This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Thi My Linh - Neonatologist - Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital. Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Thi My Linh has 12 years of experience in diagnosing and treating pediatric diseases.Purulent meningitis is a very dangerous disease, especially in young children, with atypical manifestations, easily leading to serious, life-threatening complications.
1. What is purulent meningitis?
Purulent meningitis, also known as bacterial meningitis, is a condition in which the membranes surrounding the central nervous system are attacked by bacteria, causing inflammation and pus production. Pathogenic bacteria appear in the cerebrospinal fluid cavity, damage the nervous system, causing severe effects on movement and cognition.Subjects susceptible to meningitis are children under 1 year old and people between the ages of 16 and 21.
2. Causes of purulent meningitis
The cause of meningitis can be caused by many bacteria such as: Haemophilus influenzae, Neisseria meningitidis, Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcal)...Infants and young children aged 1-24 months are susceptible to inflammation most purulent meninges. Causes of meningitis in children are mainly caused by: Listeria monocytogenes, E. coli, group B streptococcus. These bacteria attack the ears, nose and throat, enter the lungs, enter the blood into the brain or attack the brain. directly into the brain and spinal cord.
2.1. Meningitis caused by Haemophilus influenzae type b
Haemophilus influenzae type b meningitis usually occurs in infants and young children aged 1 to 36 months. At this time, the child's brain is developing, children with the disease often have very serious complications, which can die in the first days.Haemophilus influenzae type b can be transmitted through the respiratory tract, easily spreading into large outbreaks, especially in countries where Haemophilus influenzae has not been vaccinated.
2.2. Meningitis caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcal)
Streptococcus pneumoniae is the leading cause of meningitis in countries where Haemophilus influenzae has been vaccinated. Pneumococcal can attack anyone, on average, about 1-3 people out of every 1000 people have pneumococcal meningitis.Children with pneumococcal purulent meningitis are mostly complications from sinusitis, pneumonia, otitis media... pneumococcal often reside in the pharynx and attack the cerebrospinal fluid.
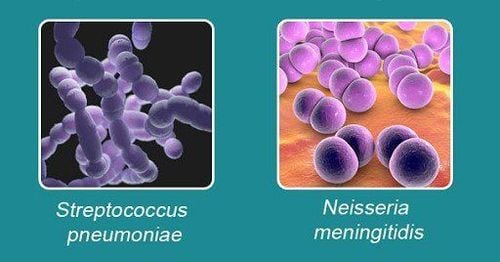
2.3. Meningococcal meningitis
The main subjects with meningococcal meningitis are young children aged 6-12 months. The rate of children over 1 year of age with the disease is usually lower. Meningococcal purulent meningitis often presents with a purpura purpura, which can be fatal within 24 hours.Disease-causing bacteria are often hidden in the throat cavity. Not everyone with meningococcal bacteria gets meningitis. Many cases have bacteria but the body is completely normal, there are no symptoms. Pathogenic bacteria can be transmitted through the respiratory tract, through casual contact.
Trắc nghiệm: các chỉ số cần chú ý về sự phát triển thể chất của trẻ
Chiều cao, cân nặng của bé ở từng giai đoạn nên là bao nhiêu là bình thường, bao nhiêu là bất thường? Cùng ThS.BS Ma Văn Thấm điểm lại xem bạn đã nắm được các chỉ số phát triển thể chất của bé chưa nhé!The following content is prepared under supervision of Thạc sĩ, Bác sĩ y khoa, Ma Văn Thấm , Nhi , Phòng khám Đa khoa Quốc tế Vinmec Dương Đông(Phú Quốc)
2.4. Purulent meningitis caused by E.Coli
E.Coli is a common cause of purulent meningitis in infants and young children, very rare cases of pyelonephritis caused by E.Coli in older children and adults. The disease can cause sepsis, which is very dangerous for young children, with a very high mortality rate.2.5. Listeria monocytogenes
Listeria monocytogenes bacteria are found in raw foods and dairy products. People who are immunocompromised or have a weak immune system such as the elderly, infants, and people with weak health... are susceptible to meningitis caused by Listeria monocytogenes.3. Symptoms of meningitis in children
3.1. Symptoms of purulent meningitis in infants
Symptoms of purulent meningitis in children are atypical. Some tell-tale signs such as:Anorexia, poor feeding, decreased feeding and feeding volume per feeding Fatigue, slow movement Crying, coaxing, sometimes screaming Indifferent and indifferent to everything around High fever or cold body temperature Sudden pauses in breathing Jaundice or pale, pale skin Convulsions bulging fontanel Shock, increased excitability Decreased muscle tone Hypoglycemia

3.2. Symptoms of meningitis in older children
Symptoms of meningitis in older children are more typical than those in infants and include:High fever Fatigue, loss of appetite Severe headache Stiff neck Nausea or vomiting Crying, yes hunched position With unclosed fontanelle there will be signs of bulging fontanelle Afraid of light Decreased consciousness, easily excitable Signs of infection, toxicity Coma Convulsions
4. Complications of meningitis in children
4.1. Complications of purulent meningitis
Brain damage, damage to cranial nerves: cords II, III, IV... Thrombophlebitis, inflammation around cerebral blood vessels... Brain abscess, subdural abscess... Hydrocephalus hydrocephalus due to cerebrospinal fluid obstruction Cerebral palsy Complications outside the nervous system such as arthritis, nephritis, pneumonia, visceral hemorrhage....4.2. The sequelae of late treatment of purulent meningitis
Having hearing and vision problems such as: deafness, blindness, strabismus, water brain syndrome... Slowed motor and intellectual development Paralysis of limbs or hemiplegia Affects the nervous system: decreased memory depression, mental disorders Epilepsy4.3. Death from purulent meningitis
Purulent meningitis causes death due to severe respiratory failure, cerebral edema, serious infectious complications in the brain, complications of pneumonia, severe nephritis, brain loss state, brain failure...Even when detected With early disease and immediate intervention, the mortality rate from meningitis is still very high.
5. How to prevent meningitis in children
Early detection and definitive treatment of respiratory diseases, ear - nose - throat infections in young children Maintain personal hygiene, keep a cool, clean place Clean ears - nose - throat daily Injections purulent meningitis vaccine. Currently, in Vietnam, there is a vaccine for meningitis caused by meningococcal, pneumococcal and Haemophilus influenzae. When a child has abnormal signs related to meningitis or respiratory infections, it is necessary to take the child to medical facilities for timely examination and treatment, to avoid serious illness, leading to serious illness. to dangerous complications.Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.