This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Master, Doctor Bui Tien Dat - Emergency Department - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Hemophilia, also known as hemophilia, is the inability of the blood to clot normally. This makes the patient very prone to bleeding, bleeding more than usual, sometimes life-threatening. The disease is hereditary, so there is no cure. The main treatment is to improve blood clotting as well as prevent bleeding. The following are the notes in the treatment of hemophilia and the ways to prevent bleeding that the patient should know to have an integrated life like everyone else around.
1. Early recognition of symptoms of hemophilia
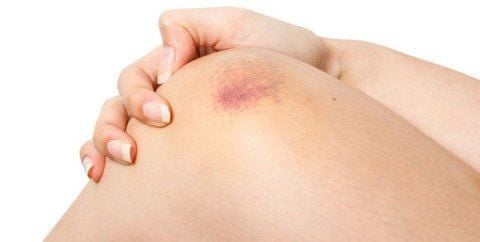
Symptoms depend on whether the disease is mild or severe. If the disease is severe, some children begin to have symptoms from birth. If the disease is mild, a baby is only discovered when bleeding is more than usual after an injury, procedure or surgery.However, regardless of the type of hemophilia, any patient can experience spontaneous bleeding for no reason. This type of bleeding usually occurs in the joint. The joints most commonly affected are ankles, knees and elbows. Blood in the joint can cause pain, swelling, stiffness, and difficulty moving the joint. Over time, repeated bleeding in the joint can lead to chronic, degenerative pain that causes long-term loss of joint function.
In addition, other symptoms of hemophilia are bleeding in the rest of the body, including:
Black stools; Blood in the urine; Abdominal pain due to bleeding into the abdominal wall; Bruising or swelling due to bleeding in the muscle; Bleeding spontaneously or following trauma to the brain or spinal cord. In the course of treatment, it is necessary to recognize early symptoms of bleeding in patients in the above organs. When there are any symptoms, the patient needs to go to the hospital soon for timely intervention by local hemostasis as well as the infusion of clotting factors.
2. How to treat hemophilia?
Hemophilia is treated depending on the severity of the disease. At the same time, how to correct clotting also depends on whether the patient is at risk of injury and whether any procedure or surgery is needed.In general, the mainstay of treatment for hemophilia is "clotting factor replacement therapy". Doctors will prescribe infusion of clotting factors extracted from whole blood (from blood donors) to treat when bleeding occurs, or periodically to prevent bleeding in high-risk subjects. Depending on which element is missing, the patient will be supplemented.
Today, due to the scarcity of donated blood, scientists are gradually researching artificial clotting products. These products promise to meet urgent needs as well as help reduce the occurrence of blood transfusion accidents.
3. How to prevent bleeding in patients with hemophilia
People with hemophilia need to be on the lookout for possible bleeding risks. The following are guidelines in preventing bleeding patients can refer to:Need to know what type of hemophilia you have ("A" or "B"); Regular visits to check blood clotting ability ; Follow your doctor's treatment instructions; Know what activities or sports to avoid; Be aware of the signs and symptoms of bleeding; Do not take aspirin or NSAID pain relievers; Plan to prepare before needing surgical intervention, surgery can cause bleeding; Good oral hygiene and annual dental visits; Bring replacement clotting factors when traveling, working; If your child has hemophilia, you should notify the caregiver, the teacher in the school. At the same time, teach children the symptoms to watch for and recognize bleeding.

4. Hemophilia and pregnancy
Pregnant women who have the hemophilia gene are at risk of passing the gene on to their unborn baby. Therefore, it is necessary to have genetic testing of the fetus if there is a carrier in the family. In addition, this is a high-risk pregnancy and requires obstetricians to monitor closely throughout the trimesters, especially the first and third trimesters:In the first trimester, ultrasound is needed to Know the baby's sex early. This is necessary because boys are at a much higher risk than girls. In addition, boys also need to be screened for the possibility of hemophilia or not.
Until the third trimester, it is necessary to prepare for safe delivery conditions because labor can happen at any time. Furthermore, women who carry the hemophilia gene have an increased risk of abnormal and heavy bleeding. Therefore, doctors will regularly check the levels of clotting factors, limit trauma during delivery as well as have the clotting factors needed to stop bleeding after labor, to avoid excessive blood loss. life-threatening maternal mortality.
In short, although hemophilia cannot be cured, if the above treatment principles are mastered, the patient can still have a normal life. In particular, it is especially important to note that the patient must know how to recognize the signs of bleeding for timely intervention, especially with young children. Besides, prenatal genetic screening is also a necessity to limit the risk of carrying the disease to the child..
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.