This is an automatically translated article.
Multiple sclerosis is a chronic disease of the central nervous system that usually occurs in women between the ages of 20 and 30. It is caused by the body's immune system attacking the protective layer around nerve fibers (myelin), which affects the brain and spinal cord.1.Causes and subjects at risk of disease
Multiple sclerosis (English name is Multiple sclerosis and abbreviated as MS) causes frequent inflammation leading to damage to the myelin sheath of nerves, resulting in scar tissue on the outer coating of cells. neurons, thereby slowing or blocking the transmission of nerve impulses.
The exact cause of this disease is not known at this time, but there are many factors that can make it more likely such as:
People have certain genes that increase the chance of getting the disease. Multiple Sclerosis Smoking may also increase the risk Some people can develop MS after a viral infection such as the Epstein-Barr virus or Human Herpes Virus type 6 causes the immune system to weaken. Their can't function properly. Infection can trigger disease or cause relapse.
2. Symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis

Bạn bị mờ mắt có thể là triệu chứng của bệnh đa xơ cứng rải rác
The symptoms of multiple sclerosis MS vary widely from person to person and can affect any part of the body. Key symptoms include:
Fatigue Stuttering Sexual dysfunction Difficulty walking Vision problems, such as blurred vision Problems with bladder control Numbness or tingling in various parts of the body Muscle stiffness and spasms Loss of balance and difficulty with limb coordination Difficulty thinking, learning, and planning Depending on the type and cause of multiple sclerosis MS , symptoms This can come and go in stages or get worse over time.
3.Classification and progression of multiple sclerosis
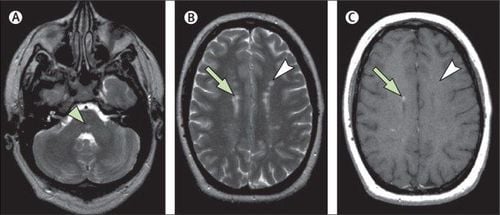
Hội chứng lâm sàng riêng (Clinically isolated syndrome - CIS)
Multiple sclerosis is classified as follows:
Clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) This syndrome is associated with a series of symptoms lasting at least 24 hours, caused by damage to the capsule. myelin in the patient's central nervous system. There are two types: monofocal and multifocal. Monofocal means that one lesion site causes one symptom, and multifocal means the patient has more than one lesion site and more than one symptom. Although these categories are typical of MS, they are not sufficient to confirm the diagnosis. Relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS) Relapsing-remitting MS is the most common form of MS at onset and accounts for approximately 85% of all cases. Relapsing-remitting MS is associated with an apparent relapse of disease activity and subsequent remission. Relapses are periods when symptoms get worse and remission is when the condition gets better. During remission, symptoms are mild or absent and the disease does not progress.
Primary progressive MS Patients with multiple sclerosis with primary progressive MS tend to have a tendency to progressively worsen neurological function after the onset of symptoms. However, a short stabilization period is still possible, but the disease is generally progressive. Within this group of classifications, the terms "Active" and "Inactive" are commonly used to describe disease activity.
Secondary progressive MS: Multiple sclerosis progressive secondary MS that begins with a series of relapses and recovers but continues to worsen over time such as rapid disability or gradual decline in function.
4. Treatment of multiple sclerosis MS
Bác sĩ cũng có thể kê toa các loại thuốc có thể làm chậm quá trình bệnh,giúp người bệnh kiểm soát tình trạng căng thẳng khi mắc bệnh này
There is currently no cure for multiple sclerosis with MS, but some treatments can improve feeling and keep your body functioning better.
Your doctor may also prescribe medications that can slow the course of the disease, prevent or treat attacks, ease symptoms, or help you manage the stress of having this illness. In addition, your doctor may prescribe some steroid medications to make MS attacks shorter and less severe. And some other medicines, like muscle relaxers and tranquilizers, to reduce muscle spasms and treat some other symptoms.
In addition to medication, the patient also needs to exercise under the guidance of a physiotherapist to maintain muscle strength, body balance and help the patient manage fatigue and pain. If walking is difficult, the patient can use a cane, wheelchair or leg brace to move more easily.
5.New Treatment Methods
In addition to the above-mentioned treatments, recent studies have opened up a new option for doctors to treat patients with multiple sclerosis, which is stem cell research and Genetics can help doctors repair damaged nerves at an early stage or stop the disease before it causes damage to happen.
Autologous hematopoietic stem cell infusion can alleviate autoimmune reactions and long-term relapses of the disease. At Vinmec International General Hospital, patients with multiple sclerosis have been treated with autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Transfusion of autologous hematopoietic stem cells is an attempt to "reboot" the immune system, whose job it is to destroy damage to the brain and spinal cord in multiple sclerosis. For autologous stem cell infusion for multiple sclerosis, hematopoietic stem cells are taken from your body (autologous infusion) from your bone marrow or blood, selected and stored before being depleted. the immune system to the full extent of the chemical. The stored hematopoietic stem cells are then passed back to the body. The new stem cells travel down to the bone marrow and over time restore the immune system.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: webmd.com,healthline.com, nhs.uk
MORE
Multiple Sclerosis: What to Know What is Multiple Sclerosis (or Multiple Sclerosis)? Causes of multiple sclerosis (MS)