This is an automatically translated article.
Diarrhea is a medical condition defined when a person has loose or watery stools 3 or more times in a day. In some cases, diarrhea is the body's protective response, helping to rid itself of the bacteria. However, if diarrhea lasts for a long time, it has a very serious impact on health. At that time, antidiarrheal drugs are an effective solution, including Loperamide.
1. How does Loperamide antidiarrheal work?
Loperamide is a synthetic opiate, but at normal doses Loperamide has very little effect on the central nervous system, the drug only works to reduce intestinal motility, reduce secretions in the gastrointestinal tract and increase muscle tone contractions in the anus. In addition, Loperamide also has the effect of prolonging the transit time of food through the intestines, increasing the transport of fluids and electrolytes through the intestinal mucosa, thereby reducing the loss of water and electrolytes, and reducing the amount of stool produced. Fort.
2. When is Loperamide prescribed for diarrhea? Loperamide is used in cases of acute diarrhea and some cases of chronic diarrhea. Accordingly, acute diarrhea is the first indication of Loperamide, a drug for the prevention or treatment of dehydration and electrolytes, this effect of Loperamide is especially important for patients who are young children and the elderly. debilitated age. Besides, the second leading indication of Loperamide is to reduce waste volume in ileostomy or colectomy procedures.
Loperamide has a role in treating symptoms only, is not helpful in treating the cause of diarrhea such as infection, and cannot replace oral rehydration and electrolyte therapies.
3. Contraindications of Loperamide
Loperamide is contraindicated in cases such as:
Hypersensitivity; Inhibition of intestinal motility should be avoided; Liver damage (if used, it will lead to an overdose due to the accumulation of the drug); Severe colitis, pseudomembranous colitis; Dysentery syndrome, abdominal distention; Abdominal pain but no diarrhea; Children under 6 years old.
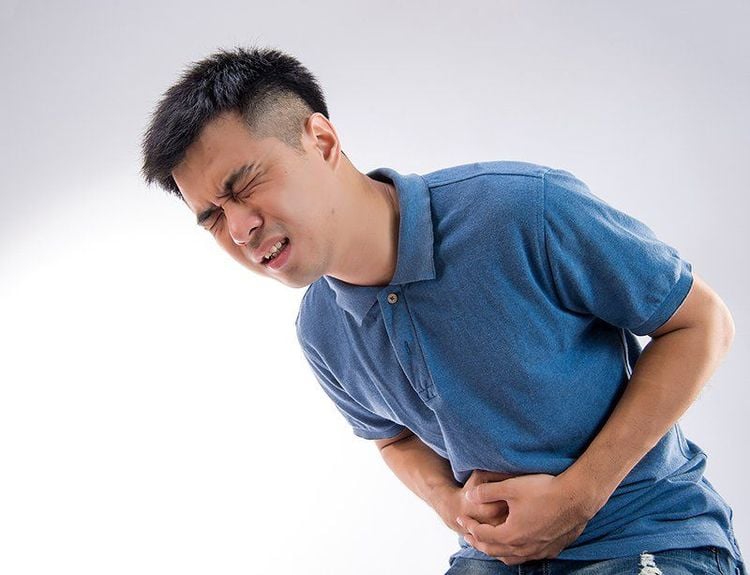
Không dùng Loperamid khi đau bụng nhưng không tiêu chảy
4. Dosage of antidiarrheal drug Loperamide
4.1. Adults Acute Diarrhea: The initial dose is 4mg, then continue taking 2mg with each loose stool for up to 5 days. Usual dose: 6-8 mg/day, maximum: 16 mg/day. Chronic diarrhea: starting dose of 4mg, then continue taking 2mg with each loose stool until diarrhea stops. Maintenance dose 4 - 8 mg/day divided into 2 oral doses, maximum 16 mg/day. If the clinical condition does not improve within 10 days of taking the maximum dose of 16 mg, then symptoms will not be controlled with additional Loperamide. 4.2. Children Loperamide too often is not recommended for children with acute diarrhea. In addition, Loperamide is not recommended for use in children under 6 years of age.
Children from 6 to 12 years old: use Loperamide at a dose of 0.08-0.24 mg/kg/day, divided into 2 or 3 doses. Or:
Children from 6 to 8 years old: 2mg/time, 2 times/day. Children from 8 to 12 years old: 2mg/time, 3 times/day. Daily maintenance dose: 1mg/10kg/day, only taken after loose stools. The total daily dose of Loperamide should not exceed the dose of the first day.
5. Note when using anti-diarrheal medicine Loperamide
Treatment of diarrhea with Loperamide is only symptomatic treatment. Diarrhea wants to be completely treated, the cause must be treated, after knowing the cause and using appropriate drugs, the doctor will prescribe Loperamide to control diarrhea. For cases of infectious diarrhea (usually accompanied by fever), when the bacteria causing the diarrhea has not been identified or antibiotics have not been used to treat the infection, the patient must not arbitrarily use Loperamide. The use of antidiarrheal drugs when the infection has not been resolved will easily lead to the bacteria stagnation inside, unable to be excreted through the feces according to the body's self-protection mechanism.
In many patients with acute colitis, pseudomembranous colitis, the use of drugs that inhibit peristalsis or slow intestinal transit time has been measured to be toxic to the colon, so it is necessary to stop Immediately after treatment with Loperamide, swelling in the abdomen occurred.
Note for adults, Loperamide should not be used more than 8mg in 24 hours if self-medicating, or no more than 16mg if taken as directed by your doctor. Diarrhea can easily cause severe dehydration, so patients need to drink plenty of fluids and minerals (electrolytes). It is necessary to monitor and notify the doctor immediately if signs of dehydration appear (extreme thirst, decreased urination, muscle pain, weakness, fainting...).
When there are signs of dehydration due to diarrhea, rehydration of fluids and electrolytes is extremely important, if there is no improvement within 48 hours, the patient should not continue taking Loperamide but must consider the cause of the cause. diarrhea.

Loperamid cần được sử dụng theo chỉ định của bác sĩ
Inform the doctor if the patient's diarrhea does not improve after 2 days of treatment, or if the condition worsens or as soon as new symptoms appear. If the patient sees blood in the stool, accompanied by fever or upset stomach/abdominal pain, bloating/swelling, etc., this indicates that the health condition has become serious, need to seek help. medical assistance immediately.
Overdosage of Loperamide can lead to respiratory depression and central nervous system effects, causing abdominal cramps, constipation, gastrointestinal irritation, nausea and vomiting. This condition usually occurs when the daily dose of Loperamide is up to 60mg Loperamide. Monitor for signs of CNS depression, intravenously 2 mg naloxone (0.01 mg/kg in children), may be repeated if necessary, up to a total dose of 10 mg.
Loperamide drug has an effect on the ability to drive and use machines, causing fatigue, dizziness, headache... caution should be taken when taking Loperamide while driving or when alertness is needed to operate the machine. hook. Animal studies have shown that Loperamide does not cause cancer, does not cause birth defects, does not reduce fertility... However, caution should be exercised and the potential benefits and risks must be weighed. when using Loperamide for pregnant women, especially in the first 3 months. Loperamide may be excreted in breast milk, so the use of Loperamide is not recommended for nursing women.
Loperamide is used in cases of acute diarrhea and some cases of chronic diarrhea. To ensure the effectiveness of treatment, patients need to take the drug according to the prescription of the doctor or pharmacist.
Vinmec International General Hospital is a high-quality medical care address with a team of doctors and pharmacists with many years of experience and good expertise. When having health problems, customers can contact the hospital to be examined and have the best indications for drug treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.