This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with resident Doctor Le Thanh Tuan - Gastroenterologist - General Surgery Department - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Pancreatic pseudocyst is a pancreatic pseudocyst. Treatment of pancreatic pseudocysts needs to be done properly, especially in the case of complications to limit the risk of death.
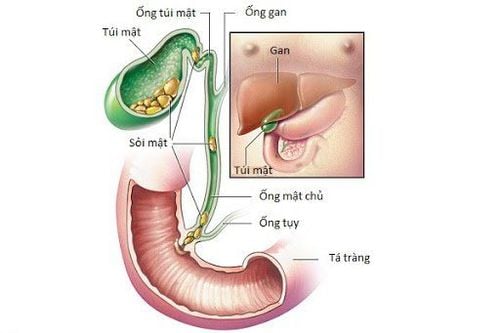
1. What is a pancreatic pseudocyst?
Pancreatic pseudocyst is a common lesion in the pancreas, having the form of a cyst, the cyst wall is covered with an epithelial layer consisting of necrotic, fibrous, and granular tissues.Pancreatic pseudocysts usually appear in the body and tail, or in the head of the pancreas.
The cause of pancreatic pseudocyst is mainly acute or chronic pancreatitis. In addition, it can also be seen after pancreatic trauma (common in young people).
The mechanism of formation of pancreatic pseudocyst due to acute pancreatitis is the obstruction of the pancreatic duct, causing increased pressure and leading to tear of the ductal duct, causing an overflow of pancreatic juice inside the duct and blood in the cavity, thereby forming a pseudocyst. secondary necrotic tissues.
2. Symptoms of pancreatic pseudocyst

Persistent pain due to epigastric trauma or pancreatitis Vomiting, loss of appetite, weight loss Fever, jaundice Feeling a tumor in the epigastric region Severe pain epigastrium, hypotension, pale skin due to blood loss due to bleeding in pancreatic pseudocyst
3. Complications of pancreatic pseudocyst
Pancreatic pseudocyst, if not detected and treated, can cause dangerous complications such as infection, blockage, bleeding in the cyst or rupture of the cyst.3.1 Pancreatic cyst infection is the most common complication with cyst wall thickening, the amount of necrosis in the fovea is not much. Clinically, signs of complications are high fever, abdominal pain, and high white blood cell count in blood tests.
3.2 Obstruction of the duodenum and common bile duct This complication is rare, caused by an enlarged cyst and compression of the duodenum or common bile duct.
The cause of this complication may be mucosal necrosis, intestinal leakage into the pseudocyst, damaging the blood vessels and causing bleeding (usually bleeding from the splenic or gastroduodenal artery, or a branch).
Blood flowing in the cyst can migrate into the peritoneal cavity, causing symptoms such as hypotension, abdominal pain. As infection progresses, acute pancreatitis with extensive necrosis may increase bleeding.
3.4 Pancreatic cyst rupture Complications of pancreatic pseudocyst rupture can occur when the cyst size is too large. If the cyst ruptures into the gastrointestinal tract, it can cause cystic-digestive fistula, resulting in decreased pressure and atelectasis of the pancreatic cyst. If the cyst ruptures into the peritoneal cavity or pleural space, it may lead to a cysto-pleural fistula or ascites. If the cyst ruptures into the retroperitoneum, it can lead to duodenal perforation (rare).
In addition, the cause of cyst rupture can also be due to thin pancreatic pseudocyst wall, pancreatic enzyme secretion, fluid pressure in the cyst lumen, patients with pancreatic pseudocyst for a long time are not detected and treated.
4. Treatment of pancreatic pseudocyst
Treatment methods for pancreatic pseudocysts include:
4.1 Medical treatment Treating symptoms, supporting the general condition when the patient has no indication for surgery or procedure.
Medical treatment is also indicated in cases where cysts can resolve spontaneously without intervention (uncomplicated cysts, thin cyst walls, intact pancreatic ducts, cysts appearing before 4 weeks after pancreatitis or pancreatic injury). Medical treatment includes analgesia and parenteral nutrition support.
4.2 Percutaneous cyst drainage Indicated in cases of pancreatic pseudocysts with infectious complications, contraindicated in cases of pancreatic duct obstruction, septal cysts or necrotic tissue.
This method has the advantage of being gentle and is performed as follows: Locate the cyst in contact with the abdominal wall, insert the needle through the skin into the cyst, insert the catheter, save and fix the catheter.
4.3 Gastroduodenal endoscopy and cyst drainage Gastroduodenal endoscopy and cyst drainage is a technique applied to cases of pancreatic pseudocyst adherent to the stomach or duodenum wall, draining the pseudocyst pancreas through the pancreatic duct.
The technique is performed as follows: Insert the endoscope to the duodenum and place endoprothese, when the cyst is regressed, perform an endoscopy to withdraw the endoprothese. This method has a high success rate, low recurrence rate, but can cause complications such as bleeding, acute pancreatitis, perforation of the gastroduodenal wall. Before surgery, the patient should undergo endoscopic ultrasound.
Depending on the relationship of the wall of the cyst with the adjacent organs to perform anastomosis with the posterior wall of the stomach, the lateral wall of the duodenum or the jejunum. This method has a high success rate and a very low recurrence rate.
4.5 External drainage Indicated in cases of pancreatic pseudocyst with infectious complications, thin cyst wall and complications of compression, the patient cannot perform major surgery.
4.6 Cystectomy Indicated in cases of localized cysts, especially in the tail of the pancreas. The method of removing the tail of the pancreas with cysts is rarely applied.
In case of complicated pancreatic pseudocyst, it is necessary to combine specific treatment as follows:
Infection: Drainage of the cyst combined with antibiotic treatment. Obstruction, compression: Drain the cyst. Bleeding: Surgical treatment of hemostasis with arteriovenous techniques, angiography, occlusion of bleeding arteries. Cyst rupture into the peritoneal cavity: Wash the abdomen, drain the abdominal cavity, drain the cyst. Pancreatic pseudocyst, if not detected, can cause complications, in which bleeding in the cyst, rupture of the cyst are dangerous complications that need to be treated properly to promptly save the patient's life.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.