This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Le Thi Phuong - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital.Oxytocin is a drug used in obstetrics and gynecology that causes uterine contractions in both frequency and intensity. Oxytocin is an international generic name for a syringe drug, with a concentration of 1 ml 5 IU and 10 IU.
1. Indications to use Oxytocin
1.1. Before giving birth Oxytocin is used to induce labor in cases where it is forced to actively terminate the pregnancy due to a number of risks without the need for cesarean section such as:Pregnancy beyond the due date; Pregnancy toxicity ; Stillbirth ; Fetal malformations, severe birth defects; Intrauterine growth retardation; Pregnant women with gestational hypertension, preeclampsia, cancer, cardiovascular (without heart failure) and autoimmune disease. In addition, oxytocin is also used to induce uterine contractions in cases of induction of labor or labor that has progressed abnormally, such as:
Premature rupture of membranes, premature rupture of membranes, lack of amniotic fluid or infection bacteria; Weak uterine contractions; Prolonged labor; The membranes have ruptured but haven't gone into labor, or haven't had contractions. 1.2. After delivery After the pregnancy has passed or the cesarean section has been delivered, the doctor may prescribe oxytocin infusion to prevent and actively manage the following cases:
Bleeding stage 3 of labor; Treatment of postpartum hemorrhage; Bleeding after miscarriage, or abortion.

2. Contraindications
Oxytocin infusion is absolutely contraindicated when there is no indication for vaginal delivery (cannot deliver vaginally) in the following cases:Fetal-pelvic head disproportion; Abnormal pregnancy; Placenta/placenta central or presumptive tumor; Severe placental abruption; Intense contractions; Acute and chronic fetal distress; Test yes/no attack with pathological manifestations; Pregnant women with cardiovascular disease causing disturbances in cardiac output or serious chronic diseases...; Medical facilities have no operating room and facilities, and no surgeons. In addition, some relative contraindications to oxytocin include a scarred uterus from a previous cesarean section; multiple pregnancy, polyhydramnios; umbilical cord prolapse while the fetus is still alive; or the mother has a sexually transmitted disease such as genital herpes or genital warts.
3. Usage and dosage of oxytocin in obstetrics
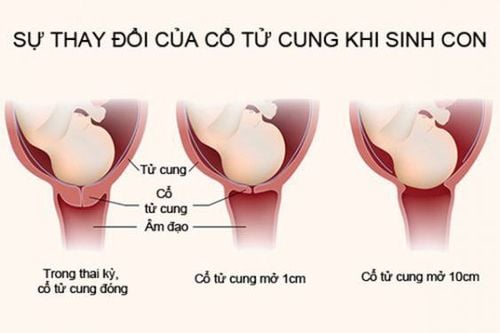
Mix 5 units of oxytocin into 500 ml of 5% glucose solution / 0.9% sodium chloride solution / Ringer lactate solution; Slow intravenous drip (TTM), the initial dose is about 5 - 8 drops/minute until uterine contractions appear; The doctor conducts amniocentesis, tearing the amniotic membrane wide; Closely monitor fetal heart rate, labor by obstetric monitor and uterine contractions; Adjust the dose of oxytocin drops to achieve a contraction frequency appropriate to the course of labor; Depending on the condition of the delivery, oxytocin may be given slowly or in combination with a tocolytic to soften the cervix if contractions are rapid. Record the progress of labor on a chart. Obstetric oxytocin infusion is considered effective when the mother has regular contractions, the cervix is fully dilated, the lower tract is possible, and the fetal heart rate is good, the position is good, and the baby is healthy.
After childbirth, oxytocin can be used to actively manage the 3rd stage of labor, as well as prevent and treat bleeding due to uterine atony according to the right regimen.
3.2. Dose Induce Intravenous Labor with an automatic infusion pump at an initial dose of 0.001 - 0.002 IU/min, increasing every 30 minutes to 0.001 - 0.002 IU/min, until a maximum of 3 or 4 uterine contractions are achieved. in 10 minutes. Note the maximum recommended rate of 0.02 IU/min, no more than 5 units in 24 hours, and do not administer the entire dose during delivery.
Prophylaxis of postpartum haemorrhage 5 IU slow IVF right after the placenta is removed. If intramuscular injection has been performed to induce labor or induce labor, the rate of infusion must be increased a few hours later in the third phase. Intramuscular ergometrin can be selected instead of oxytocin when rapid action is not required.
Treatment of postpartum bleeding (placental abruption) Slow IVF 5-10 IU or 10 IU intramuscular injection; For severe cases, a total IV dose of 40 IU at an infusion rate of 0.02 - 0.04 IU/min is recommended.
4. Note when using oxytocin in obstetrics
In order for the delivery of oxytocin to induce labor in obstetrics and gynecology to be safe and maximize its effectiveness, it is necessary to keep the following notes in mind:Requires assessment of both mother and child before inducing labor stomach with oxytocin; It is necessary to closely monitor fetal heart rate, monitor uterine contractions as well as cervical dilation, and breech position to promptly handle during oxytocin infusion; In case the birth of the commander lasts more than 6 hours but does not progress well, cesarean section is required; To maintain stability, oxytocin must be stored in a tightly closed container at a temperature of 15 – 30°C; Some side effects of oxytocin infusion can include headache, dizziness, nausea, heart palpitations, vasodilation, low blood pressure, and skin rashes.
5. Complications and management when using Oxytocin in obstetrics

For severe contractions, it should be treated quickly by:
Discontinue oxytocin infusion; Combination of tocolytic drugs such as threatened rupture and uterine rupture regimens; Closely monitor the frequency of contractions, as well as the fetal heart rate, about 30-45 minutes; Caesarean section or assisted delivery depending on the condition if uterine contractions do not subside after 45 minutes. 5.2. Acute fetal distress in labor If delivery by oxytocin infusion is not well monitored or managed late, there is a risk of fetal distress, or even death. Therefore, when detecting signs of fetal distress, oxytocin infusion must be stopped and properly handled according to the regimen of fetal distress. In case the oxytocin infusion has been stopped for 15 minutes and still has no results, it is imperative to have surgery to save the pregnancy or perform obstetric forceps if eligible.
5.3. Other complications Threat of rupture - uterine rupture: Occurs when oxytocin infusion causes rapid and strong contractions, treated by surgery to save mother and child; Placenta abruption: Refer to the protocol of placental abruption; Smooth muscle relaxation: Occurs if high doses of oxytocin are used directly in combination with anesthesia or anesthesia for pregnant women. Water intoxication: When high-dose oxytocin infusion is long-term, treatment is symptomatic, combined with reducing fluid infusion as well as adjusting electrolytes. Cardiovascular effects: When using high doses >45mUI/min or when administered intravenously directly; causing maternal hypotension, reduced coronary artery perfusion, even cardiac arrest; Effects on the fetus: There is a risk of postpartum asphyxia, or increased bilirubin/blood is the cause of neonatal jaundice. Oxytocin infusion for the purpose of inducing or inducing labor requires a prescription by qualified obstetricians and is only performed in large hospitals with adequate medical facilities and equipment. This requirement is to ensure the ability to control the infusion rate of the human resources team and to be ready to deal with potentially serious complications that may occur to the mother and fetus. For smaller medical facilities or clinics, oxytocin is only used in obstetrics to prevent and treat bleeding after placental abruption.
Vinmec International General Hospital has full professional qualifications and technical means to effectively implement oxytocin infusion method in obstetrics. There is a team of well-trained and experienced obstetricians and gynecologists, a complete and modern system of medical equipment, professional service quality, high technical efficiency, contributing to pregnancy health care for both mother and baby.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.