of the lung
Xẹp phổi là dấu hiệu lâm sàng cho thấy hit sặc chu phẫu
4. Treatment of perioperative aspiration aspiration
Open airway and treat respiratory inflammation Oxygen therapy (Oxygen, intubation, mechanical ventilation) Corticosteroids and antibiotics are necessary Tracheal irrigation with 1.4% Sodium Bicarbonate solution Treatment of hypotension secondary to damage to the alveolar capillary membrane causing a reduction in intravascular volume is often seen and treated with intravenous fluids.5. Preventive measures for perioperative aspiration
Measures to prevent perioperative aspiration are as follows:Place the patient in the position of the head 30-45 degrees with the head tilted to one side. Gastric suction Limit the use of long-acting sedatives, Opioids. Limit ventilation to the stomach prior to intubation Perform the Sellick maneuver properly in anesthetized patients with a full stomach Check and maintain an appropriate endotracheal tube Cuff pressure (20-30 cmH2O). ) Clean the patient's oral cavity before extubating the endotracheal tube. Routine resolution of muscle relaxants. Perioperative aspiration can leave dangerous complications during surgery, so it is necessary to take measures to prevent complications. this evidence.
Vinmec International General Hospital is the address for examination, treatment and prevention of many diseases. With a system of modern facilities, a team of well-trained and experienced doctors and nurses, will bring satisfaction to customers.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.
SEE ALSO:
Pericardiovascular assessment and management What you need to know about aspiration pneumonia Diseases that can be diagnosed early by chest X-ray