This is an automatically translated article.
There are many treatments available for parathyroid cancer, such as surgery (most commonly), chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and supportive care therapy. Each treatment method has its advantages and disadvantages, so to choose the best cancer treatment, patients need to consult with their doctors.
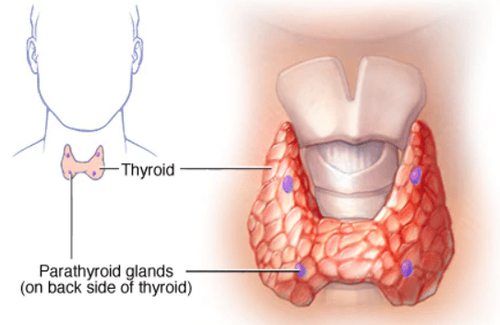
1. About parathyroid cancer
Parathyroid tumors are usually benign (non-cancerous) and are collectively referred to as parathyroid adenomas. However, in some cases it can exist as a malignancy (parathyroid cancer), but very rarely.
In an expert's opinion, having certain genetic disorders can increase the risk of parathyroid cancer, such as multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) and isolated hyperparathyroidism. familial nature (FIHP). In general, early recognition of causes and symptoms will help patients have the right treatment for their health condition.
2. How is parathyroid cancer diagnosed?
The performance of diagnostic tests is important, helping to determine the stage and extent of cancer in the patient's body. For parathyroid cancer, diagnostic tests usually include:
General physical exam: An examination of the patient's overall health and past medical history. Serum tests: Blood samples are taken to check serum calcium levels and parathyroid glands. Your doctor will conduct venipuncture, where blood samples will be taken from specific veins. Diagnostic imaging: X-ray tests can help look inside a person's body and see if the cancer has spread. The imaging studies used include ultrasound, CT scan (CAT scan), Photon emission computed tomography (SPECT scan), X-ray, bone density testing, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). ), Sestamibi scan or angiogram. Your doctor may also recommend a urinalysis to evaluate for parathyroid cancer. In general, the diagnosis of parathyroid cancer is relatively difficult because the malignant cells and the cells of a benign parathyroid tumor look similar. Diagnostic criteria for parathyroid cancer usually include symptoms, parathyroid hormone levels, serum calcium, and tumor features.
Parathyroid cancer can spread to other sites through the lymph, tissue system, and blood. The stage of the cancer can determine how far the tumor has spread, thereby considering the specific course of treatment. In fact, parathyroid cancer does not have a standard staging process but is only described as localized (in situ) or metastatic.
3. Some treatment options for parathyroid cancer
There are now different types of treatment for patients with parathyroid cancer. Treatment includes good control of hypercalcemia in patients with overactive parathyroid glands. Currently, there are 4 treatments for parathyroid cancer used, including:
Surgery. Radiotherapy. Chemotherapy. Supportive care. Several new types of treatment are in clinical trials. However, any treatment for parathyroid cancer carries the risk of side effects. Therefore, patients can join a clinical trial before, during, or after starting cancer treatment to evaluate the best treatment for themselves.
4. Measures applied in the treatment of parathyroid cancer
4.1. Surgery for parathyroid cancer Surgery is the most common treatment for parathyroid cancer and is used for localized or metastatic cancer. Because parathyroid cancer grows very slowly, once the cancer has spread to other organs, it can be removed surgically, helping patients manage the effects of the disease in the long run. . Before surgery, patients may need to control hypercalcemia.
Several surgical measures are used in the treatment of parathyroid cancer, including:
Parathyroidectomy: Surgical removal of the entire parathyroid gland and its surrounding tissues. Sometimes removal involves lymph nodes, tissues, muscles, half of the thyroid gland on the same side of the body as cancer, or nerves in the neck. Tumor surgery: Surgery to remove as much of the tumor as possible, for patients whose tumors cannot be completely removed. Metastatic resection: Surgery to remove any cancer that has spread to distant organs such as the lungs. Surgery for parathyroid cancer can damage nerves in the vocal cords, causing loss of voice. As a result, the patient may be prescribed additional procedures to help address the speech problem caused by this injury.
4.2. Radiation therapy for parathyroid cancer Radiation therapy is a treatment for parathyroid cancer that uses high-energy X-rays or other types of radiation to kill cancer cells or inhibit their growth. There are 2 main types of radiation therapy for patients with parathyroid cancer, including:
External radiation therapy: Using a machine outside the body to send radiation to the cancer site. Internal radiation therapy: Using radioactive materials through needles, catheters, ... are placed directly on or near the site of the cancer. The way radiation therapy is given depends on the type and stage of the cancer being treated. External radiation therapy is most commonly used in the treatment of parathyroid cancer.
4.3. Chemotherapy for parathyroid cancer Chemotherapy is the use of drugs to treat parathyroid cancer, which helps stop the growth of cancer cells by killing cells or preventing them from dividing in the body. body. When chemotherapy is given by mouth or injected into a muscle/vein, the drug enters the bloodstream and reaches cancer cells throughout the body (called systemic chemotherapy). If chemotherapy is placed directly into the cerebrospinal fluid, a body cavity (such as the abdomen), or a certain organ, the drug mainly acts on the cancer cells in that area (regional chemotherapy). In general, how chemotherapy will be given depends on the type and stage of the parathyroid cancer.
4.4. Supportive Care Supportive care is used to help relieve problems caused by parathyroid cancer or its treatment. Supportive care focuses on alleviating symptoms of hypercalcemia, including:
Giving the patient medication to increase urine output. Use intravenous (IV) fluids. Use of drugs that inhibit the production of parathyroid hormone. Use medications that block the absorption of calcium from food into the body.
5. Side effects of parathyroid cancer treatment
Any cancer treatment has many potential side effects. These problems often occur when treatment affects healthy tissues and organs in the body. Below are the side effects that patients may experience during treatment for parathyroid cancer , including :
Anemia . Decrease/loss of appetite. Bleeding/bruising due to thrombocytopenia. Delirium. Constipation. Edema, diarrhea and fatigue. Have fertility problems in both men and women. Hair loss. Have flu-like symptoms. Decrease in neutrophils. Infection. Have memory problems/reduced concentration. Lymphedema. Nausea/vomiting. Peripheral neuropathy. Pain. Changes in skin, nails, sleep. Bladder/urinary problems. When any of the symptoms mentioned above occurs, the patient should notify the doctor immediately for proper treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: cancer.gov, oncolink.org