This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Dr. Nguyen Van Duong - Interventional Cardiologist - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Myoglobin test is one of the useful and highly specific evaluation tests to timely detect acute myocardial infarction, thereby helping doctors to have appropriate treatment or prevention methods. So what is the myoglobin test in myocardial infarction and how is it done?
1. What is myoglobin?
Myoglobin is a globular protein that exists in cardiac muscle cells and skeletal muscle cells of humans in particular and of animals in general. Protein Myoglobin acts as a storage part as well as oxygen supply for muscle activity. Myoglobin is structurally similar to hemoglobin - the oxygen-binding protein found in red blood cells. Both of these proteins contain Heme - this is the type of molecule that allows them to combine with oxygen. Therefore, both of these proteins can work alternately to ensure the most favorable oxygen transport in the body.For example, when exposed to venous blood, myoglobins make oxygen connections easier, so they aid in the rapid transport of oxygen from the blood to the muscle cells.
In the blood, Myoglobin binds mainly to plasma globulin - a complex filtered by the kidneys. When the concentration of myoglobin exceeds the binding capacity of the plasma, this protein is present in the urine, causing the urine color to change to brown or dark red.

2. What support does Myoglobin in myocardial infarction test?
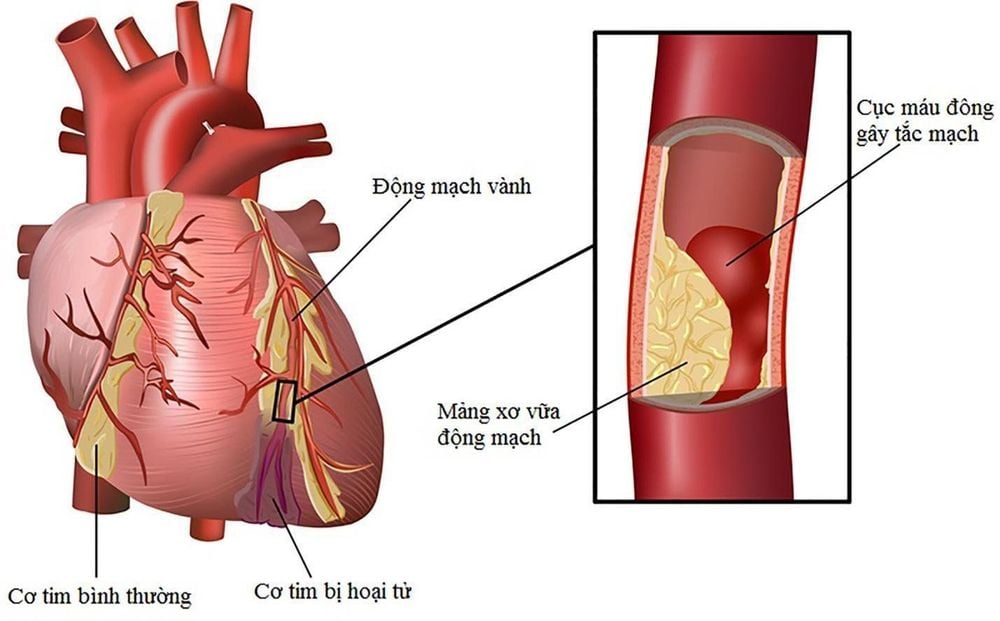
As mentioned above, Myoglobin is a low molecular weight and Heme related protein that is very common in cardiac as well as skeletal muscle.When myocardial necrosis occurs, the concentration of Myoglobin tends to increase rapidly and is easily detected in the first 1 to 4 hours. The predictive value from Myoglobin is highly significant for myocardial cell necrosis. Therefore, the myoglobin test in myocardial infarction has become a useful tool for the exclusion or early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction.
More generally, if myocardial cell damage occurs due to some cause, such as myocardial infarction or trauma..., the amount of Myoglobin will increase and release into the circulation of the muscle. body. The condition usually peaks in about 8 to 12 hours and returns to normal within 24 hours.
It should also be noted that, Myoglobin is a poison when it enters the kidneys, but it passes through the kidneys in excess. So, if Myoglobin levels go too high without remedy, they can also cause serious kidney damage.
In short, the Myoglobin value can reflect the extent of heart damage, thereby predicting the patient's myocardial infarction status as well as taking appropriate prevention methods.
3. Things to know about Myoglobin test in myocardial infarction
The purpose of the Myoglobin test is to diagnose a patient's myocardial infarction before 3 hours.3.1. Specimens for Myoglobin Test To perform specimen collection, patients do not need to fast before blood collection. The test will be done by drawing blood and putting it in a heparin-coated test tube (plasma test).
After drawing blood, the measurement of myoglobin concentration can be carried out in two ways:
Myoglobin agglutination on a slide: this is the method commonly used because the results are quick in a few minutes. Radioimmunoassay: the time to give results is slower, less used in emergency patients. 3.2. What is a normal Myoglobin value? As a rule, Myoglobin concentrations below 85ng/mL or less than 85 mug/L are considered normal.
See also: How is the Myoglobin test performed?

4. What are the benefits of the Myoglobin test?
Myoglobin is an important and useful indicator in the early diagnosis of myocardial infarction as soon as chest pain occurs within 3 to 4 hours. If the myoglobin value is in the normal range, it can partly predict that the patient is not having a myocardial infarction.In addition, the Myoglobin test can also be used to diagnose recurrent myocardial infarction.
5. What factors affect the results of the Myoglobin test in myocardial infarction?
This test is not always able to accurately quantify Myoglobin levels. Sometimes, the following factors can cause test results to change:Patient's specimen has broken red blood cells or the patient has had radioisotope scans recently . Patients with too many intramuscular injections can also cause myoglobin in the blood to increase without pathology. In addition, certain medications, such as statins or theophylline, can also increase myoglobin levels.
6. In addition to myocardial infarction, myoglobin can also increase due to what cause?
An increase in myoglobin is not always caused by a myocardial infarction. So, if your myglobin levels increase, this does not guarantee you will have a heart attack, but it can also be caused by other problems such as:Muscular dystrophy. The patient has a muscle enzyme deficiency or has muscle damage. Myocarditis . Convulsions. CKD. Malignant hyperthermia or shock, convulsions... Multiple trauma, polymyositis. Acute lower extremity ischemia. Some infections... In short, the Myoglobin test in myocardial infarction is a useful test in excluding myocardial infarction, especially in the acute state.
To protect heart health in general and detect early signs of heart attack and stroke. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has been and continues to deploy Cardiovascular Screening Package - Basic Cardiovascular Examination. The patient examination package detects cardiovascular problems at the earliest through tests and modern imaging methods. The package is for all ages, genders and is especially essential for people with risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline for support.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: sciencedirect.com













