This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Minh Tuan - Pediatrician - Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.Neonatal lupus erythematosus is a rare autoimmune disease that appears soon after birth. Affected babies often have a characteristic red rash on their skin. The most significant potential complication is congenital arrhythmia.
If left untreated in the first few months of life, the baby may need a permanent pacemaker or it can be life-threatening. Therefore, lupus erythematosus in children needs to be diagnosed and actively treated in the first days, improving the long-term prognosis for children.
1. What is neonatal lupus erythematosus?
Neonatal lupus erythematosus is an autoimmune disease that occurs when autoantibodies are passed from mother to baby.These autoantibodies can affect a child's skin, heart, liver, blood, and brain. Lupus erythematosus is very rare in newborns, with an incidence of 1 in 20,000 pregnancies. At the same time, most mothers during pregnancy do not have any symptoms and are often unaware that they have circulating autoantibodies.
2. What is the cause of neonatal lupus erythematosus?
Neonatal lupus erythematosus is caused by circulating autoantibodies. Antibodies are made by the immune system to help the body fight foreign substances, called antigens. Antigens include pathogenic microorganisms, toxins, and other substances. During pregnancy, antibodies move across the placenta from the mother to the blood of the developing fetus.This is a normal and important process because the fetus cannot make antibodies to protect itself. In neonatal lupus, certain antibodies called autoantibodies also cross the placenta. Autoantibodies are antibodies that mistakenly damage healthy tissue (autoantigens).
These autoantibodies attack healthy fetal tissues, leading to various symptoms associated with neonatal lupus. In about 80% of cases of children with lupus erythematosus, the Ro antibody is strongly positive. In 50% of those cases, the La antibody was also positive. With a recent retrospective review, 100% of mothers who gave birth to infants with lupus were reported to have antinuclear antibodies (ANA) in their blood. This is an autoantibody that is very common in autoimmune conditions such as lupus erythematosus or Sjogren's syndrome.
To date, the process by which maternal autoantibodies affect the fetus is not fully understood. At the same time, neonatal lupus is a rare condition that occurs more often in girls than in boys.
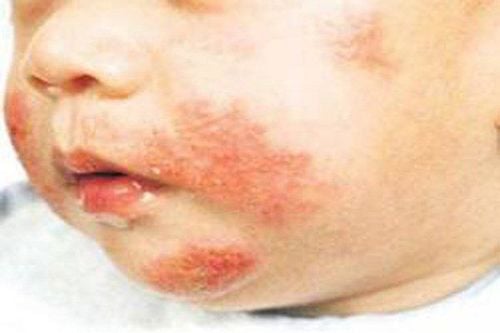
3. What does a newborn with lupus look like?
Neonatal cutaneous lupus may resemble the cutaneous lupus seen in adults. It is also the most common symptom associated with neonatal lupus. The rash manifests as red, ring-shaped, and transient skin lesions that usually develop during the first few weeks of life and clear up completely after a few months. In rare cases, skin lesions may persist throughout childhood.Erythema often occurs on the face and scalp, rarely on the trunk, arms and legs. Some sick infants may also exhibit unusual sensitivity to sunlight, and it is considered a trigger for the development of the rash.
In addition to the skin rash, 60% of cases of neonatal lupus erythematosus also present with cardiac arrhythmias and this is the main cause leading to the mortality rate of the disease up to 30%. The occurrence of congenital arrhythmias in newborns can be as common as skin rashes. This is the most serious complication when a child's heart muscle conduction is completely blocked, which is permanent and potentially life-threatening. In addition, children's hearts are also at high risk for structural defects in the heart, heart failure.
Newborns with lupus may also have a low red blood cell count, a low platelet count that impairs blood clotting. 50% of patients experience liver abnormalities with abnormally large liver size and cholestatic hepatitis.
This is a rare condition, characterized by cessation or reduction of bile flow from the liver, causing cholestasis, leading to hepatitis and jaundice. Fortunately, liver enzymes were only transiently elevated and the child had no other serious abnormalities.

4. How is neonatal lupus diagnosed?
The initial diagnosis is based on the child's skin manifestations and then the presence of autoantibodies in the blood through laboratory tests.However, neonatal lupus erythematosus may already be suspected during pregnancy if the fetal heart rate is found to be slow. At this time, the mother will have an echocardiogram of the fetus and also immediately check for anti-Ro and La antibodies. A skin biopsy may not be needed if the baby has the classic ring-shaped rash of neonatal lupus and the mother also has typical blood test results.
However, skin lesions of infants with neonatal lupus also require differential diagnosis from other acquired or autoimmune diseases with similar symptoms, such as Langerhans cell histiocytosis, granulomatous disease, Atopic dermatitis, psoriasis... Besides, some infections can occur in the weeks immediately before or after birth, including congenital rubella, congenital syphilis, cytomegalovirus infection and group Streptococcus B...
Although infants with confirmed neonatal cutaneous lupus should undergo a complete physical examination to screen for other lupus lesions. In it, especially important is the heart rate monitor. Other necessary tests are complete blood count, kidney and liver function tests. From the results of the tests, the child will be diagnosed and treated at a pediatric rheumatologist or a cardiologist.
5. How is neonatal lupus treated?
The treatment of neonatal lupus needs to be individualized for each patient. Skin symptoms usually resolve spontaneously without specific treatment within the first few months of life. However, children need to be actively protected from sunlight, for example by applying sunscreen specially designed for babies and covering clothes when outdoors.More severe skin lesions may be considered topical steroids.
For arrhythmia complications, if neonatal lupus causes the baby's heart rate to be excessively slow, a permanent pacemaker should be implanted early to prevent sudden death. If the assessment shows less severe heart disease, the child should be periodically monitored for cardiac function throughout childhood. Other treatments on the cardiovascular system are aimed solely at improving symptoms and providing support.
In case the attack of antibodies of this autoimmune disease is too severe, destroying the structure and function of the organ systems, the child needs to be prescribed steroid immunosuppression. In addition, other drug classes can also be prescribed such as antimalarial drug hydroxychloroquine, intravenous immunoglobulin...
For mothers who have given birth to a child with neonatal lupus erythematosus, need to be referred. See an immunologist or rheumatologist with experience in this field to evaluate for autoimmune disease and plan prevention for future pregnancies.
Neonatal lupus erythematosus, although a rare autoimmune disease, can be very severe. Early detection of this pathology in the antenatal and perinatal period is especially important in the prognosis and prognosis of the child, preventing severe damage to the organs due to autoimmune antibodies in lupus erythematosus. caused in children.
During pregnancy, pregnant women should have ultrasound and complete screening tests to detect the disease early and have a treatment plan. At Vinmec International General Hospital, there is a package maternity service as a solution to help pregnant women feel secure because of the companionship of the medical team throughout the pregnancy. When choosing Maternity Package, pregnant women can:
The pregnancy process is monitored by a team of highly qualified doctors Regular check-ups, early detection of abnormalities The package pregnancy helps to facilitate Convenience for the birthing process Newborns are taken care of by a Master. Doctor. Nguyen Minh Tuan has over 27 years of experience in the field of Pediatrics. Doctor was former Deputy Department of Pediatrics - Da Nang Obstetrics and Gynecology Hospital before working as a Pediatrician at the Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital as it is today.
References: ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, dermcoll.edu.au, rarediseases.org
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.