This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Dang Thi Ngoc Chuong - Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology, Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Neonatal jaundice is divided into physiological and pathological jaundice. In severe cases of jaundice, the baby may need a neonatal exchange as soon as possible. The change of blood will help children get rid of jaundice and avoid serious sequelae, even death.
1. Learn about jaundice in babies
Neonatal jaundice is a condition that causes the skin and whites of the eyes to appear yellow. This is a sign that there is too much bilirubin in the baby's blood. Jaundice usually appears in the first week after birth, most newborns have mild jaundice. Then the symptoms should go away after 1-2 weeks without causing any problems. However, in rare cases, if Bilirubin levels remain high and untreated, they can cause brain damage (cerebral palsy, sequelae) leading to many serious problems and adverse effects. to children for life, even death.2. Causes of neonatal jaundice
Newborns often have jaundice for 2 main reasons:Physiological jaundice: After birth, there is a phenomenon of destruction of red blood cells, causing indirect bilirubin levels to increase, causing jaundice. Pathological jaundice: infection, ABO, Rh, thyroid incompatibility.. Pathological jaundice due to hemolysis due to Rh factor incompatibility. This is one of the rare but very important causes of pathological jaundice in newborns. The cause is due to the blood group incompatibility between the Rh + factor in the father's blood and the Rh- in the mother's blood, so the baby born with jaundice may also have anemia, an enlarged liver, and an enlarged spleen.

3. How to handle and treat pathological jaundice
In mild cases of jaundice, the child may be given phototherapy to relieve the jaundice. However, if the patient has severe pathological jaundice, phototherapy does not respond to treatment, and the bilirubin level is dangerously high, then neonatal transfusion may be indicated. Neonatal exchange transfusion is a technique used to maintain bilirubin levels below neurotoxic levels and is also used to treat certain other conditions such as polycythemia vera or severe sepsis. Newborn blood exchange is considered a quick and effective treatment method applied by many hospitals.3.1. Whole blood exchange Whole blood exchange when the child has SEVERE jaundice to the palms of the hands and feet < 1 week old , and has neurological symptoms : straining , eye support . If the total bilirubin level continues to rise, it will cause brain damage (cerebral palsy, sequelae) and nuclear jaundice.
3.2. Partial blood draw The child may be indicated for a partial exchange if laboratory results show that polycythemia vera (Hct > 65%) is clinically symptomatic.
4. Newborn blood exchange method and procedure
4.1 Newborn blood exchange method In case of Rh disagreement: It is best to use Rh- blood like the mother for replacement. As for the case of ABO disagreement, we have 3 options:Method 1: Use red blood cells to wash ABO like the mother and plasma from the same group as the baby or physiological saline (Sodium chloride 0.9%) mixed in proportion 1⁄2 (1 red blood cells, 2 plasma).
Method 2: Or use fresh blood group O with low concentration of anti-A and B antibodies
Method 3: Or choose blood to replace according to the table:
Child blood group: O; Mother's blood group: Any => choose blood group: O Child's blood group: A ; Mother's blood group: A-AB => select blood group: A-O Child's blood group: A ; Mother's blood group: O-B => select blood group: O Child's blood group: B ; Mother's blood group: B-AB => select blood group: B-O Child's blood group: B ; Mother's blood group: O-A => select blood group: O Child's blood group: AB ; Mother's blood group: AB => select blood group: Any child's blood group: AB ; Mother's blood group: O, A, B => choose blood group: O
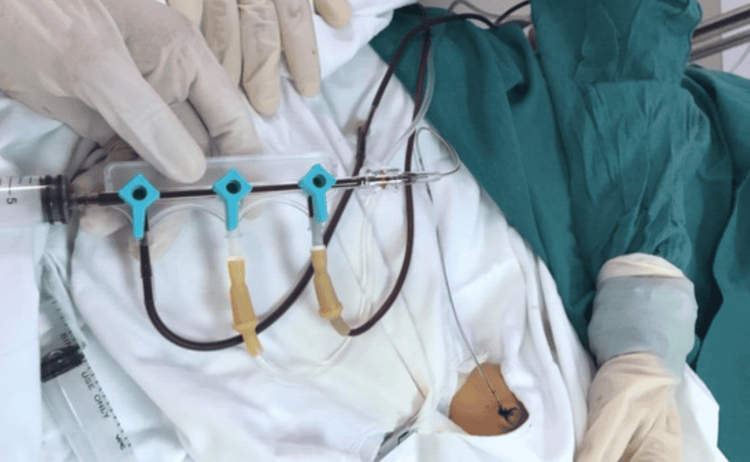
Stage 1: Withdraw 5-10ml of the patient's blood for testing before the blood exchange.
Stage 2: Perform pumping blood from the syringe into the blood vial
Stage 3: Withdrawing blood from the blood bag to replace the syringe
Then 4: Injecting blood from the syringe into the pediatric patient.
The amount of blood injected will be equivalent to the amount of blood withdrawn from the pediatric patient. Based on the child's weight to determine the amount of blood drawn each time:
<1500g: 5ml/time
1500-2500g: 10ml/time
2500-3500g: 15ml/time
>3500g: 20ml/time
Every 100ml of blood change Give to pediatric patients 1ml of 10% Calcium Gluconate. Before the end of the blood transfusion, the doctor will take blood to test for bilirubin, Hct, Hb, electrolytes...
During the blood exchange process, the child may experience some common reactions such as:
The child is shocked, the heart rhythm disorder needs to be adjusted to reduce the speed of pumping and withdrawing blood. If the child has hypothermia, be sure to stay warm during the exchange. If there is an embolism due to gas, it is necessary to review the pumping system, ensure that the 4-prong system is closed without air bubbles. To prevent the child from getting sepsis, it is necessary to ensure absolute sterility, give the child systemic antibiotics after during a blood transfusion. Hemolysis due to incompatibility: A direct Coombs test can be performed to select a suitable replacement blood group. Children with severe pathological jaundice, if not exchanged early, will be very critical, leaving brain complications or death. On the contrary, if treated early and properly, the child will stop jaundice and leave no sequelae. Therefore, early recognition of signs of pathological jaundice in infants is very important to be able to bring the child to the hospital in time.
Specialist I Dang Thi Ngoc Chuong has worked at Children's Hospital I, Thu Duc Hospital and University Hospital of Medicine and Pharmacy in Ho Chi Minh City. With strengths in neonatal diagnosis and examination - neonatal resuscitation, Dr. Chuong is currently a pediatrician at Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital and a member of the Ho Chi Minh City Pediatric Association. Bright.
SEE ALSO:
Attention to correct neonatal jaundice Change of blood in newborns with jaundice due to high blood Bilirubin Differentiating physiological jaundice and jaundice due to biliary atresia in newborns
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.