This is an automatically translated article.
The article was consulted with Specialist Doctor I Le Thi Thu Hang - Dermatologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Psoriasis is a slow-growing, chronic, scaly maculopapular rash that is resistant to treatment and has no obvious symptoms. Although the rash is psoriasis and lichen planus, the disease does not respond to treatments for psoriasis, lichen, and other conditions.
1. Classification of lichenoid and parapsoriatic disease
Plaque psoriasis:Small plaque psoriasis, also known as finger plaque psoriasis. Large plaque psoriasis is also known by other names: atrophic parapsoriatic, reticular mottled psoriasis, or lichenoid parapsoriatic. Psoriasis lichen (formerly known as droplet psoriasis):
Chronic lichen planus. Powdery mildew and acute smallpox.
2. Plaque psoriasis
It occurs mainly in middle-aged and elderly people, especially in the 50s. Male/female ratio = 3/1. Divided into 2 types: large array and small array.2.1. Small plaque psoriasis
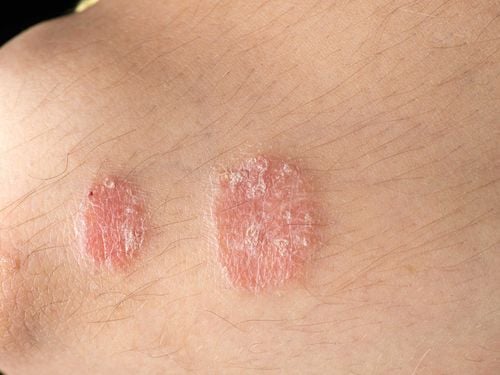
Clinical: mainly seen in adult males, lesions are pink-brown or red, oval-shaped, numerous, well-defined, flat with healthy skin surface, 2-5cm in size, scaly above thin, sometimes resembling fingers, arranged in the same direction on the ribs, chest, or medial limbs. Function: may or may not itch. Progression: benign disease, chronic progression of unknown duration, some cases spontaneously resolved after many years. Histopathology: nonspecific dermatitis. Some cases (about 1/3) had clustered epidermal lymphocytic leukemia, spotty parakeratosis, edema, papillomatosis, and mild spongiform cells. Progression: benign disease, chronic progression of unknown duration, some cases spontaneously resolved after many years. Definitive diagnosis: Based on clinical and histopathology. Differential diagnosis + Dry eczema.+ Redness of the skin pre-mycosis.
+ Erythema multiforme.
Treatment of psoriasis: use topical corticosteroids.

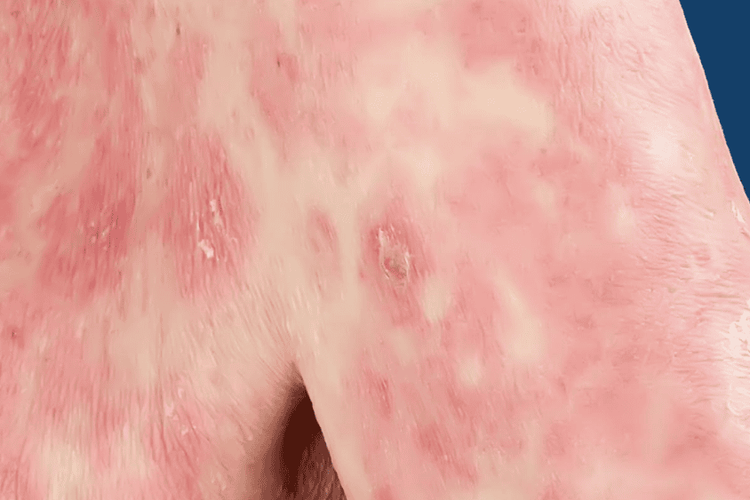
2.2. Large plaque psoriasis
ClinicalDisease is common in adults, men, rare in children. Lesions are patches of 10-20cm in size, red or brown, indistinct limits, with small scales on the top, few in number. Common locations on the trunk, limbs, especially in the buttocks, thighs, women often in the chest. There are two common forms: - Large plaque psoriasis, not atrophy. Characterized by large chalky scaly red patches, gray-brown or dull, slightly infiltrated.
- Large, atrophic plaques of psoriasis: characterized by irregular streaks of atrophy of the skin, vasodilatation, and hyperpigmentation into streaks forming a patchy network.
Function: mild itching. Histopathology
In most cases, the histopathology can be nonspecific inflammation or chronic spongiform cellulitis. In the form with skin atrophy and some cases without atrophy, histopathology shows the picture of mycosis fungoides.
Progression
The disease persists for many years. Plaque parapsoriasis is thought to be an early stage of mycosis fungoides, as most cases progress to mycosis fungoides, especially when there is intense pruritus, infiltrative lesions and deep red coloration. Therefore, this disease is also classified in the chapter of diseases caused by skin lymphoma.
Based on clinical and histopathology.
Differential diagnosis
Dermatomyositis: in addition to skin lesions, there are also signs of muscle damage, increased muscle enzymes (CK). Systemic lupus erythematosus. Dry pigmented skin. Chronic radiation dermatitis. Treatment of small plaque psoriasis: moisturizers, topical corticosteroids, coal products: polytar, goudron, anthralin. UVB or UVB-NB or PUVA. It is recommended to check every 3-6 months to assess the progression of the lesion. Large plaque psoriasis: must be treated aggressively with the aim of preventing progression to mycosis fungoides. - Use topical corticosteroids with strong activity.
- Whole body: retinoid, methotrexate.
- Patients need to be examined every 3-6 months, biopsies are recommended to monitor disease progression.
3. Lichen-like powdery mildew
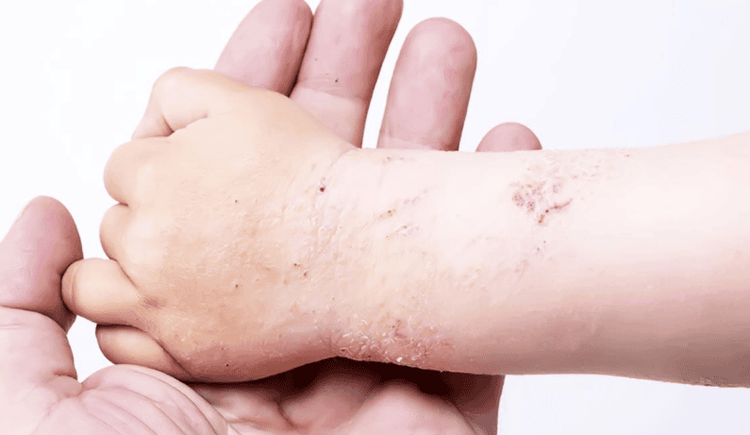
Lichenoid powdery mildew is common in children and young adults. The cause of the disease is unknown. The illness comes on spontaneously, suddenly, or can appear after a flu, febrile infection, or a history of medication. Therefore, it is thought that it may be an increased sensitivity of the body to certain antigens.3.1. Chronic lichen planus
ClinicalBasic lesions: are firm, slightly raised, red-pink or gray-brown papules, resembling syphilis papules, at first as small as a pea, then growing, on the papule, white-gray scales appear on the papule. , dry and adherent to the lesion. Lesions are scattered throughout the trunk and extremities. Scaling off the whole patch but sticking to one side is called the lead clamp sign or the sealant sign. Different from psoriasis, the scabs are easy to peel into thin layers, after a few days the scabs fall off on their own, the skin color gradually returns to normal. In addition to typical papules, red macules with scaly skin are seen, sometimes only scaly or pinkish scales like gray exudate. Such is the multifaceted nature of the lesion. Function: no itching. Overall condition is less affected. Histopathology
Non-specific, the epidermis has parakeratosis, nucleated keratinocytes, prolonged interpapillary germ.
The spine layer has scattered monocyte infiltrate, there is a phenomenon of fluid drainage between the squamous cells, broken bridges. Some studies have found that there are also small abscesses in the epidermis, similar to those in psoriasis. The dermis is edematous, infiltrating monocytes and lymphocytes, but less often than in other parapsoriatic forms, polymorphonuclear leukocytes are sometimes seen. Progression
Benign disease with long-term progression, continuous recurrence. The recurrence may be due to the influence of the weather. In some cases, the lesions clear up completely within a while, but it is thought that this is only a period of stabilization of the disease.
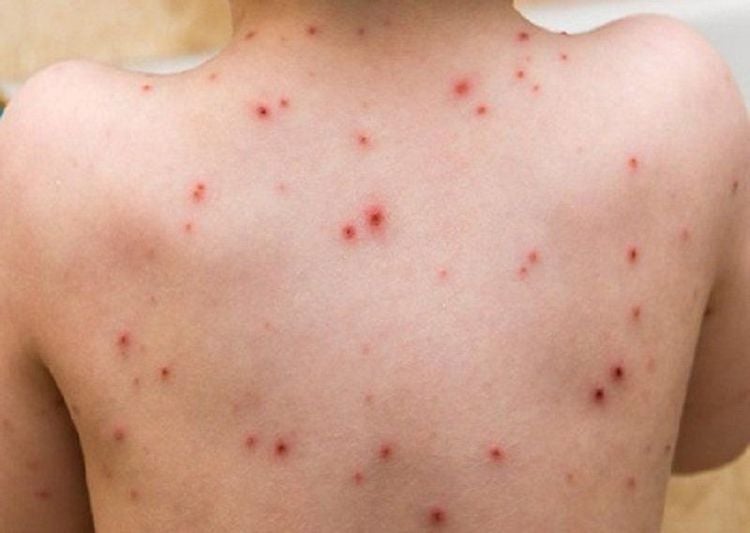
3.2. Powdery mildew and acute smallpox
ClinicalUsually first seen on the trunk of the body as red maculopapular and edematous, central can see vesicles and hemorrhages. Close examination, deep vesicles, smallpox appearance are important signs for diagnosis. These papules are ulcerated, necrotic and scaly; When healed, it leaves a concave, dark, smallpox-like scar and may increase or decrease skin pigmentation. There are no lesions on the face, palms, and feet. The mucosa is rarely injured. After one or more lesions, the disease gradually improves, possibly turning into chronic lichen planus. Systemic symptoms sometimes mild fever, headache, weakness, increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate, enlarged peripheral lymph nodes. Severe, rare form: lichenoid pustule and smallpox acute necrotic ulcer with high fever, acute onset, skin lesions as diffuse papules, followed by extensive interconnected necrotic ulcers and pain . The lesion margin is red and the margin is high. There are scabs on the lesion. The mucosa is also damaged. Severe systemic symptoms: high fever, enlarged peripheral lymph nodes, abdominal pain, myalgia, neurological disorders, mental disorders, arthralgia, interstitial pneumonia.
Epidermal necrosis, hemorrhage, and dense infiltrate of perivascular lymphocytes in the superficial dermis.
Progression
Progressive disease can be acute, subacute or chronic. In the past, it was thought that this was a benign disease, which resolved on its own within a few months to a few years. But recently, there is evidence of progression of a chronic disease, with exacerbations, of severity.
Diagnosis
Definitive diagnosis: based on clinical and histopathology. Differential diagnosis : chronic lichen planus should be distinguished from: necrotizing papillomatosis; Flat lichen; Chicken pox ; Gilbert's rosacea ; Allergy to the drug in the form of pustules; Herpes; Droplet psoriasis ; Syphilis II; Psoriasis and psoriasis vulgaris. Treatment
There is no obvious effect in the treatment of the disease. With lichenoid psoriasis and acute smallpox form, it is first necessary to seek out and eliminate all triggers such as infection. There is no specific treatment for the disease, mainly symptomatic treatment. Use topical medications to soothe the skin, moisturize the skin, and apply corticosteroid cream. Systemic treatment
Tetracycline, erythromycin 2g/day for several weeks, may be effective. Pentoxifylline 400mg x 2 times/day. Severe form is treated with PUVA, methotrexate, systemic corticosteroids, topical antibiotics against infection. Dapson has also been used effectively in some cases.
4. Diet of Lichenoid Psoriasis and Psoriasis
Avoid sugar: Excess sugar in the diet aggravates inflammation. Reducing or cutting out sugar is considered an important first step in treatment.Drink plenty of water : Water helps hydrate every part of the body, including the skin. Consuming enough water during the day improves the texture of the patient's skin.
Avoid foods that cause disease
Eliminate trans fats : Hydrogenated oils are a common source of trans fats in packaged and fried foods. It is better to eliminate these foods entirely from the life of the patient because they increase inflammation. Olive oil can be used to replace other oils when processing.
Eat a lot of fish containing omega 3: salmon, herring, tuna, mackerel... are fish containing vitamin D and omega-3 fats that are beneficial for health.
Choose anti-inflammatory foods: vegetables, fruits like raspberries, blueberries, strawberries, nuts like almonds, walnuts, pistachios... all have anti-inflammatory effects.
Avoid saturated fat: many natural food sources contain saturated fat. However, it is mainly concentrated in animal food sources such as red meat, poultry and dairy products, and baked or fried foods. Avoiding saturated fats will reduce your odds of having complications.
Psoriasis and lichen planus do not currently have a radical treatment, but if treatment is not persistent, the disease will cause many serious complications, affecting quality of life.

At Vinmec International General Hospital, there is a package of examination and advice on treatment of atopic dermatitis for all customers of all ages. Customers are at risk such as allergies, being affected by ambient conditions such as weather, climate, and humidity. There are symptoms such as: There are vesicles concentrated in clusters, red papules raised above the surface of the skin or thick, lichenified, cracked, scaly patches of skin, concentrated in clusters, patches or scattered; Lesions are common in the cheeks, chin, forehead, elbow folds, and popliteals, and may be scattered throughout the body; At the lesion site, there is itchy skin, intense itching, especially at night, there may be bacterial infection at the itch...
When signing up for the package of examination and consultation for treatment of atopic dermatitis, customers will be examined and performed tests including:
Gynecological examination. Perform tests such as: quantification of IgE, fresh mycobacteria, specific IgE for respiratory - food allergens (Panel 1 Viet), test Rida Allergy Screen (panel 1). If you have a need for consultation and examination at the Hospitals of the national health system, please book an appointment on the website for service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.