This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
Menorrhagia is a menstrual cycle that lasts more than 7 days. Menorrhagia is a common menstrual disorder in premenopausal women. If this condition is not treated for a long time, it will be very dangerous to health.
1. Perimenopause and menopause
Perimenopause is the period that lasts about 2-5 years before menopause. This is the characteristic phase of low or low progesterone, increased FSH and LH. Consequences of non-ovulatory cycles and negative feedback mechanisms lead to relative hyperestrogenism.
Pre-menopause has the following clinical features:
Increased vascular permeability: Breast pain, prone to edema. Cervical mucus is clear and liquid throughout the cycle. Increased mitosis in breast tissue and endometrium leads to heterotrophic injury or endometrial proliferation. Menstrual cycle disorders: short or sparse cycles with menorrhagia, heavy bleeding, and hypermenorrhea. Premenstrual syndrome appears: weight gain, abdominal distension, lower abdomen, breast pain, mental anxiety, stress, insecurity. Menopause is the absence of a period for 12 consecutive months. Occurs peacefully or with disturbances: hot flashes, dizziness, headache, psychosis, fatigue, numbness of the extremities, weight gain. Or no uterine bleeding after discontinuing progestogen therapy in premenopausal disorders.
Trắc nghiệm: Sự hiểu biết của bạn về kinh nguyệt
Kinh nguyệt có vai trò quan trọng đối với sức khỏe sinh sản, do đó nữ giới cần chủ động trang bị kiến thức để theo dõi và kiểm soát tình trạng sức khỏe. Bài trắc nghiệm sau đây sẽ giúp bạn hiểu hơn về chu kỳ kinh nguyệt của bản thân.2. Causes of menorrhagia in premenopausal women
Menorrhagia in premenopausal women is largely due to age: Over time, ovarian function declines, resulting in an imbalance of sex hormones. As a result, menstruation is usually absent, and the luteal phase is poor or absent. Manifested by prolonged or heavier menstrual days.

However, menorrhagia at perimenopause must be ruled out the physical causes:
Gynecological infections Benign tumors, cervical polyps Cancerous diseases (ovarian, cervical, endometrial, endometrium, etc.) vagina). Follicular hyperplasia in premenopausal women is 10 times higher than in those aged 20-45. If this is the cause of menorrhagia and is not treated early, it can develop malignant count.
Premenopausal menorrhagia in women can also be a manifestation of malignancies. Without detection and intervention, the prognosis for recovery will be poor.
Menorrhagia, even functional, can cause chronic anemia. Obstructing living and working activities. If it lasts too long, it will be very dangerous.
3. Treatment of menorrhagia in perimenopause
Treatment of menorrhagia in perimenopause should exclude a physical cause such as infection or malignancy. Depending on the cause, different treatment options are available.
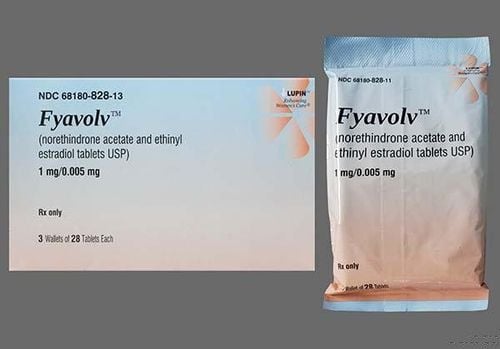
3.1 Drug treatment Iron pills: To get more iron into the blood to help it carry oxygen if there are signs of anemia due to menorrhagia. Ibuprofen (Advil): To help relieve pain, menstrual cramps, and bleeding. In some women, anti-inflammatory drugs can increase the risk of bleeding. Birth control pills: To help stabilize your menstrual cycle and reduce the amount of bleeding. Intrauterine Contraception (IUC): To help make periods more regular and reduce bleeding through drug-releasing devices that are placed in the uterus. Hormone therapy (drugs containing estrogen or progesterone): To reduce the amount of bleeding. Desmopressin spray (Stimate®): To stop bleeding in people with certain bleeding disorders, such as von Willebrand's disease and hemophilia, by releasing stored clotting proteins or defining factors in the lining of blood vessels to help clot blood and temporarily raise levels of proteins in the blood. Antifibrinolytics (tranexamic acid, aminocaproic acid): To reduce the amount of bleeding by stopping the clot from breaking off after it has formed.

3.2 Surgical treatment Endometrial curettage: a procedure in which the top layer of the uterine lining is removed to reduce menstrual bleeding. This procedure may need to be repeated from time to time. Hysteroscopy: surgery that uses a special instrument to view the inside of the uterus, which can be used to help remove polyps and fibroids, correct uterine abnormalities, and remove the lining of the uterus for control menses. Endometrial ablation: surgery that uses different techniques in which all or part of the lining of the uterus is removed to control menstrual bleeding. Hysterectomy: surgical removal of the entire uterus after this procedure, a woman can no longer become pregnant and will stop menstruating. Menorrhagia is a common problem in perimenopausal women. But, many women don't know that they can get better help and treatment. Because they are embarrassed to talk to the doctor about this problem. Talking openly with your doctor is important in making sure you get the right diagnosis and prompt treatment.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health System nationwide for medical examination and treatment or contact for an appointment HERE.