This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Dr. Phung Tuyet Lan - Head of Pediatric Inpatient Unit 3 - Pediatric Center - Vinmec Times City International Hospital
Follicular ovarian tumors are quite common in girls and can occur at any age from infancy to adolescence. These tumors can be discovered incidentally through imaging methods or in combination with some symptoms such as abdominal pain, palpable tumor, precocious puberty, virilization. Although the majority of these tumors in children are benign or cystic in nature, early diagnosis and close follow-up are essential to reduce the risk that ovarian torsion can affect reproductive function. as well as improving the prognosis in cases of malignancy .
1. Ovarian cysts in fetus and newborn
The most common are fetal and neonatal follicles, the mechanism is thought to be due to ovarian stimulation by maternal and fetal gonadotropins. The exact incidence of ovarian cysts in the fetus is unknown, but the incidence in female infants is estimated at 1:2500.1.1. Clinical symptoms and diagnosis
Most fetal ovarian cysts are unilateral, diagnosed incidentally on ultrasound, rarely with other malformations. The size and nature of the cyst can determine the nature: cysts are likely to be physiological (simple cysts) when <2cm in size, containing clear fluid; Cysts are likely to be pathological (complex cysts) when >2cm in size, walled, solid, calcified, bleeding in the cyst...
Ovarian cysts in newborns often present with Asymptomatic abdominal or pelvic cystic tumors. Ultrasound can detect simple cysts (physiological cysts) or complex cysts (bleeding cysts, ovarian torsion...)
Usually ovarian cysts are detected in the fetal and neonatal period spontaneously. regress in the first few months but may persist for more than 12 months. Complications may be encountered such as ovarian torsion, ruptured cyst, bleeding in the cyst, intestinal obstruction or urinary tract compression, inguinal hernia, loss of ovarian function...
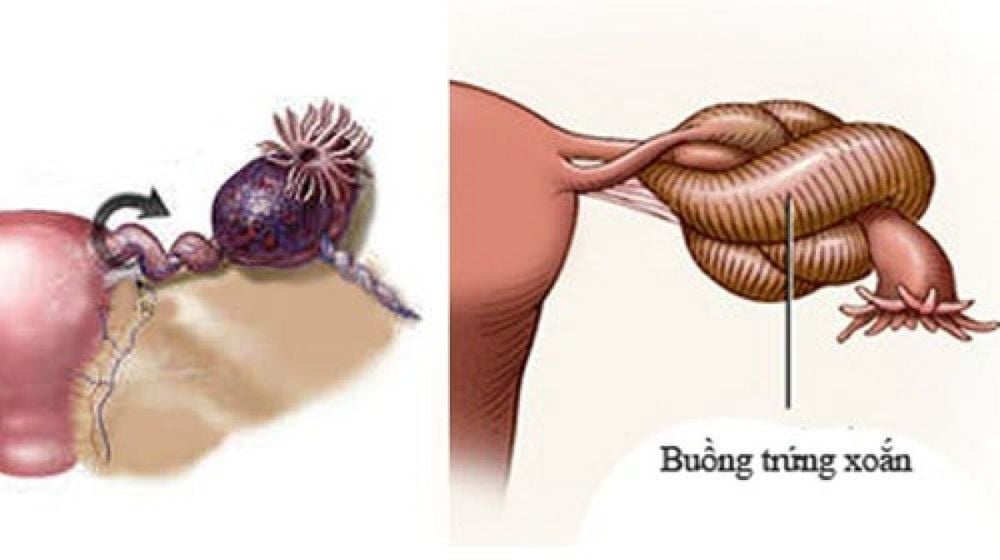
1.2. To solve
Fetal ovarian cysts are closely monitored by ultrasound every 3-4 weeks depending on size, nature on ultrasound and risk of complications. Most of these tumors do not have an indication for intervention (aspiration of the cyst) and the baby can be delivered via the lower route. After birth, the baby continues to be monitored by ultrasound every 4-6 weeks until the cyst regresses. After 4 months, the cysts remain unchanged or show signs of enlargement, can continue to monitor or surgical intervention or aspiration.
2. Ovarian cysts in children and pre-adolescents
The incidence of ovarian cysts in this age group is lower than in fetuses, infants and adolescents because gonadotropin levels decrease after birth and remain low until puberty. The majority of simple cystic tumors in girls of this age are caused by follicles that do not regress on their own. Some of the cystic tumors have active hormone levels that lead to peripheral precocious puberty. Other possible causes include central precocious puberty of unknown cause, McCune Albright syndrome, thyroid disease, ovarian tumor....

2.1. Clinical symptoms and diagnosis
In pre-adolescent girls, the most common clinical presentation is asymptomatic abdominal mass, abdominal enlargement, or incidental finding on imaging studies. Large tumors can be accompanied by symptoms of lower abdominal pain, constipation, urinary disturbances, acute abdominal pain situations that can be confused with appendicitis or peritonitis in complicated cases ( ovarian torsion, cyst bleeding, cyst rupture). Girls with hormone-active cysts may present with precocious puberty (premature mammary gland development and/or vaginal bleeding) or virilization (clitoris hypertrophy, acne). Diagnosis is based on ultrasound to determine tumor from the ovary and classification of simple or complex cysts, some laboratory tests such as quantification of cancer markers to rule out malignancy (Alpha fetoprotein, Beta HCG, AMH, Inhibin) are indicated in cases of complex cysts.

2.1. To solve
Prepubertal cystic tumors according to clinical presentation and features found on ultrasound. Simple cystic tumors that are asymptomatic can be followed closely. Indications for surgery in cases of simple cysts ≥ 9cm, cysts with no signs of regression or enlargement, complex cysts, complicated cysts (twisting, rupture, bleeding).
3. Ovarian cysts in adolescents
Simple or complex ovarian cysts are quite common in adolescents. The ovaries of a menstruating adolescent may contain follicles at various stages of development. Most ovarian cysts are caused by mature follicles that do not ovulate and do not regress, the size of mature follicles can be up to 2-3 cm. A corpus luteum cyst is the result of fluid accumulation in the corpus luteum after ovulation and can reach 5-12 cm in size if bleeding is present.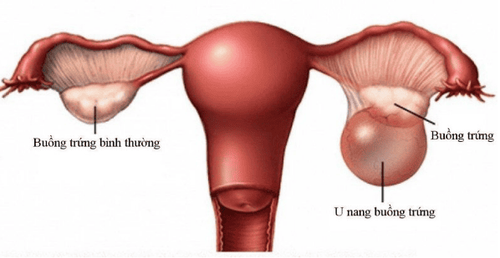
3.1. Clinical symptoms and diagnosis
Ovarian cysts in girls after puberty may be asymptomatic (discovered incidentally) or present with menstrual irregularities or pelvic pain. Large tumors may be accompanied by a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen, constipation, urinary disturbances, acute abdominal pain conditions that can be confused with appendicitis or peritonitis in complicated cases. ovarian torsion, cyst bleeding, cyst rupture). Ultrasound is a good means of tumor identification and classification. In sexually active children, a urine Beta HCG test should be done to rule out pregnancy. In some suspected cases, it is necessary to test for cancer markers to rule out malignancy (Alpha fetoprotein, Beta HCG, AMH, Inhibin).3.2. To solve
Puberty ovarian cysts depend on clinical presentation and features found on ultrasound.
Polycystic cyst: the follicles spontaneously regress within 2-8 weeks. Simple asymptomatic cysts < 6 cm in size can be observed. Indications for oral contraceptive use may be considered to prevent ovulation and new follicle formation. Indications for surgical intervention (laparoscopic cyst removal or aspiration) in the following cases: cysts persist for ≥3 months or increase in size; cyst size > 6 cm; symptomatic cystic tumor.
Luteal cyst: in case of no symptoms or intra-abdominal bleeding, follow-up for 3 months is recommended. Most corpus luteum cysts regress spontaneously during follow-up. Indications for oral contraceptive use may be considered to prevent ovulation and new follicle formation. Cystectomy in cases of non-regressing cysts.
Ovarian cysts in children need to be examined and found the cause for timely treatment. If not treated early, the disease can seriously affect fertility later in life.
Most girls are detected late, when the ovarian cyst is already large, so the treatment is difficult, time consuming, costly and has a significant impact on the baby's reproductive health. Therefore, it is recommended that parents take their children for regular health check-ups, especially at puberty (junior high school students, high school students), especially screening for early detection of ovarian cysts. eggs and other pathologies in the genital organs. If you see unusual symptoms in your baby such as lower abdominal pain, abnormally large abdomen, you should take them to the hospital for timely examination and treatment.
Avoid false thoughts such as thinking that girls have grown up and do everything on their own, so they don't need to care about their children's health so much anymore. Instead, parents should pay more attention to their children's mental health, children themselves have ovarian cysts, have silent pain but still suffer, partly because of fear, partly because of their fear. I don't know the symptoms of ovarian cysts, so I don't confide in my parents. Usually it is only when the pain is unbearable, the abdomen is abnormally large, that the parents are told. Pay more attention to your child so as not to have unfortunate consequences on his life and ability to become a mother in the future.
Vinmec International General Hospital is the address for examination, treatment and prevention of diseases in infants and young children. The examination and treatment process at Vinmec is carried out under the guidance of highly qualified and experienced lecturers with many years of working experience in the profession. Therefore, parents can rest assured with the methodical examination and treatment process at Vinmec.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
MORE:
Ovarian cysts: Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment Ovarian cysts in puberty: What you need to know How big is the ovarian cyst?