This is an automatically translated article.
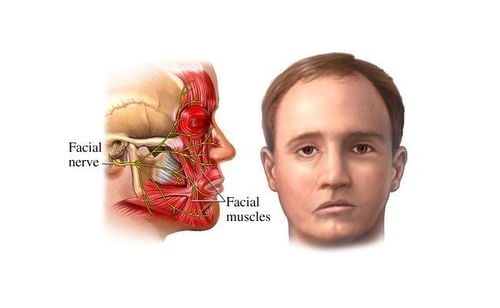
Parotid gland surgery is indicated in some cases such as parotid gland tumor, parotid gland inflammation caused by stones... Parotidectomy will mainly preserve the VII nerve, however, the parotid gland will Parotid is where the VII nerve divides into small branches that supply the facial muscles, so sometimes in the case of malignant tumors, it can cause invasive damage to the VII nerve that cannot be preserved during surgery.1. Outline
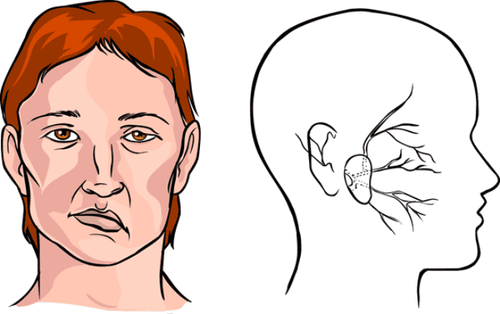
The parotid gland is one of the body's major salivary glands, located in the anterior inferior region of the external ear canal. The parotid gland is closely related to many important structures, especially the facial nerve (VII), the external jugular vein, and the terminal branches of the external carotid artery.Inflammatory parotid gland lesions, stones, ineffective medical treatment or parotid adenomas, the most effective treatment is parotid gland surgery.
Parotid gland tumors account for the highest percentage of salivary gland tumors in the head and face. Among parotid gland tumors, parotid adenocarcinoma accounts for 20% of all parotid salivary gland tumors. Salivary gland cancers generally account for 3-4% of head and neck tumors. Parotid glandectomy is the main treatment method in parotid adenoma, in the process of parotectomy, it is possible to preserve or not preserve the VII nerve, but most of the time it is preserved. In case the VII nerve has not been damaged, and in the case of nerve VII damage, it is possible to choose not to preserve the VII nerve.
However, parotid gland surgery is difficult surgery, there is a high risk of damage to adjacent components, especially damage to the VII cord. Because after exiting the skull, nerve VII penetrates and branches in the parotid gland before coming to innervate the muscles of the face. Therefore, the dissection and disclosure need the dexterity of the surgeon.
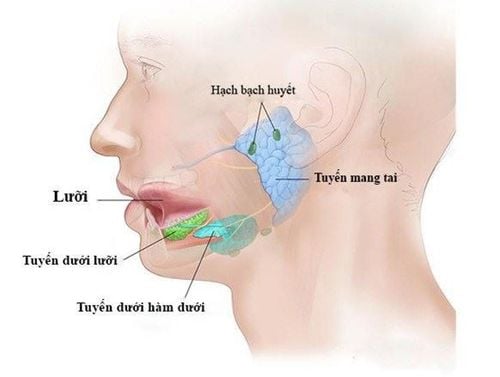
Tuyến mang tai là một trong những tuyến nước bọt chính của cơ thể
2. Parotid gland surgery with or without preserving the VII nerve
2.1 Indications and contraindications
Indications:Benign tumors or low-grade malignant tumors. Recurrent parotid gland inflammation or inflammation caused by stones for which medical treatment has not been effective. Inflammation of the gland causes enlargement, affecting aesthetics. Parotid gland removal when metastasis is suspected or confirmed. Contraindications:
Tumor of medium or high malignancy. Benign tumor in the lower pole of the parotid gland. The patient has a systemic disease that affects the anesthesia and surgery process.
2.2 Preparation
The person who prepares: Need a team of doctors, nurses, anesthesiologists and otolaryngologists with specialized training in head and neck surgery. Means: Ward money used in anesthesia, anesthetic drugs, surgical instruments and necessary means to handle accidents caused by the process of anesthesia and surgery. Patients: Examine and complete pre-operative tests, clearly explaining the surgical procedure and possible complications during surgical anesthesia.2.3 Steps to perform surgery
Patient position:The patient lies on his back, with a pillow in the shoulder area, with the head tilted to the maximum. Exposing ears, neck, parotid glands, lateral corners of eyes and mouth on the same side. The main surgeon stands on the side to be operated on, and the assistant stands on the opposite side and overhead. Anesthesia: Before surgery, the patient is given general anesthesia.
Perform surgery:
Skin incision: The incision goes from the front of the ear to the level of the ear flap, around the earlobe back to the mastoid process, around the angle of the jaw down to the neck along the horizontal line below the lower jaw line. hand. Dissection anteriorly of the parotid gland to the anterior margin of the gland adjacent to the fascia that encapsulates the bite muscle. The posterior flap is exposed from the gland. Find nerve VII: Separate the posterior border of the gland from the sternocleidomastoid muscle, the cartilage of the external ear canal. Find cord VII based on landmarks: posterior abdomen of biceps muscle, point cartilage, and mastoid process. Characteristics of wire VII is white, about 2mm in diameter and divided into small branches. Dissection of cord branches VII: Separation of glandular organization along the path of the branches to remove all the superficial lobes outside the branches. After completion, it is necessary to place a closed drain, close the skin..

Trước khi phẫu thuật người bệnh được tiến hành vô cảm toàn thân
2.3 Follow-up after surgery
After surgery, it is necessary to monitor vital signs (pulse, temperature, blood pressure, breathing rate) and possible complications after surgery such as infection, bleeding... Daily suction and withdrawal of fluids Postoperative drainage is approximately 36 to 48 hours. Change the patient's dressing on a daily basis. Cut the thread after 5-7 days. Use anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce edema and antibiotics to prevent infection after surgery.3. Complications of parotid gland surgery
After parotectomy, the patient may appear some complications such as:Facial paralysis: In the case of surgery without preserving the VII nerve due to previous damage to the VII nerve, the tumor invades or in the case of conservative surgery, but when surgically cutting off small branches of the nerve, the patient will develop facial paralysis Bleeding: Due to damage to the blood vessels involved or in the affected areas. vicinity of the parotid gland. The patient sees bright red blood draining out through the drainage. Infection: Treatment with antibiotics is required. Parotidectomy is a difficult surgery, because the priority of surgery is to preserve the VIIth nerve except in cases where there has been previous irreversible damage to the VII nerve. Therefore, for successful surgery, it is necessary to have an experienced and skillful surgeon when performing surgery.
If customers notice unusual problems, they should visit and consult with specialists.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
See also:Salivary gland cancer: Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment Salivary gland inflammation: Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment How does the salivary gland work?