This is an automatically translated article.
Psoriasis is a chronic disease with rapid flare-ups and remissions. The disease occurs due to many causes, of which 2 main causes are due to the immune system and genetic factors. The main treatment goal of the disease is to stop skin cells from growing too quickly.
1. Causes of Psoriasis
The cause of psoriasis is still unknown. However, over decades of research, scientists have come to the same conclusion about two main factors: genetics and the immune system.
Trắc nghiệm: Bận rộn có ảnh hưởng đến sức khỏe của bạn không?
Cuộc sống hiện đại khiến chúng ta vì quá bận rộn mà quên chăm sóc sức khỏe cho chính mình. Ai cũng biết rằng lịch trình làm việc cả ngày có thể khiến bạn kiệt sức, nhưng cụ thể bận rộn ảnh hưởng thế nào tới sức khỏe? Hãy cùng làm thử bài trắc nghiệm dưới đây.
1.1 Immune system Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease. In a normal body, white blood cells are deployed to attack and destroy invading bacteria and fight infections. In psoriasis, T-lymphocytes mistakenly attack skin cells.
This false attack triggers new skin cells to form too quickly. Normally, skin cells are replaced every 10 - 30 days. With psoriasis, new cells grow every 3 - 4 days. The accumulation of old cells is replaced by new cells that produce silvery scales.
The attack by T lymphocytes on skin cells also causes areas of the skin to become inflamed and red.
1.2 Genetics Psoriasis is hereditary, but only a small percentage. The disease tends to be inherited by skipping a generation. For example, if a grandfather is sick, his grandson is at high risk of getting sick. In general, you have a higher risk of developing psoriasis if a family member has it.
2. Risk factors for disease

The most common triggers for psoriasis include:
2.1 Hormonal changes Diseases often appear or flare up during puberty or menopause. During pregnancy, the symptoms of the disease gradually decrease or even disappear. But after childbirth, the disease can flare up again.
2.2 Alcohol Heavy drinkers are at higher risk, especially younger men. Alcohol can make treatments less effective.
2.3 Smoking Smoking can double your risk of psoriasis. If you have another family member with the disease, your risk is 9 times higher. Smoking makes it harder to get rid of disease symptoms. It can be more severe with pustular psoriasis, which affects the palms of your hands and soles of your feet.
2.4 Stress Scientists think that the immune system can be messed up by emotional and mental stress in the same way it responds to physical problems like trauma and infection.
2.5 Medications Some medications can make the condition worse, including:
Lithium: Treats bipolar disorder and other mental illnesses Other high blood pressure and heart medications: Propranolol ( Inderal) and other beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and quinidine Antimalarials: Chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil), and quinacrine Anti-inflammatory drugs: Indomethacin (Indocin) 2.6 HIV Psoriasis is often worse in the early stages of HIV disease. After applying HIV treatment, the symptoms of eczema also gradually decreased.
2.7 Other infections Strep infections, in particular, increase the risk of guttate psoriasis. Children will often get strep throat before their first flare-up. In addition, the disease can also flare up after other health problems such as earaches, bronchitis, tonsillitis, or respiratory infections such as colds, flu, or skin problems.
2.8 Sunlight Exposure to natural sunlight is fine for most people with psoriasis. However, in rare cases, sunlight can make the condition worse. Therefore, you should protect your skin if you go out.
2.9 Skin Injury An excessive cut, scraping, biting, infection or scratching can also cause psoriasis
2.10 Weight Obese people tend to have psoriasis and wrinkles.
2.11 Weather Psoriasis can be more severe in winter. Dry air, less natural sunlight, and cold temperatures can make symptoms worse. Therefore, you should remember to keep your skin moist in winter.
3. Diagnosis
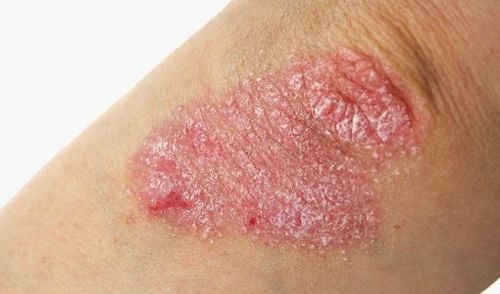
3.1 Physical Examination A physical exam can help doctors identify symptoms to diagnose illness. It's usually easy to diagnose, especially if you have plaque on areas like:
Scalp Ears Elbows Knees Navel Nails Also, your doctor may ask you about your family history. psoriasis or not.
3.2 Testing Your doctor may order a biopsy by taking a small piece of skin and checking to make sure you don't have a skin infection. There are no other tests to confirm or rule out psoriasis.
4. Psoriasis Treatment
Psoriasis has no cure. The treatment is aimed only at reducing inflammation and scaling, slowing the growth of skin cells, and removing plaque. Psoriasis treatments include:
4.1 Topical Treatment Creams and ointments applied directly to the skin are used to treat mild to moderate psoriasis.
Topical psoriasis medications include:
Topical corticosteroids Topical retinoids Anthralin Vitamin D Salicylic acid Moisturizer 4.1 Systemic treatment People with moderate to severe psoriasis, and those who do not respond respond well to these types of treatments, oral or injectable medications may be needed. Many medications have serious side effects and are often prescribed by doctors for short periods of time.
These drugs include:
Methotrexate Cyclosporine (Sandimmune) Biologic Retinoids Light therapy At Vinmec International General Hospital, a Atopic Dermatitis examination and consultation package is available to all customers all ages. Customers are at risk such as allergies, being affected by ambient conditions such as weather, climate, and humidity. There are symptoms such as: There are vesicles concentrated in clusters, red papules raised above the surface of the skin or thick, lichenified, cracked, scaly patches of skin, concentrated in clusters, patches or scattered; Lesions are common in the cheeks, chin, forehead, elbow folds, and popliteals, and may be scattered throughout the body; At the lesion site, there is itchy skin, intense itching, especially at night, there may be bacterial infection at the itch...
When signing up for the package of examination and consultation for treatment of atopic dermatitis, customers will be examined and performed tests including:
Gynecological examination. Perform tests such as: quantification of IgE, fresh mycobacteria, specific IgE for respiratory - food allergens (Panel 1 Viet), test Rida Allergy Screen (panel 1).
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: Webmd.com; Mayoclinic.org